APHG Obstacles
advertisement
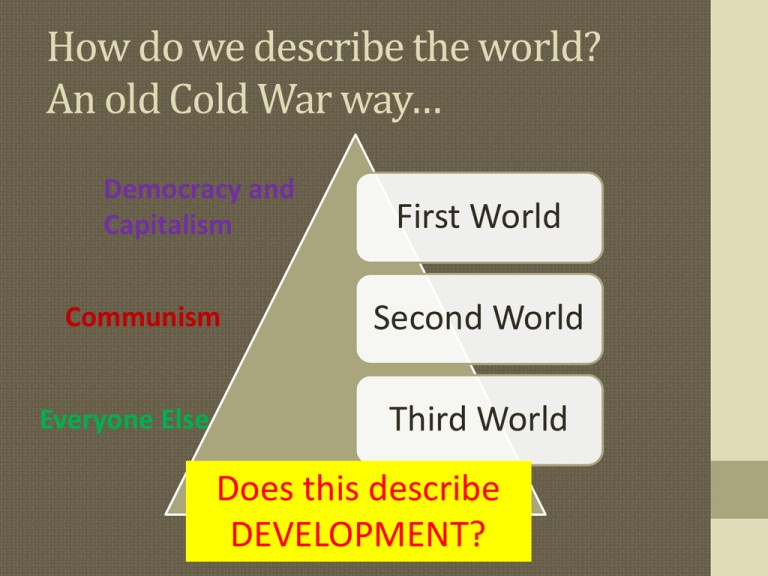
How do we describe the world? An old Cold War way… Democracy and Capitalism Communism Everyone Else First World Second World Third World Does this describe DEVELOPMENT? A Better Way? Industrialized and Service-based Communism Newly Industrializing Countries (NIC) Least Developed Countries (LDC) First World Second World Third World Fourth World Fifth World? Lack Economy and Government Economic Sectors: What is being produced? How does this relate to development? More Detailed Economic Sectors What do LDC, NIC, and MDC’s look like? United States agriculture: 1.2% industry: 21.9% services: 76.9% Lets try some examples: click here Let’s look at some factors that describe development. Here are some cool maps. What is the Solution to Development? PLAN 1: Self-Sufficiency PLAN 2: Development Through International Trade 1. What are the main ideas of each plan? 2. What are some examples of countries who have used the plans? 3. Problems with each plan? What is the Solution? PLAN 1: Self-Sufficiency • Spread investment in all sector and all regions in country. • Limit Imports and Exports (tariffs, quantity, license). • Government subsides to help some areas. • Examples? The Problems with Plan 1: 1. Inefficient Capitalism: Even the weak survive? 2. Bureaucracy: Waste of time & money. Black market? What is the Solution? PLAN 2: Development Through International Trade • Sell what you have on the world markets! (Animal, veggies, mineral, manufacturing/distribution, concentrate scarce resources on expansion of local industries. • Take that $$$ and finance in other areas of development. Examples? The Problems with Plan 2: Four Asian Tigers/ 1. Uneven Resource Distribution Dragons 2. Market Stagnation (SK, S, T, HK) - What did they sell? 3. Increase Dependence on MDC’s Arabian Peninsula - What did they sell? Development Theories Why are some more developed than others? Rostow Dependency Structuralist World Systems:Wallerstein International Trade Calls for a country to identify its distinctive or unique economic assets. According to the international trade approach, a country can develop economically by concentrating scarce resources on expansion of its distinctive local industries. Rostow’s Development Model – -The traditional society -The preconditions for take off -The takeoff -The drive to maturity -The age of mass consumption Rostow’s Model of Development Rostow’s Ladder of Development What about the other development theories? • Dependency • Pol & Econ relations control and limit development. (Dollarization) • …part of the structuralist theory • Structuralist • Structure in the world have made change difficult. (Neo-Colonialism) • It’s all HISTORY! • World Systems: Wallerstein • 3-Tier Structure (C,SP,P) Not everyone can be equal. We can look at this in different scales. Why Do LDCs Face Obstacles to Development? International trade approach triumphs The path most commonly selected by the end of the twentieth century Countries convert because evidence indicates that international trade is the more effective path toward development ▪ Example: India World Trade Organization Foreign direct investment How do you pay for development? LOANS…IMF and World Bank Millennium Development Goals by 2015 1. Eradicate extreme poverty and hunger 2. Achieve universal primary education 3. Promote gender equality and empower women 4. Reduce child mortality 5. Improve maternal health 6. Combat HIV/AIDS, malaria, and other diseases 7. Ensure environmental sustainability 8. Develop a global partnership for development Do the loan projects work? How do you pay them back? Why Do Countries Face Obstacles to Development? • Making Progress in Development • Closing the Gap • Progress in reducing the gap in level of development between developed and developing countries varies depending on the variable: • Infant Mortality Rate • Gap has narrowed from 17 to 6 (per 1,000) in developed countries and from 107 to 44 developing countries. • Life Expectancy • Gap has not narrowed. • GNI Per Capita • Gap in wealth between developed and developing countries has widened. Other Options??? • Fair Trade: protect workers and small businesses in LDC…it costs more…but it is “Fair”. (It eliminates some of the exploitation of workers) • NGOs and Microloans: Work to help the little man and woman! KIVA.org What does Development Mean? •Development implies “progress” -Progress in what? -Do all cultures view development the same way? -Do all cultures “value” the same kinds of development? How does Geography affect Development? • Dependency Theory • The political and economic relationships between countries and regions of the world control and limit the economic development possibilities of poorer areas. -- Economic structures make poorer countries dependent on wealthier countries. -- Little hope for economic prosperity in poorer countries. http://www.cnn.com/video/#/video/bestoftv/2013/04/27/exp-gps-0428-witw.cnn How Government Policies Affect Development •Governments -get involved in world markets -price commodities -affect whether core processes produce wealth -shape laws to affect production -enter international organizations that affect trade -focus foreign investment in certain places -support large-scale projects Nongovernmental Organizations (NGOs) entities that operate independent of state and local governments, typically, NGOs are non-profit organizations. Each NGO has its own focus/set of goals. Microcredit program: loans given to poor people, particularly women, to encourage development of small businesses. Summary • To develop more rapidly, developing countries must adopt policies that successfully promote development and find funds to pay for it.






![Questions for Analyzing Images [and other materials]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/009709051_1-4c9a6501cb991fe1a0d2c31541094783-300x300.png)

