Chapter 4 – The Cell In Action
advertisement

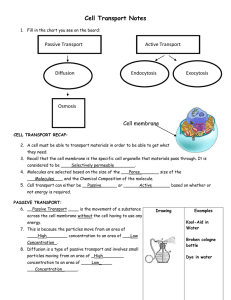
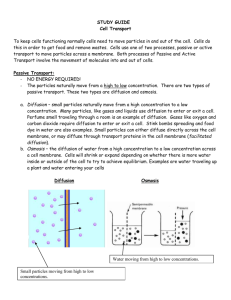
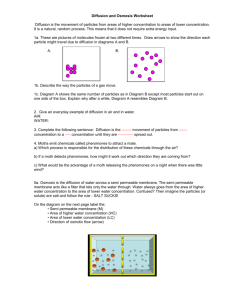
Chapter 4 – The Cell In Action What do you think? 1. 2. 3. How do water, food, and wastes get into and out of a cell How do cells use food molecules? How does one cell produce many cells? 4.1 – Exchange with the Environment Objectives: 1. 2. 3. 4. Explain the process of diffusion Describe how osmosis occurs Compare passive transport with active transport Explain how large particles get into and out of cells Diffusion Diffusion is the movement of particles from an area where their concentration is high to an area where their concentration is low. This movement can occur across cell membranes or outside of cells. Cells do not need to use any energy for diffusion of particles to occur. Osmosis The diffusion of water through the cell membrane is so important to life processes that it has been given a special name – OSMOSIS Water, like all matter, is made up of small particles. Pure water has the highest possible concentration of water particles. To lower this concentration, mix the water with something else (ex, food coloring, sugar, salt) Moving Small Particles Passive Transport – The diffusion of particles through proteins in the cell membrane from areas where the concentration of particles is high to areas where the concentration of particles is low Active Transport – The movement of particles through the proteins in the cell membrane against the direction of diffusion; requires cells to use energy Moving Large Particles Endocytosis – The process in which a cell membrane surrounds a particle and encloses it in a vesicle to bring it into the cell Exocytosis – The process used to remove large particles from a cell; during exocytosis, a vesicle containing the particles fuses with the cell membrane.