AP terms
advertisement
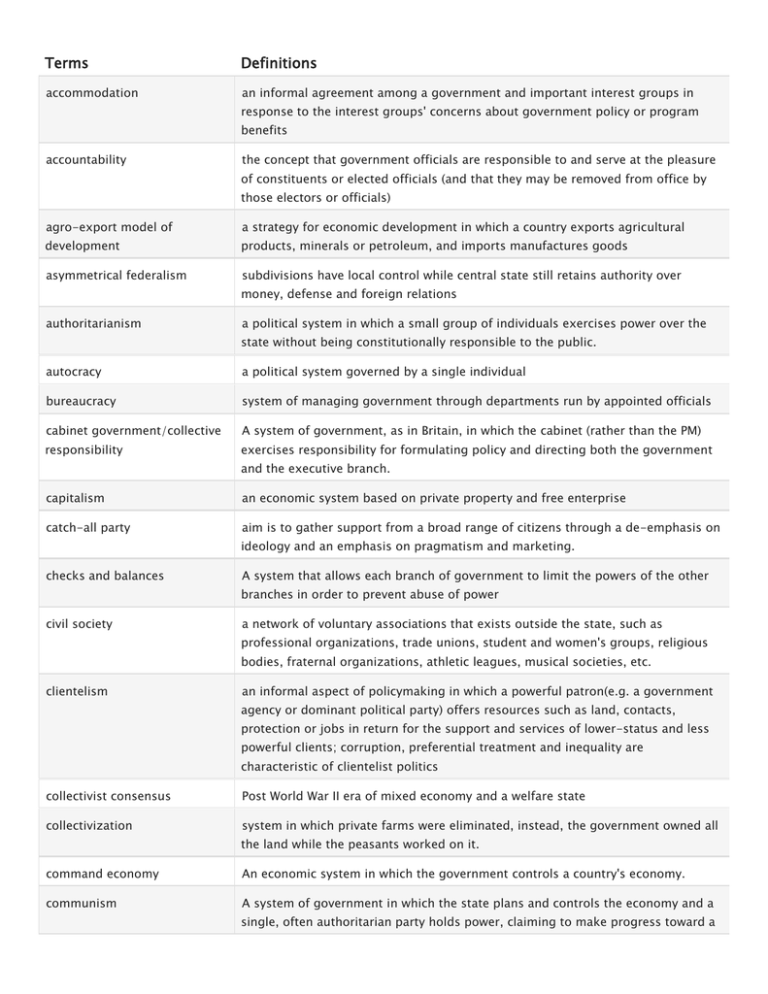
Terms Definitions accommodation an informal agreement among a government and important interest groups in response to the interest groups' concerns about government policy or program benefits accountability the concept that government officials are responsible to and serve at the pleasure of constituents or elected officials (and that they may be removed from office by those electors or officials) agro-export model of a strategy for economic development in which a country exports agricultural development products, minerals or petroleum, and imports manufactures goods asymmetrical federalism subdivisions have local control while central state still retains authority over money, defense and foreign relations authoritarianism a political system in which a small group of individuals exercises power over the state without being constitutionally responsible to the public. autocracy a political system governed by a single individual bureaucracy system of managing government through departments run by appointed officials cabinet government/collective A system of government, as in Britain, in which the cabinet (rather than the PM) responsibility exercises responsibility for formulating policy and directing both the government and the executive branch. capitalism an economic system based on private property and free enterprise catch-all party aim is to gather support from a broad range of citizens through a de-emphasis on ideology and an emphasis on pragmatism and marketing. checks and balances A system that allows each branch of government to limit the powers of the other branches in order to prevent abuse of power civil society a network of voluntary associations that exists outside the state, such as professional organizations, trade unions, student and women's groups, religious bodies, fraternal organizations, athletic leagues, musical societies, etc. clientelism an informal aspect of policymaking in which a powerful patron(e.g. a government agency or dominant political party) offers resources such as land, contacts, protection or jobs in return for the support and services of lower-status and less powerful clients; corruption, preferential treatment and inequality are characteristic of clientelist politics collectivist consensus Post World War II era of mixed economy and a welfare state collectivization system in which private farms were eliminated, instead, the government owned all the land while the peasants worked on it. command economy An economic system in which the government controls a country's economy. communism A system of government in which the state plans and controls the economy and a single, often authoritarian party holds power, claiming to make progress toward a higher social order in which all goods are equally shared by the people. consultative authoritarianism where one individual determines the course of action co-optation strategy of that manages symbiotic interdepen. by neutralizing problematic forces in specific environment corporatism a political system in which interest groups become an institutionalized part of the state or dominant political party; public policy is typically the result of negotiations among representatives of the state and key interest groups coup d'etat the constitutionally unauthorized removal of an existing government by force danwei control maintained through this system, all Chinese citizens have a lifetime affiliation with a specific industrial, agricultural, or bureaucratic nit that dictated all aspects of their lives, including housing, health care, and other social benefits. democracy/democratization the political orientation of those who favor government by the people or by their elected representatives democratic centralism a form of democracy in which the interests of the masses were discovered through discussion within the Communist party, and then decisions were made under central leadership to serve those interests developmental state A nation-state in which the government carries out policies that effectively promote national economic growth devolution the transfer of powers and responsibilities from the federal government to the states dual society a government in which the president or chief executive is from a differen political party than the political party that has a majority in, or which dominates the national legislatures economic development The improvement of living standards by economic growth. export-centered development a strategy for development in which a country exports goods and services in which strategy it has a comparative advantage; part of a neoliberal development model fascism any movement, ideology, or attitude that favors dictatorial