Applied Behavioral Research - rxsped596
advertisement

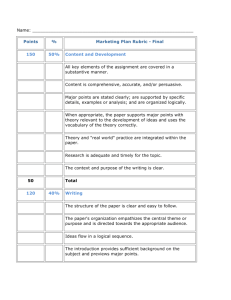
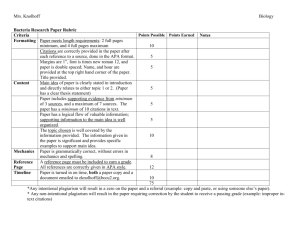
Session 2- Literature Review Check the Wiki consistently for New Postings Please let Sheldon know if links are not working or if you have any issues with the Wiki. http://rxsped596.pbworks.com/w/page/54340090/FrontPage For the NIH/CITI online Modules… ◦ Select SOCIAL-BEHAVIORAL RESEARCH Basic/Refresher ◦ Link (from wiki): https://www.citiprogram.org/Default.asp? Find a group for your research proposal project soon! We will have some time today to do this. Dr. Sanford will be coming to our next class to present the RTI project information When there is an OR in the Readings column that means you can choose to read either the 3rd or 4th reading, but the expectation is that you read the first 2 or 3 and choose one of the others. June 29: NIH CITI training modules July 1: Annotated Bibliography ◦ Each individual reviews 3 research articles regarding their topic ◦ See Example: http://rxsped596.pbworks.com/w/file/fetch/54804527/ Example%20Annotated%20Bibliography.pdf July 6: Conceptual Framework ◦ Group submits short summary of literature and presents a conceptual framework for theories that drive their proposal. Review & Quiz Group Discussion of Readings Lecture: ◦ APA Style ◦ Conceptual Models ◦ Literature Review & Research Proposal In-Class Activity: Plan your Literature Search with your group Four Functions of Educational Research: 1. Description 2. Prediction 3. Improvement 4. Explanation ….of an educational phenomenon • Quantitative: Numerical data • Qualitative: Words, pictures & artifacts • Mixed: Both types of data Independent variable= Intervention/treatment manipulated for different groups or at different times (e.g., literacy training). Predictor variable= Inherent characteristics that are different between groups (e.g., studying gender differences) Variable that the researcher is interested in measuring to determine how it is different for groups with different experiences (dependent) or characteristics (criterion) . Dependent variable: Measured/outcome variable • • Population: Group to whom you want to apply your results (e.g., teachers in a school district; N=800) Sample: Group that you have chosen from (or representative of) your population from which to collect data (e.g., n=80 teachers from a school district selected to interview/survey) Prepared by M. Hara (mhara@pdx.edu) Prepared by M. Hara (mhara@pdx.edu) Discuss the readings with at least 2 other people in a small group (15 minutes) Make sure everyone has a chance to talk. “Research questions must guide researchers’ selections of scientific methods” (p.138). “Science in education is not a hard science, but is the ‘hardest-to-do science’” (Berliner, 2002, as cited by Odom et al., 2005, p.139). Randomized Control Trials (RCT)= “Gold Standard” , but…. “Researchers cannot just address a simple question about whether a practice in special education is effective; they must specify clearly for whom the practice is effective and in what context” (p. 141). Rigorous methodology to questions of interest. Guidelines for: ◦ Researchers who design and conduct research ◦ Reviewers who evaluate the “believability” of research findings ◦ Consumers who need to determine the “usability” of research findings Guidelines for determining an evidence-based practice based on the rigor of research using a number of methods. Indicators for: Group Design (Gersten et al., 2004); Single-Subject Design (Horner et al., 2005); Correlational Design (Thompson et al., 2004); Qualitative Design (Brantlinger et al., 2005) Where do I start? Tutorial from PSU Library http://library.pdx.edu/tutorials/beginresearch/1 PSU Special Education Research Guide Site http://guides.library.pdx.edu/content.php?pid=2 33736&sid=1942844 Handout http://rxsped596.pbworks.com/w/file/5490578 1/Schroeder.Library.Lit%20Review.sped%20590%2 0Loman%206%2012.doc APA Formatting and Style Guide What is APA? The American Psychological Association (APA) citation style is the most commonly used format for manuscripts in the social sciences. APA regulates: • Stylistics • In-text citations • References APA Style: Language Language in an APA paper is: • clear: be specific in descriptions and explanations • concise: condense information when you can • plain: use simple, descriptive adjectives and minimize figurative language Types of APA Papers The literature review: • Contains a summary of what the scientific literature says about the topic of your research • Includes a title page, introduction, and list of references The experimental report: • Describes your experimental research • Includes a title page, abstract, introduction, method, results, discussion, list of references, appendices, tables, and figures General Format Your essay should: • be typed, double-spaced, with one space after punctuation between sentences • be printed on standard-sized paper (8.5”x11”) • use 1” margins on all sides • use 10-12 pt. Times New Roman or a similar font • include a page header (title) in the upper left-hand of every page and a page number in the upper righthand side of every page General Format Your essay should include four major sections: References Main Body Abstract Title page Title Page Page header: (use Insert Page Header) title flush left + page number flush right. Title: (in the upper half of the page, centered) name (no title or degree) + affiliation (university, etc.) Abstract