Overview of body systems
advertisement

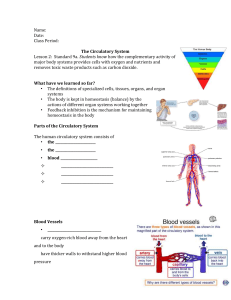
Overview of body systems Organizational Levels of the Human Body 1. Cells A.The basic units of structure and function within the human body. B.Though all cells perform the processes that keep humans alive, they also have specialized functions as well. C.Examples may be nerve cells (neurons), blood cells, and bone cells. 2. Tissues-- A group of specialized cells that work together to perform the same function. There are four basic types of tissue in the human body: A.. A.Nerve tissue — carries impulses back and forth to the brain from the body B.Muscle tissue (cardiac, smooth, skeletal) — contracts and shortens, making body parts move C.Epithelial tissue — covers the surfaces of the body, inside (as lining and/or covering of internal organs) and outside (as layer of skin) D.Connective tissue — connects all parts of the body and provides support (for example tendons, ligaments, cartilage) E.Blood, an example of a tissue, is composed of several types of cells, including red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and plasma that function to transport materials from one part of the body to another. 3. Organs--A group of two or more different types of tissues that work together to perform a specific function. The task is generally more complex than that of the tissue. For example, the heart is made of muscle and connective tissues which function to pump blood throughout the body. • 4. Systems A. A group of two or more organs that work together to perform a specific function. B. Each organ system has its own function but the systems work together and depend on one another. C. There are eleven different organ systems in the human body: circulatory, digestive, endocrine, excretory (urinary), immune, integumentary (skin), muscular, nervous, reproductive, respiratory, and skeletal. p. 80D-- draw and label the heart p.5 top HEART WORDS • Atrium– top sections of heart • Ventricle– bottom sections of heart • Septum– wall between right and left sides of heart. Separates blood with O2 from blood w/o O2. • Oxygenated– having oxygen • Red blood cells– carry oxygen using hemoglobin, red color because of Iron • White blood cells– fight infection, much larger than RBC’s • Platelets– cell fragments that plug holes to prevent bleeding p. 5 bottom HEART WORDS • Plasma– liquid part of the blood • Double circulation– blood passes through heart twice (right side lungs left side body) • Cardiovascular– dealing with heart and blood vessels • Stroke– blood clot in brain causes part of brain to go w/o oxygen and it dies. • Heart attack– blood clot in the vessels that feed the heart and that part of the heart goes w/o oxygen and dies. p. 6 top Words for respiratory system • • • • • • • Inhale– breathe in Exhale– breathe out Respiration rate--- # breaths/minute Inspiration– lungs fill up Expiration—Lungs empty Oxygen– gas we need Carbon dioxide– gas we get rid of p. 6 bottom Words for respiratory system • Lungs– where gas exchange takes place • Alveoli– small bubbles in lungs that are wrapped with blood vessels • Windpipe– air tube that connects back of mouth and nose to bronchi (tubes into lungs) • Hard palate– roof of mouth , has ridges • Soft palate– soft area behind hard palate 2/19 Bell ringer: Use the diagram below to answer the next 2 questions. • A B A. B. C. D. 2. What does figure A represent? a cell a tissue an organ a vein 3. Which figure is an organ? C D . B.. C.. D.. A. A B C D p. 7 Nose Collects air from the environment and moistens and heats the air before it enters the trachea. Trachea The windpipe; moves air from the nose to the lungs. Bronchi (s) Bronchus (p) Tubes that move air from the trachea to the lungs; one bronchus leads to each lung; part of each bronchus is outside the lung and part is inside. Lungs The main organs where gases are exchanged between air and the blood; the alveoli in the lungs are where the gas exchange takes place. Diaphragm The muscle that aids in the breathing process. p. 115D-- draw and label the respiratory system organs p. 8 circulatory system Function of the organs Heart Causes blood to flow through the body by its pumping action Vessels p. 9 Tubes that carry blood throughout the entire body Most arteries carry blood that has oxygen and nutrients to all the parts of the body. Most veins carry waste products (for example carbon dioxide) from all the parts of the body back to the heart. Capillaries are very small vessels where oxygen and nutrients leave the blood to go into the cells and carbon dioxide and other waste products enter the blood from the cells. Blood Blood is composed of red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and plasma that have different functions. p. 10 Mouth Esophagus (17 min) Begins to break down food into smaller pieces through mechanical digestion; saliva in the mouth starts the process of chemical digestion. The transport tube that carries chewed food to the stomach. Stomach (30 min) Continues the