Slide 1 - Thomas Tallis Science
advertisement
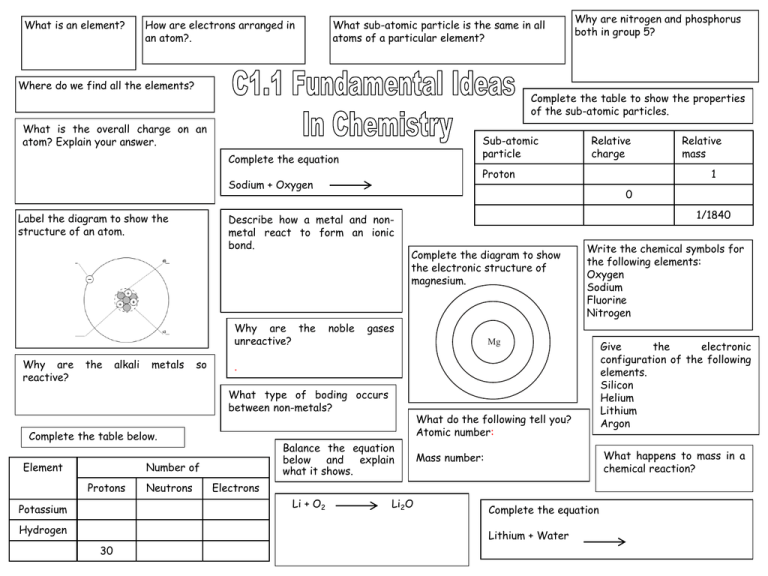
What is an element? How are electrons arranged in an atom?. What sub-atomic particle is the same in all atoms of a particular element? Where do we find all the elements? Complete the table to show the properties of the sub-atomic particles. What is the overall charge on an atom? Explain your answer. Sub-atomic particle Complete the equation Label the diagram to show the structure of an atom. the alkali metals so noble 1/1840 Complete the diagram to show the electronic structure of magnesium. Mg Neutrons Hydrogen Li2O Complete the equation Lithium + Water 30 Give the electronic configuration of the following elements. Silicon Helium Lithium Argon What happens to mass in a chemical reaction? Mass number: Electrons Li + O2 Potassium What do the following tell you? Atomic number: Balance the equation below and explain what it shows. Number of Protons Write the chemical symbols for the following elements: Oxygen Sodium Fluorine Nitrogen gases What type of boding occurs between non-metals? Element 1 . Complete the table below. Relative mass 0 Describe how a metal and nonmetal react to form an ionic bond. Why are the unreactive? Relative charge Proton Sodium + Oxygen Why are reactive? Why are nitrogen and phosphorus both in group 5? What is an element? Substanve made of only one type of atom. How are electrons arranged in an atom?. In different energy levels. What sub-atomic particle is the same in all atoms of a particular element? Protons Where do we find all the elements? In the periodic table What is the overall charge on an atom? Explain your answer. Neutral The number of electrons, which are negtive, is equal to the number of protons, which are positive Label the diagram to show the structure of an atom. electron neutron proton nucleus Why are the alkali metals so reactive? They only have one electron in their outer energy level. Complete the table to show the properties of the sub-atomic particles. Sub-atomic particle Complete the equation Sodium + Oxygen Describe how a metal and metal react to form an bond. Metal loses electrons, becomes a positive ion Non-metal gains electrons becomes of positive ion Sodium oxide nonionic and and What type of boding occurs between non-metals? Covalent Balance the equation below and explain what it shows. Number of Protons Neutrons Electrons Potassium 19 21 19 Hydrogen 1 0 1 Zinc 30 35 30 2Li + O2 Relative charge +1 1 Neutron 0 1 Electron -1 1/1840 Write the chemical symbols for the following elements: Oxygen O Sodium Na Fluorine F Nitrogen N Mg What do the following tell you? Atomic number: number of protons in an atom Mass number: number of protons and neutrons in an atom Li2O 2 atoms of lithium React with one molecule of oxygen To form 1 molecule of lithium oxide Relative mass Proton Complete the diagram to show the electronic structure of magnesium. Why are the noble gases unreactive? They have a full outer shell of electrons. Complete the table below. Element Why are nitrogen and phosphorus both in group 5? They both have five electrons in their highest energy level Give the electronic configuration of the following elements. Silicon 2, 8, 4 Helium 2 Lithium 2, 1 Argon 2, 8, 8 What happens to mass in a chemical reaction? It is conserved. Complete the equation Lithium + Water Lithium+ Hydrogen Hydroxide Give the chemical name and formula for limestone. What is a thermal decomposition reaction? Describe a positive test for carbon dioxide. Write word and symbol equations to show what happens when water is added to calcium oxide. Give 2 environmental problems with the extraction of limestone. Use the following formula CaCO3to complete the table below: Write word and symbol equations for the thermal decomposition of limestone Symbol Why don’t all the group 1 metal carbonates decompose in the lab? Element Number of atoms in compound Ca C O Give an advantage to residents of having a limestone quarry in the local area. Complete the following equations Calcium + Carbon Hydroxide Dioxide Complete the flow chart to show how different substances can be made from limestone. Ca(OH)2 + CO2 Limestone Complete the following equations to show what happens when an acid reacts with a carbonate. Magnesium + Hydrochloric Carbonate Acid + Carbonate + Mix with ______ Mix with sand Copper Sulphate Nitric Acid Heat with clay Zinc + Nitrate + Carbon + Water Dioxide + Water ____________ Concrete Give one use of calcium hydroxide Give the chemical name and formula for limestone. Calcium carbonate CaCO3 What is a thermal decomposition reaction? Breaking down a substance using heat Give 2 environmental problems with the extraction of limestone. •Quarries destroy habitats •Vehicles used to transport limestone increase carbon dioxide emissions •Dust pollution Why don’t all the group 1 metal carbonates decompose in the lab? Bunsen burner does not reach high enough temperatures Describe a positive test for carbon dioxide. Limewater turns from clear to cloudy CaO + H2O Ca(OH)2 Symbol Element Calcium carbonate Calcium + Carbon oxide dioxide Ca Calcium 1 CaCO3 CaO + CO2 C Carbon 1 O Oxygen 3 Calcium + Water Carbonate Ca(OH)2 + CO2 CaCO3 + H2O Give an advantage to residents of having a limestone quarry in the local area. •Provides jobs •Increases local trade Number of atoms in compound Complete the flow chart to show how different substances can be made from limestone. Limestone Complete the following equations to show what happens when an acid reacts with a carbonate. Magnesium + Hydrochloric Carbonate Acid Magnesium + Carbon + Water Chloride Dioxide Copper + Sulphuric Carbonate Acid Copper Sulphate Nitric Acid Calcium hydroxide Write word and symbol equations for the thermal decomposition of limestone Calcium + Carbon Hydroxide Dioxide + Calcium + Water Oxide Use the following formula CaCO3to complete the table below: Complete the following equations Zinc Carbonate Write word and symbol equations to show what happens when water is added to calcium oxide. + Carbon + Water Dioxide Zinc + Carbon + Nitrate Dioxide Water Heat with clay Cement Mix with sand Mortar Mix with sand and aggregate Concrete Give one use of calcium hydroxide Neutralising acidic soils or lakes What is an ore? Why do we have to use chemical reactions to extract most metals? What is the name given to the group of metals in the centre of the periodic table? What is meant by reduction? What is an alloy? What does it mean if a metal is found native? Give an example. Write word and symbol reduction of iron oxide. Why are aluminum and titanium expensive to extract? for the Give two problems with the extraction of copper. . Give two reasons for recycling metals Why is iron from the blast furnace limited in terms of usefulness? What is electrolysis? equations Why can’t aluminium be extracted by reduction with carbon? Explain why copper can be extracted using scrap iron. What element is used to reduce metal oxides? Why must compounds be molten for electrolysis to work? Name two novel methods of extracting copper and describe each. Why are metals such as copper and gold normally made into alloys? What properties of copper make it useful for: Piping? Draw a labeled diagram to show the structure of steel. Give a property of Low carbon steels: High carbon steels: Stainless steels: What two things are metals good at conducting? Electrical wiring? Why is electrolysis expensive? so What properties of aluminium and titanium make them useful? What is an ore? A naturally occurring rock that contains enough metal to make it economic to extract. Why do we have to use chemical reactions to extract most metals? They are reactive so are found in the crust as compounds. What is the name given to the group of metals in the centre of the periodic table? Transition metals What does it mean if a metal is found native? Give an example. Metal found as it’s element e.g Gold Give two problems with the extraction of copper. Copper rich ores are becoming scarce Mining and extraction cause major environmental problems Give two reasons for recycling metals •Extracting them uses up limited resources •Extraction requires large amounts of energy •Extraction is harmful for the environment Why is iron from the blast furnace limited in terms of usefulness? It contains about 4% carbon so is brittle Why can’t aluminium be extracted by reduction with carbon? Aluminium is more reactive than carbon Explain why copper can be extracted using scrap iron. Iron is more reactive than copper so displaces it from its salt. Draw a labeled diagram to show the structure of steel. carbon iron What is an alloy? Mixture of a metal with other elements Write word and symbol reduction of iron oxide. Why are aluminum and titanium expensive to extract? there are many stages in the processes large amounts of energy are needed. What is electrolysis? Using electricity to