government, centralized control of private enterprise, repression of all opposition, and extreme nationalism federalism a form of government in which power is divided between the federal, or national, government and the states foreign direct investment Direct investments in productive assets by a company incorporated in a foreign country, as opposed to investments in shares of local companies by foreign entities. An important feature of an increasingly globalized economic system. formal sector salaried or wage-based work registered in official statistics. fragmented authoritarianism authority divided among several groups/powers fundamentalism Literal interpretation and strict adherence to basic principles of a religion (or a religious branch, denomination, or sect). free trade unrestricted trade between countries fusion of powers a system of governance in which the authority of government is concentrated in one body globalization growth to a global or worldwide scale gross domestic product the sum total of the value of all the goods and services produced in a nation gross domestic product per the total value of a nation's goods and services divided by its population capita import-substituting a strategy for industrialization in which a country manufactures domestically industrialization goods that it previously imported in order to satisfy the demands of its domestic market informal sector the portion of an economy largely outside government control in which employees work without contracts or benefits insider privatization a method of privatization where workers are allowed to use vouchers to acquire shares in the enterprises where they worked. interest groups organizations that seek to represent the interests(usually the economic interests)of their members in dealing with the government international financial financial institutions that have been established (or chartered) by more than one institutions country, and hence are subjects of international law. intergovernmental (IGOs) organizations composed of representatives appointed by the state gov's organizations that have agreed to become members of the organization interventionist describing an activist government and/or state that is involved in a wide range of political, economic, and social arenas judicial review review by a court of law of actions of a government official or entity or of some other legally appointed person or body or the review by an appellate court of the decision of a trial court keynesianism economic theory, based on the ideas of British economist John Maynard Keynes, that argues that the government can stimulate the economy by increasing public spending or by cutting taxes laissez-faire a policy based on the idea that government. law-based state/rule of law a state of order in which events conform to the law legitimacy political authority conferred by law or by a state or national constitution liberalism/liberalization an economic theory advocating free competition and a self-regulating market and the gold standard market economy an economy that relies chiefly on market forces to allocate goods and resources and to determine prices monetarism an economic theory holding that variations in unemployment and the rate of inflation are usually caused by changes in the supply of money nation a community of people that shares territory and a government nationalization changing something from private to state ownership or control neo-liberalism A strategy for economic development that calls for free markets, balanced budgets, privatization, free trade, and minimal government intervention in the economy. non-governmental international organizations that operate outside of the formal political arena but organizations that that are nevertheless influential in spearheading international initiatives on social economic and environmental issues nomenklatura marxism-leninism the system of patronage in Communist countries An expanded form of Marxism that emphasizes Lenin's concept of imperialism as the final stage of capitalism and shifts the focus of struggle from developed to underdeveloped countries. mixed-market economy economic system that combines both private ownership and government ownership of the means of production para-statal sector state-owned, or state-controlled, corporations created to undertake a broad range of activities, from the control and marketing of agriultural production to the provision of banking services and the operation of airlines, other transportation facilities and public utilities parliamentary democracy government ruled democratically by a national representative body that has supreme legislative powers party of power patronage parties with strong official sponsorship patrimonial state