process of mechanical digestion; and secretes gastric juices that continue the process of chemical digestion started in the mouth. Small intestines (20 hours) The organ where most of the chemical digestion of food takes place; nutrients from food are also absorbed through the small intestines. The organ where water is absorbed from the food Large and taken into the bloodstream; prepares the intestines remaining undigested food for elimination from the (1-2 hours) body. p. 11 Rectum and anus The rectum is a short tube that stores solid waste until it is eliminated from the body through the anus. Liver A secondary organ of the digestive system that produces bile, which is used by the body to break up fat particles. A secondary organ to the digestive system that Gallbladder functions to store bile produced by the liver. Pancreas A secondary organ to the digestive system that functions to produce digestive juices that help to further break down the food in the small intestine. p.61D label the organs of the digestive system p. 12 The excretory system p. 13 The two kidneys get rid of urea, excess water, Kidneys and some other waste materials released by the cells. These are eliminated as urine. Ureters Tubes which connect each kidney to the bladder Bladder A saclike muscular organ which stores urine until it is released from the body. Urethra Tube through which urine passes before it is removed from the body p. 14 p. 129D diagram of the urinary/excretory system p. 15 The nervous system Brain An organ of the central nervous system, which has three distinct parts that all serve to control and coordinate the activities of the body. The cerebrum controls thoughts, voluntary actions, and the sensations related to the five senses. The cerebellum helps with balance and coordination. The brain stem is located at the base of the brain and controls vital and involuntary processes (for example, breathing, the beating of the heart, and digestion). Spinal cord A bundle of nerves that begins at the brain stem and continues down the center of the back through the vertebrae. It connects with the peripheral nerves. Peripheral nerves A network of nerves that branch out from the spinal cord and connect to the rest of the body and transmit signals to and from the brain through the spinal cord. p. 16 p. 183D the diagram of the nervous system and neuron cell (178D) Vocabulary terms--10 heart words (80D) p.17 • Heart—muscular organ that pumps blood through body • Valve-- flap between chambers of heart that prevent the backflow of blood • Artery—blood vessels that carry blood away from heart • Vein—blood vessel that carries blood back to heart • Capillary—carries blood into tiny vessels then to each cell then they connect to the veins • Aorta—largest artery in circulatory system carries blood from left ventricle to body • Diffusion—process that molecules (O2 and CO2)move into cells and RBC’s from lungs or bloodstream • Blood pressure—the pressure exerted on the walls of the blood vessels • Hemoglobin—iron containing protein that holds onto oxygen and makes up most of RBC’s • Hypertension—disorder that blood pressure is constantly higher than normal p. 18 top Nerve words • Nerve– fiber that connects sensors in body to brain and brain to muscles. • Brain– organs made of nerves that decode nerve messages and decide what to do. • Impulses– electrical messages that travel through the nerves. • Sense organs– how we gather information about our surroundings • Neuron –nerve cell 2/27 quizzes Bell ringer quiz: number 1-4 3. Which is the correct pathway for the nutrients in a bite of an apple? 1. Which organs are part of the A. circulatory system → cell → circulatory system? digestive system A. Lungs, nose, windpipe B. cell → digestive system → B. Heart, blood, veins, arteries circulatory system C. Mouth, Stomach, small intestine C. digestive system → circulatory system → cell 2. Your heart, arteries and veins work together to carry blood to all parts of D. circulatory system → digestive your body. What is the name of this system → cell group of body parts? a. Organism 4. Which of the following is the correct b. Organ system order? c. Organ a. Tissueorgancello. s. d. Tissue b. O.s.cellorgantissue c. d. Cell tissueorgan o.s. Organcelltissueo.s. 2/27 Vocab quiz 1. Can contract or shorten to cause you to move 2. Covers surfaces of the body 3. Carries messages or impulses between brain and body parts 4. Provides supports and connects all parts a. b. c. d. Connective tissue Epithelial tissue Muscle tissue Nerve tissue 2/26 bell ringer quiz answers Bell ringer quiz: number 1-4 3. Which is the correct pathway for the nutrients in a bite of an apple? 