remove a metal from its ore. What is meant by reduction? The removal of oxygen What element is used to reduce metal oxides? Carbon Why are metals such as copper and gold normally made into alloys? They are too soft to use in their pure form Give a property of Low carbon steels: malleable High carbon steels: hard Stainless steels: resistant to corrosion What two things are metals good at conducting? Heat Electricity Iron oxide + Carbon 2Fe2O3 +3 C equations for the Iron + Carbon dioxide 4Fe + 3 CO2 Why must compounds be molten for electrolysis to work? So the positive metal ions are free to move to the negative electrode Name two novel methods of extracting copper and describe each. Phytomining - plants absorb the metal compounds; plants then burned to produce ash to release metal compounds Bioleaching – uses bacteria to produce a leachate from which metal can be extracted What properties of copper make it useful for: Piping? Resistant too corrosion; hard but easy to shape Electrical wiring? Ductile; good conductor of electricity Why is electrolysis so expensive? It uses large amounts of energy What properties of aluminium and titanium make them useful? Low density Resistant to corrosion What is a hydrocarbon? Why are alkanes considered to be saturated? Name two gases that cause acid rain Name the first 3 alkanes, give their formulae and draw their structure. Why is crude oil called a mixture? What is the general formula for an alkane? Give 2 examples of biofuels. For alkanes, describe how the following properties of a molecule change with increasing size: ■ boiling point ■ viscosity What type of bonding occurs in alkanes? Give the formula for the following molecule Describe how fractional distillation can be used to separate crude oil. What are particulates? What are the advantages of using biofuels instead of fossil fuels? ■ flammability What is the name used to describe the reaction between an element and oxygen to form an oxide? What process is used to separate crude oil? What is a biofuel? Write word and symbol equations for the combustion of propane. Why are carbon dioxide and water produced when an alkane burns? What dangerous gas is produced when a fuel burns in a limited supply of oxygen? Why is it dangerous? Give a disadvantage of using biofuels instead of fossil fuels? Give an environmental consequence of: Carbon dioxide Particulates What is a hydrocarbon? Compound made of hydrogen and carbon atoms only. Why are alkanes considered to be saturated? They have the maximum number of hydrogen atoms possible per molecule Why is crude oil called a mixture? It contains many different hydrocarbons that are not chemically bonded to each other. What is the general formula for an alkane? CnH2n + 2 For alkanes, describe how the following properties of a molecule change with increasing size: ■ boiling point Bigger molecules have higher bps ■ viscosity Bigger molecules are more viscous ■ flammability Bigger molecules are harder to light What type of bonding occurs in alkanes? Covalent What are particulates? Small solid particles of soot and unburnt hydrocarbons What is a biofuel? Fuel made from plant matter Write word and symbol equations for the combustion of propane. Propane + Oxygen Carbon + Water Dioxide C3H8 + 5O2 Name the first 3 alkanes, give their formulae and draw their structure. Methane CH4 Ethane C2H8 Give 2 examples of biofuels. Biodiesel Ethanol What is the name used to describe the reaction between an element and oxygen to form an oxide? Oxidation Name two gases that cause acid rain Sulphur dioxide Nitrogen oxides 3CO2 + 4H2O What process is used to separate crude oil? Fractional distillation Propane C3H10 Give the formula for the following molecule C6H14 What are the advantages of using biofuels instead of fossil fuels? Renewable Uses plant waste Less pollution Why are carbon dioxide and water produced when an alkane burns? The hydrogen and carbon in the fuel react with oxygen in the air. Describe how fractional distillation can be used to separate crude oil. •Crude oil is evaporated •The gases are condensed at different temperatures •Larger molecules collect first at base of column (higher temperatures) What dangerous gas is produced when a fuel burns in a limited supply of oxygen? Why is it dangerous? Carbon monoxide Prevents transport of oxygen in the blood Give a disadvantage of using biofuels instead of fossil fuels? Uses crops that could be food / require lots of land