World Issues 12 Population
advertisement

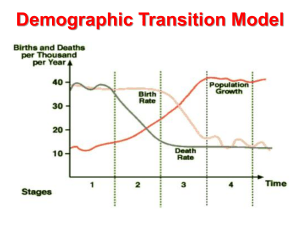
World Issues 12 Population Population Numbers Current population of: Canada? United States? Brazil? Japan? The World? 34 620 000 312 540 000 192 400 000 128 000 000 7 Billion Fast Facts of Canada - (stats Canada) • By 2034 Canada can reach anywhere between 40 and 47 million people. •Life expectancy of a new born in Canada for a male is 78; girl 83. • In 2006, nearly 80% of Canadians were living in urban areas. • 2001 to 2006, seniors increased by 11.5% while children declined by 2.5% (under 15). Canada – Stats Canada http://geodepot.statcan.ca/Diss/Hig hlights/Page3/AnimatedMap_e.cfm World Fast Facts 1. 2. 3. Every second 5 people are born and 2 people die. About half of the population are under age 25. 1 in 10 people lived in cities in 1900. By 1994 that figure had grown to 1 in 2. Christian (33%) and Muslim (22%) are the most practised religion Arabic, Chinese, English, French, Spanish, and Russian are the mother tongue or Second language for about half of the world`s population. As of 2009, the median age of the world was 28.4 years. Important Population Definitions Demography – the study of population and its’ changes and patterns. Population Density – the average number of people per square kilometre. Population Growth Rate – in %, refers to the speed at which a population grows per year. (ie. World = 1.092%) Birth rate – refers to the number of live births in a country per 1000 population per year. (ie. World = 19.12/1000) Death Rate – refers to the number of deaths in a country per 1000 population per year. (ie. World = 8.12/1000) Natural Increase – birth rate higher then death rate. Natural Decrease – death rate higher then birth rate. Infant Mortality Rate - # of infant deaths per 1000 live births. (World is at 41.61/1000 live births.) Definitions Continued Doubling Time - # of years required for a population to double. Overpopulation – condition where organism’s numbers exceed the carrying capacity of its habitat. Most commonly refers to the relationship between human population and its environment. Dependency load – The ratio of people under 15 and over 65 in any population, most commonly shown to reveal the strain on the working class. Population Momentum – When the rates of growth are expected to decline but the actual population members continue to grow. Why is this happening in Canada? Carrying capacity – the max number of people that a habitat can support. Total fertility rate – The average number of children each women will have in her lifetime. Hans Rosling on global population growth • Swedish medical doctor • discovered konzo, a paralytic disease • Academic and public speaker • co-founded Gapminder Foundation http://www.ted.com/talks/hans_rosling_on_gl obal_population_growth.html Demographic Transition Model Stage 1 Stage 2 High Stationary Early expanding (Egypt, India) •High birth rates and low death rates. •High birth rates and death rates. •Population growth rates are stable. •Not many countries are at this stage anymore. Population explosion due to natural increase. The concern is the growing population in the developing world and the impact on environment. Stage 3 Stage 4 Stage 5 Late Expanding (Brazil) Low Stationary (USA, France, Japan, UK) 5th Date Low death rates and rapidly declining birth rates. Birth rates have fallen so population growth is low. Birth rates drop below the death rate. Period of greatest natural increase. Most developed nations fall into this stage. The population at this stage is growing older. Families still remain large due to the need for support for the elderly. What has influenced this stage has been the changing role of women, the use of contraceptives and a increase in the cost of living. Many European nations are currently entering this stage. Improved medical care, fewer children needed. Good family planning and good health. Demographic Transition Model Demographic Transition Model Activity • Use this template to fill out the DTM. • The DTM has three lines: Birth rate, Death rate, and Natural Increase. Label the stages and the two axis. Identify the three lines on the bottom right hand corner. Use the finished product as a study guide for your population test.