1. Which organs are part of the A. circulatory system → cell → circulatory system? digestive system A. Lungs, nose, windpipe B. cell → digestive system → B. Heart, blood, veins, arteries circulatory system C. Mouth, Stomach, small intestine C. digestive system → circulatory system → cell 2. Your heart, arteries and veins work together to carry blood to all parts of D. circulatory system → digestive your body. What is the name of this system → cell group of body parts? a. Organism 4. Which of the following is the correct b. Organ system order? c. Organ a. Tissueorgancello. s. d. Tissue b. O.s.cellorgantissue c. d. Cell tissueorgan o.s. Organcelltissueo.s. 2/27 Vocab quiz answers 1. Can contract or shorten to cause you to move 2. Covers surfaces of the body 3. Carries messages or impulses between brain and body parts 4. Provides supports and connects all parts a. b. c. d. Connective tissue Epithelial tissue Muscle tissue Nerve tissue 1. 2. 3. 4. C B D A Booklet quiz 1. The main role of this system is to provide the gas exchange between the blood and the environment. Which body parts perform this function? • 7-3.3 2. What is the organ system to which the brain belongs? 3. Which is the correct pathway for the nutrients in a bite of an apple? A. circulatory system → cell → digestive system B. cell → digestive system → circulatory system C. digestive system → circulatory system → cell D. circulatory system → digestive system → cell 4. What is the function of the digestive system? A. A. A. B. C. D. nose, trachea, lungs brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerves heart, blood vessels, blood mouth, esophagus, stomach • 7-3.2 B. C. D. excretory nervous digestive respiratory B. C. • D. to break down food material to move oxygen throughout the body to rid the body of waste material to respond to stimuli 5. What carries oxygen enriched blood from the heart? A. capillaries B. lungs C. arteries D. veins • 7-3.2 6. What carries carbon dioxideenriched blood back to the heart? A. capillaries B. lungs C. arteries D. veins • 7-3.2 7. Which organ is responsible for the constant pumping of blood, which sends oxygen-enriched blood to the rest of the body? A. lung B. heart C. brain D. liver 8. This secondary organ of the digestive system functions to store bile produced by the liver. This organ is the — A. pancreas. B. gall bladder. C. kidney. D. bladder. • 7-3.2 9. A sac-like muscular organ which stores urine until it is released from the body is the — A. kidney. B. pancreas. C. urethra. D. bladder. • 7-3.2 10. The transport tube that carries chewed food to the stomach is the — A. B. C. D. esophagus. stomach. intestine. mouth. Booklet quiz answers 1. The main role of this system is to provide the gas exchange between the blood and the environment. Which body parts perform this function? • 7-3.3 2. What is the organ system to which the brain belongs? 3. Which is the correct pathway for the nutrients in a bite of an apple? A. cell → digestive system → circulatory system B. circulatory system → cell → digestive system C. digestive system → circulatory system → cell D. circulatory system → digestive system → cell 4. What is the function of the digestive system? A. A. A. B. C. D. nose, trachea, lungs brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerves heart, blood vessels, blood mouth, esophagus, stomach • 7-3.2 B. C. D. excretory nervous digestive respiratory B. C. • D. to break down food material to move oxygen throughout the body to rid the body of waste material to respond to stimuli 5. What carries oxygen enriched blood from the heart? A. capillaries B. lungs C. arteries D. veins • 7-3.2 6. What carries carbon dioxideenriched blood back to the heart? A. capillaries B. lungs C. arteries D. veins • 7-3.2 7. Which organ is responsible for the constant pumping of blood, which sends oxygen-enriched blood to the rest of the body? A. lung B. heart C. brain D. liver 8. This secondary organ of the digestive system functions to store bile produced by the liver. This organ is the — A. pancreas. B. gall bladder. C. kidney. D. bladder. • 7-3.2 9. A sac-like muscular organ which stores urine until it is released from the body is the — A. kidney. B. pancreas. C. urethra. D. bladder. • 7-3.2 10. The transport tube that carries chewed food to the stomach is the — A. B. C. D. esophagus. stomach. intestine. mouth. 5. What carries oxygen enriched blood from the heart? A. capillaries B. lungs C. arteries D. veins • 7-3.2 6. What carries carbon dioxideenriched blood back to the heart? A. capillaries B. lungs C. arteries D. veins • 7-3.2 7. Which organ is responsible for the constant pumping of blood, which sends oxygen-enriched blood to the rest of the body? A. lung B. heart C. brain D. liver 8. This secondary organ of the digestive system functions to store bile produced by the liver. This organ is the — A. pancreas. B. gall bladder. C. kidney. D. bladder. • 7-3.2 9. A sac-like muscular organ which stores urine until it is released from the body is the — A. kidney. B. pancreas. C. urethra. D. bladder. • 7-3.2 10. The transport tube that carries chewed food to the stomach is the — A. B. C. D. esophagus. stomach. intestine. mouth. Bell ringers 3/4/15 Write the questions and your answer choice. 1. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 A. i uses 2. o sil iglottis so asal agus A. rac ea B. C. ro c us eart leural ac D. Which number represents the lungs? 