ICT in Medicine
advertisement

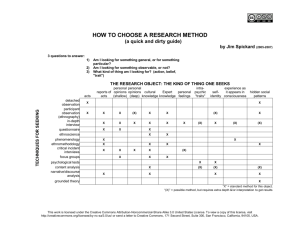
ICT in Medicine FatMax 2007. Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 2.5 License ICT in Medicine MEDICINE + ICT = “TELEMEDICINE” Patient Records Communications Internet ICT in Medicine Expert Systems Equipment Research FatMax 2007. Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 2.5 License Patient Records One obvious use of ICT in medicine is the introduction of databases to store patient records • Currently moves are being made to transfer all paper records over to a £12bn NHS database • Central storage of records • All the benefits of databases! FatMax 2007. Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 2.5 License Patient Records Faster access to patient records Transfer of patient data will be quicker e.g. between GPs and hospitals Less storage space needed CENTRALISED DATABASE Data analysis tools e.g. identify patients at risk Doctors writing easier to read!!! Multimedia capabilities e.g. scans, x-rays etc. all available in one record FatMax 2007. Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 2.5 License Patient Records Security Concerns (insufficient safeguards) “Over-reliance” on ICT Time/cost of inputting large volumes of data from old paper based records CENTRALISED DATABASE Doctor training – it actually takes longer for some doctors to complete electronic records Who sees the information? Some concern over the content of electronic records FatMax 2007. Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 2.5 License Internet The Internet is awash with a wide variety of medical “tools” for both professional and layperson • Online diagnosis – expert systems • Medical dictionaries • “Alternative” treatments • Support groups for every imaginable illness FatMax 2007. Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 2.5 License Internet Services 24/7 access to information Reduces the burden on GPs Patients can make informed choices e.g. alternative treatments Reduces the burden on hospitals ONLINE SERVICES Support for patients from other sufferers Cheaper prescription drugs Note: this is usually illegal Access to research for professionals FatMax 2007. Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 2.5 License Internet Services Reliability of websites? Inaccurate self-diagnosis Sale of dangerous so-called “prescription drugs” ONLINE SERVICES Digital Divide – who has access to Internet services? Temptation for Govt. to replace “core” services with cheaper web-based provision FatMax 2007. Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 2.5 License Medical Equipment Lots of equipment used in the field of medicine is dependant on ICT to function effectively • • • Scanners (e.g. CAT, MRI etc.) use computers to process data Microprocessors are used in a variety of medical devices Computer guided lasers in surgery FatMax 2007. Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 2.5 License Medical Research ICT has changed the way in which medical research is conducted • • • Modelling the effects of new drugs – reduces the need for vivisection and clinical trials ICT is used to conduct clinical trials Collaboration between international teams e.g. Human Genome Project FatMax 2007. Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 2.5 License Equipment/Research New types of surgery possible Reduces waiting times in hospitals Better quality of life for the disabled Collaboration between healthcare professionals EQUIPMENT/RESEARCH Management of clinical trials online Miniaturisation of medical devices Cost reductions – estimated saving of $200 million and two years on the cost of developing new drugs FatMax 2007. Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 2.5 License Equipment/Research Hardware/software can have flaws and break down Cost – the capital cost of an MRI scanner is over £1million!!! EQUIPMENT/RESEARCH Training – doctors and surgeons need to retrain to use new equipment “Over-reliance” on ICT Can never replace clinical trials FatMax 2007. Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 2.5 License Expert Systems A computer system that simulates the knowledge and expertise of a human specialist e.g. a doctor • • • Some people prefer the anonymity of a “robot doctor” Can be kept up-to-date and continually added to - acquiring knowledge faster than any human Some people prefer a “human touch” FatMax 2007. Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 2.5 License Communications 1 Advances in telecommunications are revolutionising the delivery of out-patient healthcare • • Remote diagnosis can be used to diagnose and treat patients remotely Self monitoring – patients can monitor/treat their own conditions at home without the need for a visit to hospital FatMax 2007. Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 2.5 License Communications 2 Advances in telecommunications are revolutionising the way health care professionals are able to share information • • Wireless transmission provides a vital link between paramedics and hospitals Videoconferencing can be used by professionals to share expertise with colleagues all over the world FatMax 2007. Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 2.5 License Summary/Revision Use the your textbook or the Internet to make your OWN notes on developments in ICT in Medicine Your notes should cover the benefits/drawbacks of increased use of ICT in Medicine FatMax 2007. Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 2.5 License