Single ruler treats state as his own personal property, and appoints public offices to his own favor. prebendalism the form of patron-client politics that legitimizes the exploitation of government power for the benefit of office holders and their followers presidencialismo the traditional concentration of power, formal and informal, in the office of the Mexican president presidential system a system of government in which the legislative and executive branches operate independently of each other privatization the process of putting ownership of productive resources into the hands of non governmental organizations and people procedural democracy Decision making process involving; universal participation, political equality, majority rule, and responsiveness proportional representation representation of all parties in proportion to their popular vote purchasing power parity a monetary measurement of development that takes into account what money buys in different countries redistributive politics Shift wealth from rich to poor regime the organization that is the governing authority of a political unit rent/rent-seeking behavior Expenditure of scarce resources (capital, human, natural) to produce or gain an asset that generates economic rent. rentier state A state that derives a substantial portion of its revenues on a regular basis from payments by foreign concerns in the form of rent. repression a state of forcible subjugation separation of powers the division of power among the legislative, executive, and judicial branches of government shari'a the code of law derived from the Koran and from the teachings and example of Mohammed single member district An electoral district in which voters choose one representative or official. single-member plurality based on the principle of having only one member (as of a legislature) selected electoral system from each electoral district socialism a theory or system of social organization that advocates the vesting of the ownership and control of the means of production and distribution, of capital, land, etc., in the community as a whole. state a political community that occupies a definite territory and has an organized government with the power to make and enforce laws without approval from any higher authority state capitalism an economic development strategy in which the state guides the process of private industrial and agricultural development, encourages the formation of investment capital and the establishment of businesses, and protects domestic businesses from foreign competition state corporatism a political system in which the state requires all members of a particular economic sector to join an officially designated interest group, with the result that the state gains substantial control over interest groups and interest groups channel or control their members' political and economic advocacy state-owned enterprises A business owned by the government structural adjustment refers to the set of adjustments or so-called reforms that are required by international banks as a condition for future loans and for refinancing on payments due on existing loans substantive democracy Domocracy is in the substance of gov. policies, and not in the policy making procedure tacit social contract Unwritten agreement that grants Soviet power in exchange for guaranteed employment, free social services, a lax work environment, and limited interferences in personal life. technocrats highly educated bureaucrats who make decisions based on their perceptions of technical ideas rather than political ones. theocracy the belief in government by divine guidance totalitarianism a form of government in which the ruler is an absolute dictator (not restricted by a constitution or laws or opposition etc.) velayat-e faqih The guardianship of the religious jurist. Concept elaborated by Ayatollah Khomeini to justify political rule by the clergy. unfinished state A state characterized by instabilities and uncertainties that may render it susceptible to collapse as a coherent entity unitary state An internal organization of a state that places most power in the hands of central government officials vanguard party a political party that claims to operate in the 'true' interests of the group or class it purports to represent, even if this understanding doesn't correspond to the expressed interests of the group itself. welfare state a government that undertakes responsibility for the welfare of its citizens through programs in public health and public housing and pensions and unemployment compensation etc. westminster system a democratic, parliamentary system of government modeled after that of the United Kingdom system; series of procedures for operating a legislature.





