Standards
advertisement

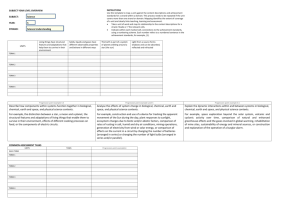
EGLCEs & EHSCEs For Beginners 1 Curriculum History Snapshot • Center Based Schools never had a curriculum that was developed for our population • ISD workgroup met to create the model Curriculum for Participation and Supported Independence • State created the Frameworks (GLCEs) to build a statewide curriculum. 2 What Does this mean to me? • The state has mandated that all schools use the State Framework Curriculum (GLCEs) to instruct students. • ISD Workgroup incorporated the state benchmarks/EGLCEs into the Model Curriculum for Participation and Supported Independence • Staff need to show that they are using benchmarks to mark student progress (EGLCEs) These are tested in the MI Access 3 GLCEs CBI CURRICULUM EGLCEs & EHSCEs SUPPORTS MI ACCESS Participation and Supported Independence Curriculum Supports EARLY CHILDHOOD STANDARDS 4 WHAT IS IN THE FRAMEWORK? The framework includes the resources needed to develop a standards-based curriculum. 5 Content Standards and GLCES A list of core curriculum content standards and benchmarks (GLCEs) for grades K-12 in the areas of: English language Mathematics, Science Social science. 6 Content Standards and Benchmarks cont. The Standards describe what all students should know and be able to do in each of the subject areas. The Domains in each strand are broader, more conceptual groupings. In several of the strands, the “domains” are similar to the “standards” The Benchmarks / GLCEs indicate what students should know and be able to do at various developmental levels (i.e., early elementary school, later elementary school, middle school, and high school). 7 What are GLCEs • Grade • Level • Content • Expectations 8 What are EGLCEs ? Stretched or Extended GLCEs Created for students functioning at the Participation, Supported Independence and Functional Levels • Extended • Grade • Level • Content • Expectations 9 EHSCEs Are for the High School Level Students • Extended • High • School • Content • Expectations 10 Standards, Domains, Strands???? Science Standards Benchmarks (EGLCEs) • Strands Example: Strand – Life Science Standard – All students will use classification systems to describe groups of living things. EGLCEs –Participation – Identify observable characteristics and/or body parts of a variety of animals (L.OR.P.III.2.e.1a) 11 Standards, Domains, Strands???? English Language Arts (ELA) • Strands Domain Benchmarks (EGLCEs) Example: Strand – Reading Domain – Writing Process EGLCEs –Participation – Generate own name and simple labels to demonstrate ownership and/or convey meaning (e.g. labeling a picture assigning a message to a picture) W.PR.e4.P.EG03a 12 Standards, Domains, Strands???? Math Domain Benchmarks (EGLCEs) • Strands Example: Strand – Measurement Domain – Units and systems of measurement EGLCEs –Participation – Associate activities with the approximate time of day. Examples: Meals, Going to school/going home M.UN.e4.P.EG01a 13 Math Calculation 14 GLCEs CBI CURRICULUM SUPPORTS EGLCEs & EHSCEs MI Access Participation and Supported Independence Curriculum Supports EARLY CHILDHOOD STANDARDS 15 How to read the numbers! Example 1 Extended Benchmark Coding Example L.OR.P.EB.III.2.e.1a L Using Life Science Knowledge OR Organization of Living Things P Participation EB Extended Benchmark III. 2.e.1 Number for the MI Curriculum Benchmark III - is for Strand # 3 e - is for elementary a Linked to previous benchmark 16 How to read the numbers! Example 2 Extended Benchmark Coding Example L.OR.P.EB.III.2.e.1ADDm L Using Life Science Knowledge OR Organization of Living Things P Participation EB Extended Benchmark III. 2.e.1 Number for the MI Curriculum Benchmark III - is for Strand # 3 e - is for elementary ADDm Add this extended elementary benchmark to middle school (m) 17 English Language Arts Elementary and Middle School (Grades K-8) GLCEs Organization STRAND 2 Writing (W) Strand 1 (R) STRAND 3 Speaking, Listening, and Viewing (S) Domains WS: FL: NT: IT: CM: MT: CS: AT: Word Study Fluency Narrative Text Informational Text Comprehension Metacognition Critical Strands Attitude GN: PR: PS: GR: SP: HW: AT: Genre Process Personal Style Grammar and Usage Spelling Handwriting Attitude CN: DS: RP: Conventions Spoken Discourse Response 18 Mathematics Elementary and Middle School (Grades K-8) GLCEs Organization 1 Numbers and Operations (N) STRAND 2 Algebra (A) STRAND 3 Measurement (M) STRAND 4 Geometry (G) STRAND 5 Data and Probability (D) Domains ME: Meaning, notation, place value, and comparisons MR: Number relationships and meaning of operations FL: Fluency with operations & estimations PA: Patterns, relations, functions, and change RP: Representation FO: Formulas, expressions, equations, and inequalities UN: Units and GS: Geometric systems of shape, properties, measurement and mathematical arguments TE: Techniques and formulas LO: Location and for measurement spatial relationship PS: Problem SR: Spatial reasoning solving involving and geometric measurement modeling TR: Transformation and symmetry RE: Data representation AN: Data interpretation and analysis PR: Probability 19 MCF v.2000 Science Elementary, Middle School, and High School (Grades K-12) Benchmark Organization STRAND 1 STRAND 2 STRAND 3 STRAND 4 STRAND 5 Constructing New Scientific Knowledge (C) Reflecting on Scientific Knowledge (R) Using Life Science Knowledge (L) Using Physical Science Knowledge (P) Using Earth Science Knowledge (E) Standards CN: Constructing New Scientific Knowledge RO: Reflecting on Scientific Knowledge CE: Cells ME: Matter and Energy OR: Organization of Living Things CM: Changes in HE: Heredity MO: EV: Evolution Matter Motion of Objects WV: Waves and Vibrations EC: Ecosystems GE: Geosphere HY: Hydrosphere AW: Atmosphere and Weather SS: Solar System, Galaxy, and Universe 20 SCIENCE STRAND: USING LIFE SCIENCE KNOWLEDGE (L) STANDARD: ORGANIZATION OF LIVING THINGS (OR) All students will use classification systems to describe groups of living things. Level of Independence (Full, FI, SI, P) Assessable at: (Classroom/LEA/ISD,State) Elementary School Middle School III.2.e.3 Describe life cycles of familiar organisms. Key concepts: Life cycle stages— egg, young, adult; seed, plant, flower, fruit; larva, pupa. Real-world contexts: Common plants and animals such as bean plants, apple trees, butterflies, grasshoppers, frogs, birds. High School III.2.m.2 Describe the life cycle of a flowering plant. Key concepts: Flowering plant parts and processes— roots, stems, leaves, MCF v.2000 Science flowers, fruits, seeds, embryo, Benchmark pollen, ovary, egg cell, germination, fertilization. Tools: Microscope, hand lens. Real-world contexts: Common flowering plants, such as bean, tulip. L.OR.FI.EB.III.2.e.3a L.OR.FI.EB.III.2.m.2a Identify life cycles of familiar Identify stages of the life cycle of organisms. flowering plants. Functional Independence Key concepts: Life cycle stages. Key concepts: Flowering plant parts— Extended Benchmark Egg, young, adult. Baby, child, roots, stems, leaves, flowers, seeds, Classroom/LEA/ISD and State adult. Seed, plant, flower, fruit. processes—germination. Real-world contexts: Family, pets, Real-world contexts: Gardening, butterfly gardens, caring for plants. visiting an orchard. III.2.h.2 Describe the life cycle of an organism associated with human disease. Key concepts: Infection process— disease, parasite, carrier, host, infection. Tools: Microscope, hand lens. Real-world contexts: Life cycle of organism(s) associated with human disease(s), such as Lyme disease— tick, malaria—mosquito, parasites. L.OR.SI.EB.III.2.e.3a Match the life cycles of familiar organisms. Key concepts: Sapling—mature Supported Independence tree, corn—corn stalks, berry— Extended Benchmark Classroom/LEA/ISD and State bushes, pumpkin—vine. Real-world contexts: Growing small plants, gardening. L.OR.SI.EB.III.2.m.2a Sequence parts of life cycles of flowering plants. Key concepts: Seed—sprout, young plant—mature plant. Real-world contexts: Growing small plants, gardening, visiting a working farm (for example, life cycle of a tomato plant). L.OR.SI.EB.III.2.e.3ADDh Sequence parts of life cycles of insects. Key concepts: Egg—larva—pupa— adult. Real-world contexts: Mosquitoes, ticks. L.OR.P.EB.III.2.e.3a Identify parts of life cycles of familiar organisms. Participation Key concepts: Baby, mom, dad, Extended Benchmark adult, young/old. Classroom/LEA/ISD and State Real-world contexts: Family. L.OR.P.EB.III.2.m.2a Identify parts of life cycles of plants. Key concepts: Seed, flower, tree, young/old. Real-world contexts: Flower pots, gardens. L.OR.P.EB.III.2.e.3ADDh Identify parts of life cycles of animals. Key concepts: Baby, mom, dad, adult, young/old. Real-world contexts: Family. L.OR.FI.EB.III.2.h.2a Identify the life cycle of an organism associated with human disease. Key concepts: Infection process— disease, parasite, infection. Real-world contexts: Visiting the doctor, caring for others. 21 EGLCE Smoothie DEMO! Brian Marcia 22 Discussion Points • We are doing a lot of this now. How can we add more activities? • How can we involve all school staff? • How do themes fit into the picture? 