What is a PHP File?
advertisement

What is a PHP File?
PHP files can contain text, HTML tags and scripts
PHP files are returned to the browser as plain
HTML
PHP files have a file extension of ".php",
".php3", or ".phtml"
A PHP file =HTML tags + PHP scripting code.
What is MySQL?
MySQL is a database server
MySQL is ideal for both small and large
applications
MySQL supports standard SQL
MySQL compiles on a number of platforms
MySQL is free to download and use
PHP + MySQL
PHP combined with MySQL are cross-platform
(you can develop in Windows and serve on a
Unix platform)
DATABASE CONNECTIVITY
PHP MySQL Introduction
What is MySQL?
MySQL is a database.
The data in MySQL is stored in database objects called tables.
Database Tables
Databases are useful when storing information categorically .A
database most often contains one or more tables.
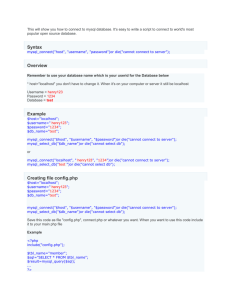
Create a Connection to a MySQL Database
Before you can access data in a database, you must
create a connection to the database.
In PHP, this is done with the mysql_connect()
function.
Syntax
mysql_connect(servername,username,password);
servername - Optional. Specifies the server to connect to. Default
value is localhost:3306"
username - Optional. - Specifies the username to log in with.
Default value is the name of the user that owns the server process
password - Optional. Specifies the password to log in with.
Default is ""
<?php
$con = mysql_connect("localhost","peter","abc123");
if (!$con)
{
die('Could not connect: ' . mysql_error());
}
// some code
?>
Closing a Connection
The connection will be closed automatically when the script ends.
To close the connection before, use the mysql_close() function:
<?php
$con = mysql_connect("localhost","peter","abc123");
if (!$con)
{
die('Could not connect: ' . mysql_error());
}
// some code
mysql_close($con);
?>
INSERT
<?php
$con = mysql_connect("localhost","peter","abc123");
if (!$con)
{
die('Could not connect: ' . mysql_error());
}
mysql_select_db("my_db", $con);
mysql_query("INSERT INTO Persons (FirstName, LastName,
Age)
VALUES ('Peter', 'Griffin',35)");
mysql_query("INSERT INTO Persons (FirstName, LastName,
Age)
VALUES ('Glenn', 'Quagmire',33)");
mysql_close($con);
?>
SELECT
<?php
$con = mysql_connect("localhost","peter","abc123");
if (!$con)
{
die('Could not connect: ' . mysql_error());
}
mysql_select_db("my_db", $con);
$result = mysql_query("SELECT * FROM Persons");
while($row = mysql_fetch_array($result))
{
echo $row['FirstName'] . " " . $row['LastName'];
echo "<br />";
}
Display the Result in an HTML Table
The following example selects the same data as the example
above, but will display the data in an HTML table:
<?php
$con = mysql_connect("localhost","peter","abc123");
if (!$con)
{
die('Could not connect: ' . mysql_error());
}
mysql_select_db("my_db", $con);
$result = mysql_query("SELECT * FROM Persons");
echo "<table border='1'>
<tr>
<th>Firstname</th>
<th>Lastname</th>
</tr>";
while($row = mysql_fetch_array($result))
{
echo "<tr>";
echo "<td>" . $row['FirstName'] . "</td>";
echo "<td>" . $row['LastName'] . "</td>";
echo "</tr>";
}
echo "</table>";
mysql_close($con);
?>
mysql_close($con);
?>
UPDATE
<?php
$con = mysql_connect("localhost","peter","abc123");
if (!$con)
{
die('Could not connect: ' . mysql_error());
}
mysql_select_db("my_db", $con);
mysql_query("UPDATE Persons SET Age=36
WHERE FirstName='Peter' AND LastName='Griffin'");
mysql_close($con);
?>
DELETE
<?php
$con = mysql_connect("localhost","peter","abc123");
if (!$con)
{
die('Could not connect: ' . mysql_error());
}
mysql_select_db("my_db", $con);
mysql_query("DELETE FROM Persons WHERE
LastName='Griffin'");
mysql_close($con);
?>