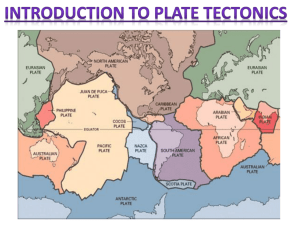
Plate Tectonics
advertisement
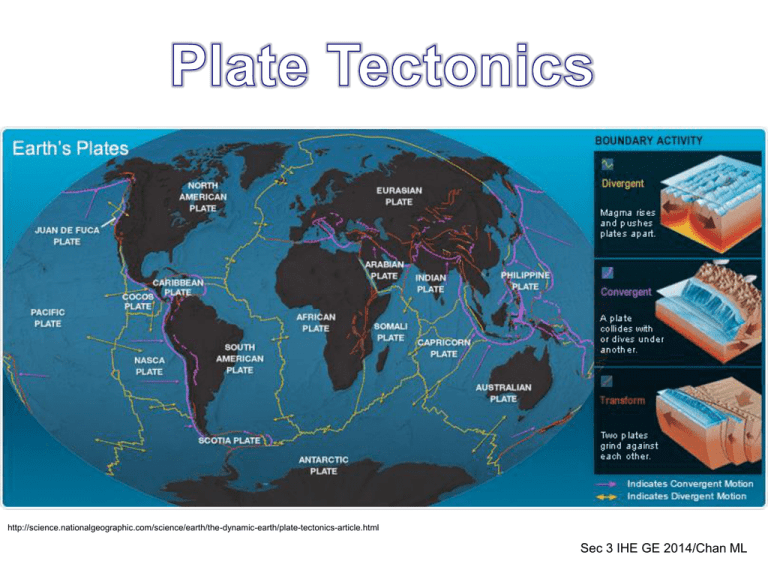
http://science.nationalgeographic.com/science/earth/the-dynamic-earth/plate-tectonics-article.html Sec 3 IHE GE 2014/Chan ML Convection Currents Rising, spreading convection currents = pull plates apart Sinking convection currents = drag plates together Divergent Plates (Constructive Boundaries) Cause: Plates move in opposite direction due to the convection movement. Effects/Landforms • new crust is created (oceanic ridges) • Oceans are born and grow wider • When a diverging boundary occurs on land a 'rift', or separation will arise and over time that mass of land will break apart into distinct land masses and the surrounding water will fill the space between them. • Earthquakes • Volcanoes http://www.platetectonics.com/book/images/Divergent1.gif Oceanic-Oceanic The divergent Mid-Atlantic Ridge rises above sea level at Thingvellir, with the North American plate to the west and the Eurasian plate to the east. Formation of Oceanic Ridge (answer) • As the N. American and Eurasian plates move apart (divergent movement) in a constructive boundary due to convection currents • Tensional stresses cause fractures in the lithosphere to occur • The zone where the plates separate is the spreading centre, • Allowing basaltic magma to well up, cool and solidify; thus becoming / forming new sea floor (this process is called sea floor spreading) • As the plates continue to move apart, more basaltic magma piles up, cool and solidify; and new mountains are formed • The mountains closest to the spreading zone are the youngest • The rows of mountains rise from 2,000 to 4,000m from the ocean floor – these are the mid-oceanic ridges • Eg: Mid-Atlantic Ridge Continental-Continental • As the Nubian and Somalian plates move apart, • They are stretched and fractures are created • The land in between sinks, creating a linear depression, known as a rift valley • As a result, earthquakes are experienced in the region • Magma may also rise to the surface creating volcanoes • Eg: the East African Rift Valley Convergent Plates (Destructive Boundaries) 3 types: • Oceanic – oceanic • Oceanic – continent • Continent - continent http://www.scienceclarified.com/images/uesc_08_img0459.jpg Oceanic-Oceanic The Japanese Islands are examples of volcanic island arcs formed by the convergence of two oceanic plates. http://www.lee.edu/~cguldenzopf/Images/Historical/Historicalmw45.jpg Cause: • 2 oceanic plates collide • One plate sinks beneath the other • Subduction zone Effects/Landforms: • Trench • Volcanoes • Earthquake Formation of Trench and volcanoes (answer) Trench in a convergence between Oceanic and Continental Plate (destructive boundary) Name of plates • When a thinner and denser oceanic plate converges with a thicker and lighter continental plate • The oceanic plate descends beneath the continental • This descent is called subduction • The old oceanic lithosphere is destroyed and as it dives to the mantle, it contributes to the formation of more magma • A long narrow and deep oceanic trench is formed where the plate dips into the mantle • Eg: Peru-Chile Trench, Java Trench • The movement of the plates cause faults to occur • Rocks break and are displaced relative to each other, • the melting of the subducting oceanic plate produces silica-rich magma • Being less dense than the mantle, the magma moves up any break or fractures • When it escapes through vents to the land surface, it forms subduction volcanoes • Eg: Mt. St. Helens, Mt Pinatubo Oceanic-Continental Cause: • Oceanic plate collides with thinner & lighter continental plate • Subduction occurs Effects/Landforms • Descending plate is destroyed • Trenches are formed • Volcanoes • Earthquakes http://www.revisionworld.com/files/oceaniccont.jpg Formation of Fold Mountains (answer) • When two continental masses collide, one is pushed under the other for a short distance Name of plates • When a thinner and denser oceanic plate converges with a thicker and lighter continental plate • The oceanic plate descends beneath the continental • This descent is called subduction • The old oceanic lithosphere is destroyed and as it dives to the mantle, it contributes to the formation of more magma • The edges of these plates are also contorted and buckled up, creating a great uplift, forming fold mountains • Since sediments from the ocean floor are contorted and uplifted, marine fossils were found at the summit of fold mountains!!! • Eg: Rocky Mountains (N. America), Andes Mountains (South America) Continental-Continental Cause: • 2 continental plates collide • No subduction Effects/Landforms • Great uplift • Rocks are contorted • Earthquakes Earthquakes are shown as yellow squares. http://www.visionlearning.com/library/module_viewer.php?mid=66 Formation of Fold Mountains (answer) • When two continental masses collide, the Indian plate is pushed under the Eurasian plate for a short distance • However, there is NO subduction • Because both are light and buoyant • This process produces a great uplift as the rocks at the edges of these two plates are contorted and buckled up • Due to the absence of magma supply, there are no volcanoes in this area • Eg: the Himalayan Mountains Transform Boundaries • occur in a few places to accommodate lateral motion, in which plates slide past one another. • very rare on continents, but they are dramatic where they do occur. Example: the San Andreas Fault (USA) and The Alpine Fault (New Zealand). • Most transform boundaries occur in short segments along mid-oceanic ridges http://www.visionlearning.com/library/module_viewer.php?mid=66 Sit back and relax… well… can’t be too relaxed… Here’s a summary… don’t fall asleep https://www.youtube.com/watch?v =0mWQs1_L3fA References • Chong, Marianne (2001) Aspects of Physical Geography • Waugh, David (2009) Geography: An Integrated approach