Page Page header: do NOT include “Running head:” Abstract: centered, at the top of the page Write a 150- to 250word summary of your paper in an accurate, concise, and specific manner. Main Body (Text) • Number the first text page as page number 3 • Type and center the title of the paper centered, at the top of the page • Type the text double-spaced with all sections following each other without a break • Identify the sources you use in the paper in parenthetical in-text citations • Format tables and figures References Page • Center the title (References) at the top of the page. Do not bold it. • Double-space reference entries • Flush left the first line of the entry and indent subsequent lines • Order entries alphabetically by the author’s surnames References: Basics • Invert authors’ names (last name first followed by initials: “Smith, J.Q.”) • Alphabetize reference list entries the last name of the first author of each work • Capitalize only the first letter of the first word of a title and subtitle, the first word after a colon or a dash in the title, and proper nouns. Do not capitalize the first letter of the second word in a hyphenated compound word. References: Basics • Capitalize all major words in journal titles • Italicize titles of longer works such as books and journals • Do not italicize, underline, or put quotes around the titles of shorter works such as journal articles or essays in edited collections Making the References List APA is a complex system of citation. When compiling the reference list, the strategy below might be useful: 1. Identify the type of source: Is it a book? A journal article? A webpage? 2. Find a sample of citing this type of source in the textbook or in the OWL APA Guide: http://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/560/01/ 3. “Mirror” the sample 4. Make sure that the entries are listed in the alphabetical order and the subsequent lines are indented (Recall References: Basics) Reference List: Single Author • Last Name first, followed by author initials • Example: Berndt, T.J. (2002). Friendship quality and social development. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 11, 7-10. doi: 10.0000.XYZ. • Notice that in the title of the article only the first letter of the first word is capitalized AND it is not italicized. • Notice that the Journal: Current Directions… is italicized along with the volume number • Finally, notice that a doi number is placed at the end of the reference. This is now a new requirement of materials obtained electronically (almost every journal article now has one!) Reference List: Two to Seven Authors • List by last names and initials; commas separate authors names, while the last author is preceded by ampersand (&). • Example Kernis, M.H., Cornell, D.P., Sun, C.R., & Berry, A. (1993). There’s more to self-esteem than whether it is high or low: The importance of stability of self-esteem. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 65 (1), 1190-1204. doi: 10001XXX • Notice how the “T” after the colon is capitalized, but nothing else in the title of the article. • Notice that the volume number “65” is italicized, but the issue number “1” is in parenthesis and not italicized. Reference list more than seven authors • Same format, except… • After the sixth authors name, use an ellipses inplace of the author names. Then provided the final author name. There should be no more than seven names. Miller, F.H., Choi, M.J., Angeli, L. L., Harland, A.A., Stamos, J., Thomas, S.T., … Rubin, L.H. (2009). Web site usability for the blind and low-vision user. Technical Communication, 57 (1), 323-334. doi: 10xXX00146 In-text Citations: Basics In-text citations help readers locate the cited source in the References section of the paper. Whenever you use a source, provide in parenthesis: • the author’s name and the date of publication • for quotations and close paraphrases, provide the author’s name, date of publication, and a page number In-text Citations: Formatting Quotations When quoting, introduce the quotation with a signal phrase. Make sure to include the author’s name, the year of publication, the page number, but keep the citation brief—do not repeat the information. Caruth (1996) states that a traumatic response frequently entails a “delayed, uncontrolled repetitive appearance of hallucinations and other intrusive phenomena” (p.11). A traumatic response frequently entails a “delayed, uncontrolled repetitive appearance of hallucinations and other intrusive phenomena” (Caruth, 1996, p.11). In-text Citations: Formatting a Summary or Paraphrase Provide the author’s last name and the year of publication in parenthesis after a summary or a paraphrase. Though feminist studies focus solely on women's experiences, they err by collectively perpetuating the masculine-centered impressions (Fussell, 1975). In-text Citations: Formatting a Summary or Paraphrase Include the author’s name in a signal phrase followed by the year of publication in parenthesis. Recently, the history of warfare has been significantly revised by Higonnet et al. (1987), Marcus (1989), and Raitt and Tate (1997) to include women’s personal and cultural responses to battle and its resultant traumatic effects. In-text Citations: Formatting a Summary or Paraphrase When including the quotation in a summary/paraphrase, also provide a page number in parenthesis after the quotation: According to feminist researchers Raitt and Tate (1997), “It is no longer true to