Demographics
advertisement
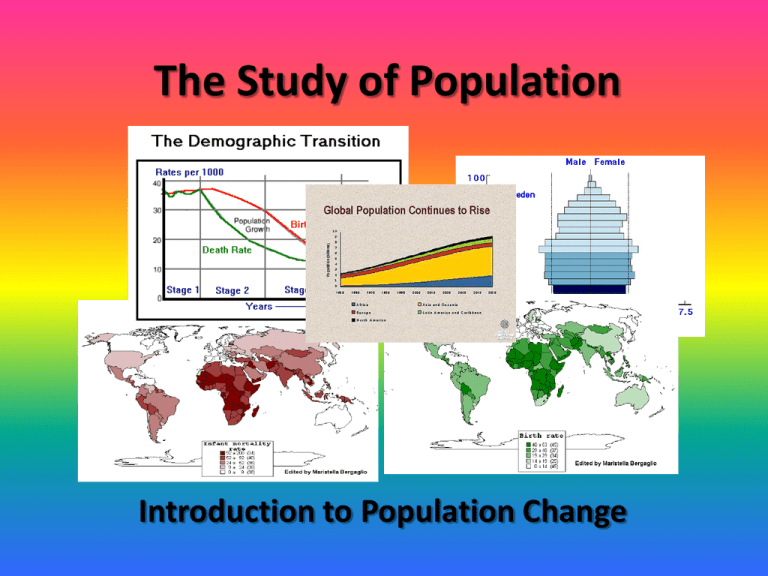
The Study of Population Introduction to Population Change What is Human Geography? • Human Geography is a branch of Geography that combines the study of economic and cultural geography to explore the relationships between humans and their natural environment, and to track the broad social patterns that shape human societies. Immigration • Movement from somewhere in the world to Canada (for a period longer than one year). – Ex. On an average day, 655 people immigrated to Canada over the course of one year....our rate of immigration is roughly 0.7% Emigration • Movement from Canada to somewhere else in the world (for a period longer than one year). – Ex. On an average day, 107 people emigrated from Canada over the course of one year...our emigration rate is roughly 0.2% Birth Rate (BR) • The relationship between the number of births in Canada and the size of the population. It gives the number of births per 1,000 people in Canada. – Ex. Canada’s birth rate is roughly 10 births per 1,000 people. Canadian and American Birth Rates since 1940 Number of births per 1,000 people – The darker green, the more births... Number of births per female – The darker green, the more children per female... Death Rate (DR) • The relationship between the number of deaths in Canada and the size of the population. It gives the number of deaths per 1,000 people in Canada. – Ex. Canada’s death rate is roughly 7 deaths per 1,000 people. Number of deaths per 1,000 babies born – The darker red, the more deaths... Natural Increase Rate • The Natural Increase Rate (NIR) is the difference between the number of births per 1,000 people in Canada and the number of deaths per 1,000 people in Canada. • Natural Increase Rate = Birth rate – Death rate = 10/1000 – 7/1000 = 3/1000 Therefore the NIR for Canada is 0.3 % Population Change in Canada until 2051 Net Migration Rate • The Net Migration Rate (NMR) is the difference between the immigration rate and the emigration rate. • Net Migration Rate = Imm. Rate – Emig. Rate = 7/1000 – 2/1000 = 5/1000 Therefore the Net Migration Rate is 0.5% World Net Migration Rate Brown = More Emigration Green = About Equal Blue = More Immigration Population Growth Rate • The Population Growth Rate (PGR) is the Natural Increase Rate added together with the Net Migration Rate • Population Growth Rate = NIR + NMR = 3/1000 + 5/1000 = 8/1000 Therefore our Population Growth Rate in Canada is roughly 0.8% World Population Growth Rate Blue / Purple = Small Growth or Declining Population Light Blue / Green = Steady Growth Yellow = Rapidly Increasing Population Doubling Time and the Rule of 70 • Doubling time is as simple as the name suggests; it is the amount of time is takes a countries population to double from its existing amount... • You can use the Rule of 70 to figure it out...simply divide 70 by the Population Growth Rate • In Canada that is 70/0.8% = 87.5 Years – Depending on immigration levels that may go up or down (i.e. It could happen faster than 87.5 yrs) World Population: ~6,700,000,000 (Feb. ’08) Population Changes • There is the assumption that because young children and the very elderly do not work on a full-time basis that they will require some type of public support (for housing, transportation, education and healthcare). • The part of the population who needs this type of support is call the dependency load. The Dependency Load is Older Adults (65+) and Children (Under 15) • Our dependency load is around 31% Population Pyramids • Population pyramids are horizontal bar graphs that represent the portion of the population that is currently a certain age. They are split every five (5) years or so and by male/female characteristics. • They show the percentage in the horizontal axis and the amount per age on the vertical axis. • Examples of Canada’s population in 1956 and 2004 are shown on Pg. 190 (Fig. 16-4) in your text. Population Pyramids Source: United States Census Bureau, International Database Population Pyramids Source: United States Census Bureau, International Database Population Pyramids Source: United States Census Bureau, International Database Changes in Population Structure • Pyramids can explain a number of different characteristics of a population over time – Ex. Post WWII, large number of babies born...today that group is around 49-60 years-old – Ex. Shift from young European immigrants Post WWII to older Asian and Middle Eastern Immigrants Changes in Population Structure • The amount of people at certain age brackets determines our needs in society – Ex. In the 1960s we needed elementary schools for the baby boomers – Ex. In the 2010s we’ll need healthcare facilities to take care of those now full grown boomers Stages of Population Change • Stage 1 • Many decades ago a high birth rate and high death rate keeps the population relatively stable • Stage 2 • At some point the death rate drops (better medicine and health care)...that combined with a higher birth rate causes growth Stages of Population Change • Stage 3 • Birth rates drop as the COL rises and education becomes more important...people begin waiting longer to have kids and they have less kids than 75 to 100 years ago. • Since the end of WWII, the increased number of women in the workforce has also caused a dip in the birth rate Stages of Population Change • Stage 4 • The birth rate drops off as well as gets closer to the death rate again (the stages go full circle)...in Canada we have not yet reached that point but for many European countries this has already happened • The impact is a low NIR and a reliance on immigration to get population growth... What are some reasons for this massive population boom?