23 The END 24 English Language Arts Elementary and Middle School (Grades K-8) GLCEs Organization STRAND 2 Writing (W) Strand 1 (R) STRAND 3 Speaking, Listening, and Viewing (S) Domains WS: FL: NT: IT: CM: MT: CS: AT: Word Study Fluency Narrative Text Informational Text Comprehension Metacognition Critical Strands Attitude GN: PR: PS: GR: SP: HW: AT: Genre Process Personal Style Grammar and Usage Spelling Handwriting Attitude CN: DS: RP: Conventions Spoken Discourse Response 25 MCF v.2000 Science Elementary, Middle School, and High School (Grades K-12) Benchmark Organization STRAND 1 STRAND 2 STRAND 3 STRAND 4 STRAND 5 Constructing New Scientific Knowledge (C) Reflecting on Scientific Knowledge (R) Using Life Science Knowledge (L) Using Physical Science Knowledge (P) Using Earth Science Knowledge (E) Standards CN: Constructing New Scientific Knowledge RO: Reflecting on Scientific Knowledge CE: Cells ME: Matter and Energy OR: Organization of Living Things CM: Changes in HE: Heredity MO: EV: Evolution Matter Motion of Objects WV: Waves and Vibrations EC: Ecosystems GE: Geosphere HY: Hydrosphere AW: Atmosphere and Weather SS: Solar System, Galaxy, and Universe 26 MCF v.2000 Science Elementary, Middle School, and High School (Grades K-12) Benchmark Organization STRAND 1 STRAND 2 STRAND 3 STRAND 4 STRAND 5 Constructing New Scientific Knowledge (C) Reflecting on Scientific Knowledge (R) Using Life Science Knowledge (L) Using Physical Science Knowledge (P) Using Earth Science Knowledge (E) Standards CN: Constructing New Scientific Knowledge RO: Reflecting on Scientific Knowledge CE: Cells ME: Matter and Energy OR: Organization of Living Things CM: Changes in HE: Heredity MO: EV: Evolution Matter Motion of Objects WV: Waves and Vibrations EC: Ecosystems GE: Geosphere HY: Hydrosphere AW: Atmosphere and Weather SS: Solar System, Galaxy, and Universe 27 SCIENCE STRAND: USING LIFE SCIENCE KNOWLEDGE (L) STANDARD: ORGANIZATION OF LIVING THINGS (OR) All students will use classification systems to describe groups of living things. Level of Independence (Full, FI, SI, P) Assessable at: (Classroom/LEA/ISD,State) Elementary School Middle School III.2.e.3 Describe life cycles of familiar organisms. Key concepts: Life cycle stages— egg, young, adult; seed, plant, flower, fruit; larva, pupa. Real-world contexts: Common plants and animals such as bean plants, apple trees, butterflies, grasshoppers, frogs, birds. High School III.2.m.2 Describe the life cycle of a flowering plant. Key concepts: Flowering plant parts and processes— roots, stems, leaves, MCF v.2000 Science flowers, fruits, seeds, embryo, Benchmark pollen, ovary, egg cell, germination, fertilization. Tools: Microscope, hand lens. Real-world contexts: Common flowering plants, such as bean, tulip. L.OR.FI.EB.III.2.e.3a L.OR.FI.EB.III.2.m.2a Identify life cycles of familiar Identify stages of the life cycle of organisms. flowering plants. Functional Independence Key concepts: Life cycle stages. Key concepts: Flowering plant parts— Extended Benchmark Egg, young, adult. Baby, child, roots, stems, leaves, flowers, seeds, Classroom/LEA/ISD and State adult. Seed, plant, flower, fruit. processes—germination. Real-world contexts: Family, pets, Real-world contexts: Gardening, butterfly gardens, caring for plants. visiting an orchard. III.2.h.2 Describe the life cycle of an organism associated with human disease. Key concepts: Infection process— disease, parasite, carrier, host, infection. Tools: Microscope, hand lens. Real-world contexts: Life cycle of organism(s) associated with human disease(s), such as Lyme disease— tick, malaria—mosquito, parasites. L.OR.SI.EB.III.2.e.3a Match the life cycles of familiar organisms. Key concepts: Sapling—mature Supported Independence tree, corn—corn stalks, berry— Extended Benchmark Classroom/LEA/ISD and State bushes, pumpkin—vine. Real-world contexts: Growing small plants, gardening. L.OR.SI.EB.III.2.m.2a Sequence parts of life cycles of flowering plants. Key concepts: Seed—sprout, young plant—mature plant. Real-world contexts: Growing small plants, gardening, visiting a working farm (for example, life cycle of a tomato plant). L.OR.SI.EB.III.2.e.3ADDh Sequence parts of life cycles of insects. Key concepts: Egg—larva—pupa— adult. Real-world contexts: Mosquitoes, ticks. L.OR.P.EB.III.2.e.3a Identify parts of life cycles of familiar organisms. Participation Key concepts: Baby, mom, dad, Extended Benchmark adult, young/old. Classroom/LEA/ISD and State Real-world contexts: Family. L.OR.P.EB.III.2.m.2a Identify parts of life cycles of plants. Key concepts: Seed, flower, tree, young/old. Real-world contexts: Flower pots, gardens. L.OR.P.EB.III.2.e.3ADDh Identify parts of life cycles of animals. Key concepts: Baby, mom, dad, adult, young/old. Real-world contexts: Family. L.OR.FI.EB.III.2.h.2a Identify the life cycle of an organism associated with human disease. Key concepts: Infection process— disease, parasite, infection. Real-world contexts: Visiting the doctor, caring for others. 28