claim that women's responses to the war have been ignored” (p. 2). In-text Citations: Signal Words Introduce quotations with signal phrases, e.g. According to X. (2008), “….” (p. 3). X. (2008) argued that “……” (p. 3). Use such signal verbs as: acknowledged, contended, maintained, responded, reported, argued, concluded, etc. Use the past tense or the present perfect tense of verbs in signal phrases In-text Citations: Two or More Works When the parenthetical citation includes two or more works, order them in the same way they appear in the reference list—the author’s name, the year of publication—separated by a semi-colon. (Kachru, 2005; Smith, 2008) In-text Citations: A Work with Two Authors When citing a work with two authors, use “and” in between authors’ name in the signal phrase yet “&” between their names in parenthesis. According to feminist researchers Raitt and Tate (1997), “It is no longer true to claim that women's responses to the war have been ignored” (p. 2). Some feminists researchers question that “women's responses to the war have been ignored” (Raitt & Tate, 1997, p. 2). In-text Citations: A Work with Three to Five authors When citing a work with three to five authors, identify all authors in the signal phrase or in parenthesis. (Harklau, Siegal, and Losey, 1999) In subsequent citations, only use the first author's last name followed by "et al." in the signal phrase or in parentheses. (Harklau et al., 1993) In-text Citations: A Work with Six and More Authors When citing a work with six and more authors, identify the first author’s name followed by “et al.” Smith et al. (2006) maintained that…. (Smith et al., 2006) In-text Citations: A Work of Unknown Author When citing a work of unknown author, use the source’s full title in the signal phrase and cite the first word of the title followed by the year of publication in parenthesis. Put titles of articles and chapters in quotation marks; italicize titles of books and reports. According to “Indiana Joins Federal Accountability System” (2008), … Or, (“Indiana,” 2008) In-text Citations: Organization When citing an organization, mention the organization the first time when you cite the source in the signal phrase or the parenthetical citation. The data collected by the Food and Drug Administration (2008) confirmed that… If the organization has a well-known abbreviation, include the abbreviation in brackets the first time the source is cited and then use only the abbreviation in later citations. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) confirmed … FDA’s experts tested… In-text Citations: The same last name/the same author When citing authors with the same last names, use first initials with the last names. (B. Kachru, 2005; Y. Kachru, 2008) When citing two or more works by the same author published in the same year, use lower-case letters (a, b, c) with the year of publication to order the references. Smith’s (1998a) study of adolescent immigrants… In-text Citations: Personal communication When citing interviews, letters, e-mails, etc., include the communicator’s name, the fact that it was personal communication, and the date of the communication. Do not include personal communication in the reference list. A. P. Smith also claimed that many of her students had difficulties with APA style (personal communication, November 3, 2002). Or, (E. Robbins, personal communication, January 4, 2001). In-text Citations: Electronic sources When citing an electronic document, whenever possible, cite it in the author-date style. If electronic source lacks page numbers, locate and identify paragraph number/paragraph heading. According to Smith (1997), ... (Mind over Matter section, para. 6). APA Headings APA uses a system of five heading levels APA Headings Here is an example of the five-level heading system: APA Tables Label tables with an Arabic numeral and provide a title. The label and the title appear on separate lines above the table, flush-left and single-spaced. Cite a source in a note below the table. Table 1 Internet users in Europe Country Regular users France 9 ml Note: The data are adapted from “The European Union and Russia”(2007). Retrieved from http://epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu APA Figures Label figures with an Arabic numeral and provide a title. The label and the title appear on the same line below the figure, flush-left . You might provide an additional title centered above the figure. Cite the source below the label and the title. The Figure 1. Internet users in Europe. Adapted from European Union and Russia: Statistical comparison by Eurostat Statistical Books, 2007, Retrieved from http://epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu Additional APA Resources • The Purdue OWL http://owl.english.purdue.edu • Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association, 6th ed. • APA’s website http://www.apastyle.org APA Style Test/Tutorial http://www.lib.usm.edu/legacy/tutorials/apat utorial/definition.html Steps in the Research/Scientific Process 1. Identify socially important issue 2. Review current literature 3. Define conceptual model 4. Define specific hypothesis(es) and research question(s) 5. Define dependent variable(s)/measure 6. Identify independent variable(s)/measures 7. Select appropriate research design 8. Obtain consents 9. Collect data 10. Analyze data 11. Communicate results Written presentation Oral presentation Steps in the Research/Scientific Process 1. Identify