Give an environmental consequence of: Carbon dioxide Global warming Particulates Global dimming What is the raw material for making plastics? Give a definition of a polymer. What is the function of a catalyst? . Why is it important to recycle plastics? What groups of molecules are produced by cracking? What is an alkene. Give a definition hydrocarbon of What is cracking? a Describe how you would test a hydrocarbon to find out if it was unsaturated. Include the expected result in your answer. What is the general formula for an alkene? Draw the structure of propene and give its molecular formula. What is the name of the process when ethanol is made from sugar? What is a biodegradable polymer? What substance is used to make a plastic biodegradable? Name this molecule Why are hydrogels useful? What catalyst is used to crack hydrocarbons in the lab? What special property does a shape memory polymer have? Draw a diagram to show the product of reaction between ethene and bromine water? Complete the diagram below to show the formation of PVC from chloroethene Give an advantage and a disadvantage of making ethanol from sugar cane. Write an equation for the formation of ethanol from ethene. l What is the raw material for making plastics? Crude oil Give a definition of a polymer. Very large long chain molecule made up of lots of small repeating units called monomers Why is it important to recycle plastics? They are made from crude oil, which is a finite resource. We are running out of landfill space Give a definition of a hydrocarbon Compound made of hydrogen and carbon atoms only Describe how you would test a hydrocarbon to find out if it was unsaturated. Include the expected result in your answer. Shake with bromine water Turns orange to colourless if unsaturated. What is the function of a catalyst? To speed up a chemical reaction. What is cracking? Breaking long chain hydrocarbons into smaller, more useful molecules. What groups of molecules are produced by cracking? Alkanes and alkenes What is an alkene. Unsaturted hydrocarbon. What is the general formula for an alkene? CnH2n Draw the structure of propene and give its molecular formula. What is a biodegradable polymer? Polymer that can be decomposed by soil microbes What substance is used to make a plastic biodegradable? Cornstarch Why are hydrogels useful? They absorb water C3H6 What is the name of the process when ethanol is made from sugar? fermentaiton Complete the diagram below to show the formation of PVC from chloroethene What catalyst is used to crack hydrocarbons in the lab? Ceramic pot What special property does a shape memory polymer have? Returns to its original shape following heating or cooling Give an advantage and a disadvantage of making ethanol from sugar cane. There is a plentiful supply of sugar cane / sugar cane is renewable (unlike crude oil) Uses crops that would otherwise be used for food / takes a lot of space Name this molecule ethene Draw a diagram to show the product of reaction between ethene and bromine water? Write an equation for the formation of ethanol from ethene. Ethene + water -> Ethanol What is the difference between a saturated and unsaturated vegetable oil? What is a disadvantage of using vegetable oil rather than water for cooking? Give two uses of vegetable oil What happens when you add oil to water? Give two sources of vegetable oil. What is an advantage of using oil rather than water in cooking? Which are healthier, unsaturated or saturated fats? Explain your answer. What is an emulsifier? Describe it’s structure. Why are vegetable oils hardened? How can you distinguish between a saturated and unsaturated vegetable oil? Name two types of emulsion. How could you turn an unsaturated vegetable oil into margarine? Give the reaction conditions. Complete the diagram to show the hydrogenation of propene. + H2 Draw a diagram to show how an emulsifier works. Give one advantage and one disadvantage of using pressing rather than distillation to extract vegetable oil. Advantage Disadvantage What is the name of the reaction when hydrogen is added to an alkene? What is the difference between a saturated and unsaturated vegetable oil? Unsaturated has a double carbon-carbon bond What is a disadvantage of using vegetable oil rather than water for cooking? Vegetable oil has a high calorific value Give two sources of vegetable oil. Fruits, seeds, nuts What is an advantage of using oil rather than water in cooking? Oil