Learning Theories - Social Studies Methods
advertisement

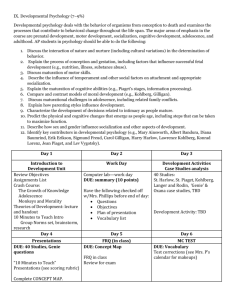
Classical Theories and Models in Psychology that Explain Learning and Development 1. Behaviorism B. F. Skinner 2. Social Learning Theory Albert Bandura 3. Information Processing Computer sciences 4. Cognitive Development Jean Piaget 5. Moral Development Lawrence Kohlberg 6. Socio-cultural Theory Lev Vygotsky 7. Bio-ecological Model Bonfrenbrener Theories of Learning and Development Famous psychologists Behaviorism B. F. Skinner Behaviorism Operant conditioning is used to control and shape behavior Basic elements: Stimulus – Response – Consequence Classroom Implication Direct instruction Knowledge is transmitted in a unidirectional pattern: from teacher to student and is confirmed through reinforcement Examples? Social (Cognitive) Learning Theory Albert Bandura Social Learning Theory People learn (emulate behavior) through observation Vicarious experience can induced modeled behavior Basic elements – attention, retention, reproduction, reinforcement and motivation. Classroom implications Examples Information Processing A group of cognitive psychologists!! Information Processing Humans process the information they receive, rather than merely responding to stimuli Mind = Computer Basic elements – attention, sensory register, working memory, long-term memory, encoding and retrieval Working-memory capacity Long-term memory capacity Patterns and recognition Classroom implications Cognitive Development Theory Jean Piaget Cognitive Development Learning takes place through the natural development of cognitive structures Basic elements – Schema, assimilation, accommodation, equilibrium, disequilibrium Four stages (in Grades 1-5 there are two stages) 1. Pre-operational Stage Egocentrism, animism, 2. Concrete operational stage Conservation, transitivity, hierarchical classification, class inclusion Moral Development Lawrence Kohlberg Moral Development Moral reasoning develops in stages, just like cognition Three stages 1. Preconventional moral reasoning Focus on self interest 2. Conventional moral reasoning Focus on family and community 3. Post conventional morel reasoning The nation, the world, what is good for EVERYONE Thinking about history revolves around moral reasoning and moral justification Sociocultural (historical) Theory Lev Vygotsky Sociocultural Theory Learning takes place through the active interaction with more capable others Language is a fundamental tool for learning and cognition Socializing intelligence! Zone of Proximal Development What a child can do independently What a child can achieve with other’s gradual help Scaffolding How do you group students for best learning? Bio-Ecological Model Uri Bonfrenbrener Bio-Ecological Model Systems within systems The individual human being (biological core) Microsystem – direct interaction with child Misosystem – interactions between and within systems Exosystem – intermediate interaction with child Macrosystem – Values, regulations, and beliefs Chronosytem – Change over time