socially important issue 2. Review current literature 3. Define conceptual model 4. Define specific hypothesis(es) and research question(s) 5. Define dependent variable(s)/measure 6. Identify independent variable(s)/measures 7. Select appropriate research design 8. Obtain consents 9. Collect data 10. Analyze data 11. Communicate results Written presentation Oral presentation “The way we think about things, not the actual practices themselves” (Kauffman, 2007, p. 241). ◦ A link to this article is posted on the wiki Guides our thinking and provides “rules”, “principles” that guides the research and practice. External Community Supports Social/Behavior Support System: School-wide PBS Academic Support System: Response to Intervention Context for: Person Centered Planning, Functional Assessment & Wraparound Strength-based shared understanding of : Values, Long-term Goals, Current Programs, Possible variables influencing behaviors PersonCentered Planning Functional Assessment FBA Identifying: Routines, Setting Events, Antecedents, & Functions of Interfering Behaviors Collaboratively Outline Behavior Supports Plan that speaks with “One Voice” Consistently Implement, Monitor, Evaluate, COMMUNICATE Ongoing Comprehensive Implementation: Wraparound Schoolwide Applications Six Guiding Principles to Model Creating an Inclusive School 1. All instruction is guided by General Education 2. All school resources are configured to benefit all students 3. School Proactively addresses social development and citizenship 4. School is data-based learning organization 5. School has open boundaries in relation to its families and its community 6. District supports school-centered approach and extensive systems-change activities required to implement a school-wide model Sailor & Roger, 2005 I. Provide Multiple Means of Representation Perception II. Provide Multiple Means of Action & Expression Physical Action Language, Expression & expressions, and Communication symbols Comprehension Executive Functioning/ Planning National Center on UDL; www.udlcenter.org III. Provide Multiple Means of Engagement Recruiting Interest Sustaining Effort and Persistence Self-regulation Schoolwide Applications Model Sailor, 2008 Practice Guide for Self Determination Loman et al., 2010 Person-Environment Fit & Schools (Thompson, Wehmeyer, & Hughes, 2010) Check on the Wiki for details & template Recommended at least 2 to 3 pages of the document due at the end of the term. Sheldon will explain this more when he gets back on Monday! You should educate readers about the topic and provide a clear rationale as to why the study is important and necessary based on the previous research and writing on the topic. The process involves finding and reading the relevant professional literature on the chosen topic and summarizing the information in a written review. Most of the research will be in the form of scholarly books, book chapters, and published journal articles. Do not plagiarize. Make sure to put all information in your own words and give credit to all authors who are used through professional citations using APA format. Within your literature review you will present the logic or conceptual framework as to why and how your current study (topics, methods, designs) is organized the way it is. Make this section compelling. Tell the reader why this is an important topic and why they should continue to read your document. Concisely explain the social importance of what you are studying. Start with a powerful statistic or statement. Take a look at some of the articles that you are reviewing for class and see how they start their articles. ½ to 1 page recommended length State your research question(s) in the form of a question that includes the independent variable(s) and dependent variable(s) within the question. For example: “Do student who participate in the Super-Duper literacy intervention [IV] perform better on statewide standardized tests [DV] in reading than students who do not receive the Super-Duper literacy intervention? Briefly and clearly state how each research question will be addressed. For example, “This research question will be answered by Briefly present the proposed theoretical and practical implications of the findings. e.g., “The results of this study may have implications for comparing the end-of-year state wide test scores of students who received the intervention and those who did not receive the intervention.” the use of the evidence-based Super-Duper Reading Intervention by elementary special education teachers…” Framed based to operationalize (clearly define so that it can be replicated) the objectives of the proposed research project. Mention the IV and DV and how they will affect each other Framed based on methodology: ◦ Experimental/Quasi-experimental/Single-subject: “Is there a causal of functional relationships between IV and DV” ◦ Correlational: “Is there a correlational relationship between IV and DV” ◦ Descriptive/Qualitative: Describe a phenomenon or issue better, “What is the prevalence of intellectual disabilities in African-American middle school students?” Find a group that you may be working with for the research proposal topic Work to find a group of 3-4 people that you may be working with for the research proposal for this course. Outline what search criteria (key words) you will use for your literature search. Discuss a possible conceptual framework that will guide your research. Please complete within the next 24 hours.