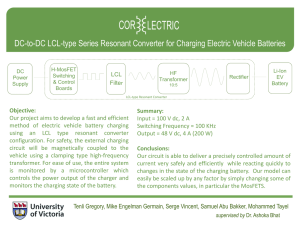
b7_-_VTT_-_Teemu_Raitaluoto_

“Electromobility in CIVITAS cities”
16/17 February 2016 – Cologne
Standardisation of ebus charging interface
Teemu Raitaluoto
Standardisation
• Motivation for the standardisation is to ensure the interoperability and connectivity for charging electric busses
• Currently tens of different solutions for charging
• The schedule for the standard prepared by CENELEC is strict
• Supply connectors and socket outlet by 12/2019
• Wireless charging 12/2019
• A lot can be learned from the standardisation of electric cars
• And bus charging standardisation can contribute to generalisation of electric harbor and mining equipment etc.
2
Use cases for standardization
• Preparing the CEN/CENELEC standard according to M/553 for electric bus charging interface requires that ebus operation is described in the form of a use case document
• There are two use case documents written by VDV/UITP/VTT together
– one for depot charging (plug) and the other for opportunity charging
(fast charging)
• The documents explain how such a system is operated in general and what is to be considered when preparing the standard
• Use cases were collected from ZeEUS Demo site experts and members of the ZeEUS eBusses Standardization Steering Group
• Contributors and interested parties include bus manufacturers, charging equipment manufacturers, transport operators, energy suppliers, cities
• Technical aspects to be standardised later by CENELEC according to industry preferences
• Mechanical, electrical, communication protocols
3
General sequence diagram
• Describes the sequences and activities of
• Approaching
• Preconditioning for energy transfer
• Connecting
• Energy transfering
• Terminating charging
• Leaving
4
Depot charging – sequence diagram
5
Opportunity charging – sequence diagram
Functional requirements
F
G
D
E
A
B
C
H
I
J
N
O
P
K
L
M
Q
R
Insulation monitoring
Charging point signalises readiness
Charging point ready for charging detected
Wish for charging
Communication set-up
Authentication
Positioning / position detection and control
Protection against unintended rolling
Provision of electromechanical contact
Readiness for charging signalised
Insulation test
Transfer of energy
Interruption of energy transfer
Resumption of energy transfer
End of energy transfer
Disconnection of mechanical contact
Release for driving
Disconnection of communication connection
Before charging
Vehicle
X
1)
Preparation of energy transfer
( vehicle speed > 0 )
Ch. Point Vehicle Ch. Point Vehicle Ch. Point
X
2)
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
1)
X
X
1)
X
X
X
2)
Energy transfer
( vehicle speed = 0 )
Vehicle Ch. Point
End of energy transfer
(vehicle speed > 0 )
Vehicle Ch. Point Vehicle Ch. Point
X
X
X
X
X
2)
X
X
X
X
X
X
1)
X
X
X X
6
Depot charging – actor relationship diagram
• Actor relationship diagram describes the actor’s relationship to each action/process step
• Actors are: bus driver, depot service provider, depot coordinator, fleet manager, other suppliers, etc. depending case by case
7
Opportunity charging – actor relationship diagram
8