How to deal with dictionary
advertisement

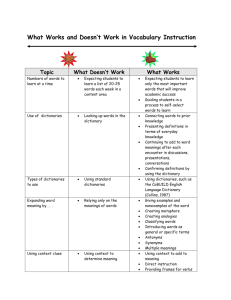
How to Use Dictionaries in English Language Learning Contents 1 Why dictionaries? 2 Which one to choose? 3 How to use it? 4 Q&A Why do English language learners need dictionaries? Why dictionaries? A craftsman who wishes to practice his craft well must first sharpen his tools. Dictionaries help us learn new words. Dictionaries help us contextualize new vocabulary. Dictionaries help us build learner autonomy. Which dictionary should an English language learner choose? Which one? With so many dictionaries on the market, sometimes it is simply baffling for the learner to choose one. Here are some things that needed to be considered: Types of dictionaries Native dictionaries vs. learner’s dictionaries Monolingual dictionaries vs. bilingual/bilingualized dictionaries Types of dictionaries Paper dictionaries Traditional; long-lasting and relatively cheap. Can be used as desk dictionaries. Online/Computerized dictionaries These dictionaries offer a vast amount of living examples, exercises and other language activities; they are also easy to use with user-friendly search engines and interface. Most of the online dictionaries are free. dictionary.cambridge.com; www.oed.com; www.ldoceonline.com; www.merriamwebstercollegiate.com; www.dictionary.com Palmtop dictionaries A big plus of palmtop dictionaries is that they hold a large amount of data in a small space, sometimes several paper dictionaries. The biggest problem lies, paradoxically, in their ease of use. Many students treat them as pocket translators rather than serious tools of study. BACK What’s the difference between a native language dictionary and a learner’s dictionary? 贫穷 大小 Big&small Example Native language dictionary Learner’s dictionary n. 1 a an umbelliferous plant, Daucus carota, with a tapering orangecoloured root. b this root as a vegetable. noun 1 [U, C] a long pointed orange root vegetable. --The Concise Oxford Dictionary (COD9) --Oxford Advanced Learner’s Dictionary (OALD6) Native language dictionary Learner’s dictionaries l spelling l spelling l pronunciation l pronunciation l meaning l meaning l grammar l collocation l register (语域) … About learner’s dictionaries To make monolingual English dictionaries easily accessible to foreign learners. The first English learner’s dictionary The New Method English Dictionary was made by Michael West in 1935. Today most learner’s dictionaries adopt a controlled defining vocabulary of 2-3000 words. A list of learner’s dictionaries Oxford Advanced Learner’s Dictionary (6th edition, 2000, OALD6 ) Collins COBUILD English Dictionary for Advanced Learners (3rd edition, 2001, COBUILD3) Macmillan English Dictionary for Advanced Learners (2002, MED) Longman Dictionary of Contemporary English (4th edition, 2003, LDOCE4) Cambridge Advanced Learner’s Dictionary (2nd edition, 2003, CALD2) Features of learner’s dictionaries • Detailed grammatical information • Attention to collocation • Rich examples • Information about word frequencies • Explanatory notes Examples Detailed grammatical information suggest […] v.tr. 1 (often foll. by that + clause) propose (a theory, plan, or hypothesis) (suggested to them that they should wait; suggested a different plan). --The Concise Oxford Dictionary (COD9) Detailed grammatical information suggest […] verb 1 ~ sth (to sb) to put forward an idea or a plan for other people to think about SYN PROPOSE: [VN] May I suggest a white wine with this dish, Sir? ◇ A solution immediately suggested itself to me (= I immediately thought of a solution). ◇ [V (that)] I suggest (that) we go out to eat. ◇ [Ving] I suggested going in my car. ◇ [VN that] It has been suggested that bright children take their exams early. ◇ (BrE also) It has been suggested that bright children should take their exams early. HELP You cannot ‘suggest somebody something’:Can you suggest me a good dictionary? --Oxford Advanced Learner’s Dictionary (OALD6) Detailed grammatical information Suggest can be followed by 1. a noun phrase, 2. a noun phrase plus a prepositional phrase to somebody (not suggest somebody something), 3. a that clause (with that being optional), 4. the –ing form of a verb phrase; 5. and that in a construction like “It has been suggested that ...” the word that is obligatory; 6. and that in British English there may be the modal auxiliary should in the verb phrase of the that clause, otherwise the verb is in its base form. Attention to collocation Longman Dictionary of Contemporary English (LDOCE4 2003) wind1 1 […] strong/high winds The forecast is for strong winds and heavy rain. | gale/hurricane force winds […] The light wind ruffled the water. rain1 1 […] heavy/torrential/pouring rain (=a lot of rain) There will be heavy rain in most parts of the country. | The light rain had stopped. Attention to collocation Knowledge (LDOCE4) have knowledge acquire/gain knowledge (= learn something) technical/scientific knowledge in-depth knowledge detailed knowledge specialist knowledge (= knowledge about a particular subject) first-hand/personal knowledge (knowledge from experiencing something for yourself) ... You need specialist knowledge to do this job. | [+ of] His knowledge of ancient civilization is unrivalled. | [+ about] the need to increase knowledge about birth control | Many of the students did not have much knowledge of American history. | salesmen with good technical knowledge of what they are selling ... Rich examples LDOCE4 contains the largest number of examples—155,000 in all. On its CD-ROM there are 80,000 additional examples plus over a million corpus sentences. Information about word frequencies LDOCE4 marks the first 3000 most frequently used words in speech and writing in the form of S1 S2 S3 W1 W2 W3 Information about word frequencies In Macmillan English Dictionary there are also three frequency bands, but they cover about 7,300 words: ★★★ 2300 very high frequency words ★★ 2360 high frequency words ★ 2640 quite high frequency words. Information about word frequencies COBUILD3 distinguishes five frequency bands totaling 14,600 words: ◆◆◆◆◆ 680 words ◆◆◆◆◇ 1040 words ◆◆◆◇◇ 1580 words ◆◆◇◇◇ 3200 words ◆◇◇◇◇ 8100 words Information about word frequencies How many English words do you have? 3000 talk about a wide range of everyday topics and read simplified English books 7000 have a basic working knowledge of English 14000 as proficient as a good English-major graduate Explanatory notes LDOCE4 WORD CHOICE: call, phone, telephone, ring In spoken English, it is usual to say that you call or phone someone: He calls me almost every day. | Phone me when you get there. In spoken British English, it is also very usual to say that you ring someone: Have you rung Kim yet? It is fairly formal and not very usual in spoken English to say that you telephone someone. [...] Explanatory notes LDOCE4 WORD FOCUS: words meaning CHEAP reasonable not too expensive | economical used about cars, systems, or methods that do not cost a lot of money to use | be good value to be well worth the price you pay | be a bargain to be very cheap Explanatory notes LDOCE4 GRAMMAR (just) in case in case is followed by the simple present, the simple past, or ‘should’: Write it down in case you forget (NOT in case you will forget). | I had a snack, just in case there was no time (NOT in case there would be no time) to eat later. | Here’s a contact number, in case there should (NOT will/would) be a problem. […] BACK What’s the difference between bilingual dictionaries and bilingualized dictionaries? A bilingual dictionary (双语词典) is one in which the headwords are in one language and the definitions in another language. Bilingualized dictionaries (双解词典) are native language dictionaries with foreign language translation. Bilingual dictionaries 《新英汉词典》(A New English-Chinese Dictionary, 2000) Bilingualized dictionaries Oxford Advanced Learner’s English-Chinese Dictionary 《牛津高阶英汉双解词 典》, 1997 Which dictionary? My advice (1) Start by using a bilingualized English learner’s dictionary and switch to the latest edition of a monolingual learner’s dictionary. Which dictionary? My advice (2) Do install a computerized dictionary on your PC. Which dictionary? My advice (3) Better not to use pocket dictionaries and palmtop electronic dictionaries without examples. When you do use palmtop dictionaries, treat them with the dignity and respect a thick paper dictionary deserves. How should language learners use their dictionaries? How to use dictionaries Now you have made your pick of dictionaries! How to use them? Here are a few guidelines. Read the guide to the dictionary and familiarize yourself with all the symbols, abbreviations, and note markers. (Turn to dictionaries for example.) When you look up a word in the dictionary, make sure you find the following information: pronunciation, its meaning in the context, examples, and collocation. Consolidate what you’ve just learned by making a few sentences of your own or by finishing the exercises provided. Pay special attention to any notes attached – differences between AmE & BrE, usage notes, etc. If possible, try to extend your knowledge of the word – other major meanings, grammar notes, synonyms/antonyms, reflections, etc. Let’s take “suggest” as an example! Everything about him suggested a carefully dressed authority. Look up this word in : Longman Dictionary of Contemporary English (4th edition, 2003, LDOCE4) Cambridge Advanced Learner’s Dictionary (2nd edition, 2003, CALD2) And their respective computerized versions. LDOCE 4 Layout All meanings listed under the same headword, each with respective synonyms CALD 2 Layout The word has 3 entries, each with a different meaning with respective synonyms, verb endings, and word building Definiti Plainer ons With related phrases Definiti Simple enough ons Phrases incorporated into examples Others Word origin, phrase bank, examples bank Language activator with synonyms listed under different contexts Others Smart thesaurus with all the synonyms and examples listed Do you have any questions?