Academic English: Avoiding Plagiarism
advertisement

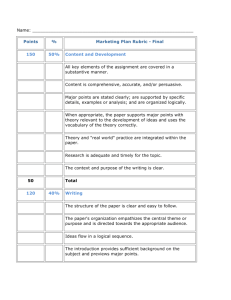
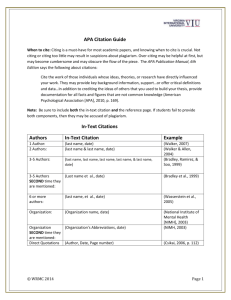
Academic English: Avoiding Plagiarism Citing Your Sources Giving Credit Where Credit is Due • When using other researchers’ ideas it’s important to give credit to those researchers. This usually involves a two step process: (1) Give a brief in-text citation (2) Include a more detailed reference at the end of your written work on a reference list or bibliography. Displaying Your Knowledge • Crediting other research also has the added benefit of allowing you to display your expertise in your field. It shows that you have read the research of others and know what research has been done. It helps to position yourself as a researcher. Substantiating Claims Made • More importantly, it helps to substantiate claims you are making. Few researchers will trust results that come from an unreferenced paper. • In short, it makes your research more believable. Citation Systems • Several types of citation systems are used. (1) APA – American Psychological Association (2) MLA – Modern Language Association (3) Chicago Manual of Style APA • Most linguistics, TESOL, or SLA journals use APA so that is what we will use. • You will not need to know MLA for the purposes of this course. In-text Citations Here are three examples of in-text citations: (1) More children prefer Big Bird to Cookie Monster (Smith, 2005). (2) Smith (2005) found that children prefer Big Bird over Cookie Monster. (3) In 2005, Smith's study demonstrated conclusively that children prefer Big Bird to Cookie Monster. Source: http://www.lib.umd.edu/guides/citing_apa.html#text In-text Citations with Direct Quotes • Here are examples with direct quotes. • Aufderheide (1996) argues that without "help from regulators to shape and constrain market conditions" (p. 28), we cannot expect the state of educational television to improve. • From the moment it hit the air, Sesame Street was "a lightning rod for all sorts of ideas about children and television" (Morrow, 2006, p. 109). Source: http://www.lib.umd.edu/guides/citing_apa.html#text Including Page Numbers If you directly quote material, provide a page number (or paragraph number for sources without page numbers). If a page or paragraph number would be helpful to the reader in locating specific ideas or paraphrases, APA format also encourages providing them. Citation and Number of Authors • The number of authors of a study affects the method of citing the study. One work by one author • nclude the author's name and the year of publication. Smith (2005) conclusively demonstrated ... ... an argument supported by decades of research (Smith, 2005). One work by two authors • Cite both names every time the reference occurs. In the text of your paper, write out the word "and" but use an ampersand in the parentheses and the reference list: as Fisch and Truglio (2001) argue ... ... as has been demonstrated (Fisch & Truglio, 2001). One work by more than two authors. • If the work has three, four, or five authors, list all names in the first reference but use only the first author's name and et al. in subsequent references. Segal, Cole, and Fuld (2002) show ... [first reference] Segal et al. show ... [second reference and thereafter] One work with six or more authors • Cite only the last name of the first author followed by et al. in all references in the text. Smith et al. rebut the notion ... • You must also create a reference in your reference list for each source you cite in your text. • Every source must appear every source must appear that appears in your text in the list of references; in the list of references in your text. • Be sure to proofread carefully so that author names and dates in both citations match perfectly.