1 2 3 4 Which number represents the diaphragm? Bell ringers 3.5.15 Write the questions and your answer choice. 1. Which number represents the larynx? A. B. C. D. 1 2 3 4 2. Which number represents the bronchi? • A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 3.6.15 Bell ringers quiz . 1. Which number represents the larynx? A. B. C. D. 1 2 3 4 2. Which number represents the bronchi? • A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 3. Which number represents the lungs? 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 A. 4. Which number represents the diaphragm? i uses o sil iglottis so asal A. agus rac ea B. C. ro c us D. eart leural ac 1 2 3 4 5. In examining a patient, the doctor listens to the patient’s heart to test the condition of which system? A. skeletal B. Nervous C. respiratory D. Circulatory 6. How many loops does the human circulatory system contain? A. 0 B. 1 C. 2 D. 3 7. It carries messages or impulses between brain and body parts, this is the _____ tissue. a. Epithelial b. Nervous c. Connective 8. ________ tissue provides support and connects all parts of the body. a. Epithelial b. Nervous c. Connective 9. Which of the following is the correct order? a. Tissueorgancello. s. b. O.s.cellorgantissue c. Cell tissueorgan o.s. d. Organcelltissueo.s. 10. What are organs made of? a. Tissue b. Chromosomes c. Organ system d. organelles Double check answers– circle incorrect answers 1. D 2. B 3. A 4. C 5. D 6. C 7. B 8. C 9. C 10. A 3/6 Booklet quiz 1. List 4 types of tissue ______, _____, _____, and ______. 2. Muscular organ that pumps blood 3. It can be caused by clots in vessels in heart Type of tissue Function of tissue Connective 4 5 Carries messages 6 Moves blood, food and bones epithelial 7 Types of vessels Functions of vessels 8 Carries blood rich with oxygen vein 9 10 Carries blood to every cell a. Connects and supports body parts b. Covers outer surfaces c. Muscle d. nerve a. Artery b. Capillaries c. Carries blood with little oxygen 1. epithelial, connective, nerve, muscle 2. Heart 3. Heart attack 4. A 5. D 6. C 7. B 8. A 9. C 10.B 3/16/15 Bell ringer: 2 1 2. Which number points to a muscle? A. B. C. 3 D. 1 2 3 none of these 1. Which number points to a bone? A. B. C. D. 1 2 3 none of these 3. Which number points to a joint? A. B. C. D. 1 2 3 none of these p. 20. INTEGUMENTARY system Layers of the skin Function of the layer Epidermis Outer layer of skin, covers the body, waterproof, layers of dead cells dermis Layers of living cells, second layer from outside, has blood vessels and nerves Subcutaneous Cushions the bones as well as helps layer( fatty) maintain the body’s temperature, stores extra energy in form of fat Integumentary system—skin, hair, and nails • P. 32 D draw and label • What do these do? A. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. Sebaceous gland Erector muscles Sweat gland Artery Vein Nerves Fat tissue Hair follicle What do these do? A. Sebaceous gland—(oil glands) keep skin moist and hair sealed b. Erector muscles—makes hair stand up when cold or scared c. Sweat gland—cools the skin d. Artery– carries each cell food and oxygen e. Vein— picks up carbon dioxide and waste f. Nerves– picks up messages like heat/cold, pain, pressure, etc. g. Fat tissue– cushions and insulates bones and muscles h. Hair follicle– where the living part of hair is found p. 14 bottom Nerve words • Paralyzed– break in the nerve pathway, no control below that break • Spine –bones that make up the backbone or spinal column. • Spinal cord– thick cord or rope that runs through the bones and carries messages. • Reflex– body responds to nerve messages without thinking about it p. 13D Draw and label the skeletal system p. 16 ORGAN SYSTEM STRUCTURE SKELETAL BONES—(beg 300+ adult 206)bones are framework CARTILAGE—soft rubbery substance at the ends of bones, nose and ears FUNCTION Support mass of body, make RBC’s, Enclose/protect organs, allow movement Ease movement, give shape, prevent bones grinding p.17 Notes on skeleton 1. There are 206 bones in the average human body. 2. Bones are made of layers, with marrow in the center. 3. The marrow is responsible for making blood cells. 4. The spongy layer of bone is to add support without adding a lot of mass or weight. 5. The skeleton is designed to provide structure and support to the body. p. 18 muscular system Types of muscles function SKELETAL muscles—attached to bones Voluntary SMOOTH muscles—looks like ribbons, line blood vessels, digestive tract, uterus and vagina CARDIAC muscle--makes up heart, combination of smooth and skeletal Move bones Move blood, food, and babies Involuntary involuntary Moves blood p.19 Notes on muscular system • There are more than 600 muscles in the body. • The muscles create most of the heat in the body. • The muscles move your body, move things within your body, and respond to the nerve messages. • Muscles move bones (skeletal), blood, food, and babies (smooth), and pump blood.