has a higher boiling point so food cooks quicker Food tastes better / is crispier Which are healthier, unsaturated or saturated fats? Explain your answer. Saturated – they can raise blood cholesterol (which can lead to cardiovascular disease) Draw a diagram to show how an emulsifier works. Head – attracted to water Give two uses of vegetable oil Cooking Fuel / biodiesel What happens when you add oil to water? They don’t mix / form separate layers What is an emulsifier? Describe it’s structure. Substance that makes two immiscible substances mix. Has a hydrophilic (water-loving) head and hydrophobic (water hating) tail Why are vegetable oils hardened? The hydrogenated oils have higher melting points so they are solids at room temperature, making them useful as spreads and in cakes and pastries Give one advantage and one disadvantage Emulsifier of using pressing rather than distillation molecule to extract vegetable oil. Advantage Quicker; cheaper Disadvantage Product is less pure / may need further treatment Tail – attracted to oil How can you distinguish between a saturated and unsaturated vegetable oil? Add bromine water. Unsaturated turns bromine water colourless. Saturated stays orange. Name two types of emulsion. salad dressings,, paints, ice creams, cosmetics How could you turn an unsaturated vegetable oil into margarine? Give the reaction conditions. Add hydrogen; Nickel catalyst 60oC Complete the diagram to show the hydrogenation of propene. + H2 What is the name of the reaction when hydrogen is added to an alkene? Hydrogenation Label the diagram of the earth Why is an increase in the levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide harmful for marine life? Explain the differences in the amount of carbon dioxide in the early atmosphere compared to today. Why do earthquakes and volcanic eruptions happen? What parts of the Earth do we get our minerals from? How can the gases in the air be separated? What is a tectonic plate? What evidence is there that the plates are moving? How did the Earth’s early oceans form? Explain why the plates move Label the pie chart with the names and percentages of gases to show the composition of the Earth’s atmosphere today. Why is there so little carbon dioxide in today’s atmosphere?. Why was theory rejected? Wegener;s initially . Give 2 pieces of evidence that support Wegener;s theory. What did the MillerUrey experiment show? What was responsible for the composition of Earth’s early atmosphere? Label the diagram of the earth Crust Mantle Why is an increase in the levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide harmful for marine life? Carbon dioxide dissolves in the oceans, making them more acidic. Why do earthquakes and volcanic eruptions happen? Sudden movements at plate boundaries Core Atmosphere What parts of the Earth do we get our minerals from? The crust, the atmosphere and the oceans How can the gases in the air be separated? By fractional distillation as they have different boiling points. Why was Wegener;s theory initially rejected? No evidence at time Theory of land bridge more popular Present day animals not similar on different continents What is a tectonic plate? Section of the crust Explain why the plates move Radioactive decay in the core Releases heat that is transferred to the mantle And causes convection currents What did the MillerUrey experiment show? That amino acids could be formed from the interaction of hydrocarbons and ammonia with lightning. Explain the differences in the amount of carbon dioxide in the early atmosphere compared to today. Plants photosynthesised Used up carbon dioxide Produced oxygen What evidence is there that the plates are moving? Sea floor is spreading How did the Earth’s early oceans form? As the earth cooled, the water vapour in the atmosphere condensed Why is there so little carbon dioxide in today’s atmosphere?. Most of it is dissolved in the oceans or trapped in sedimentary rocks as carbonates or fossil fuels. What was responsible for the composition of Earth’s early atmosphere? Volcanic eruptions Label the pie chart with the names and percentages of gases to show the composition of the Earth’s atmosphere today. Trace gases (argon, water vapour) – 1% Oxygenn – 20% Nitrogen – 80% Carbon dioxide – 0.003% Give 2 pieces of evidence that support Wegener;s theory. Land masses on different continents have coastlines that fit together Similar fossils found on different continents