Topic 21
advertisement

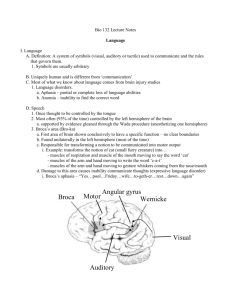
Biology 463 - Neurobiology Topic 21 Language Lange Language • Language – System by which sounds, symbols, and gestures used for communication – Process • Language comes into brain through visual and auditory systems • Motor system: Produces speech, writing • Processing between sensory and motor systems; Essence of language The role of the CNS in development of language: • The brain is the coordinating center of all linguistic activity • it controls both the production of linguistic cognition and of meaning and the mechanics of speech production • our knowledge of the neurological bases for language is quite limited, though it has advanced considerably with the use of modern imaging techniques • discipline of linguistics dedicated to studying the neurological aspects of language is called neurolinguistics Carl Wernicke Paul Brocca Neuroscientists in the 19th century discovered two areas in the brain that are crucially implicated in language processing: • the first area is Wernicke's area, which is located in the posterior section of the superior temporal gyrus in the dominant cerebral hemisphere • people with a lesion in this area of the brain develop receptive aphasia, a condition in which there is a major impairment of language comprehension, while speech retains a natural-sounding rhythm and a relatively normal sentence structure. • the second area is Broca's area, located in the posterior inferior frontal gyrus of the dominant hemisphere. • people with a lesion to this area develop expressive aphasia, meaning that they know what they want to say, they just cannot get it out. Language Areas of the brain: • Angular Gyrus is represented in orange • Supramarginal Gyrus is represented in yellow • Broca's area is represented in blue In addition to the original two areas, it has now been shown that there are five primary areas related to language in the human brain. • Wernicke's area is represented in green • Primary Auditory Cortex is represented in pink. The Wada Test, named after Japanese Canadian neurologist Juhn Atsushi Wada is used to establish cerebral language and memory representation of each hemisphere. • test is conducted while the patient is awake • a barbiturate (usually sodium amobarbital) is introduced into one of the internal carotid arteries via a cannula • the drug is injected into one hemisphere at a time • the effect is to shut down any language and/or memory function in the respective hemisphere • the patient is engaged in a series of language and memory related tests Juhn Atsushi Wada Wada Test – Used to determine hemisphere dominant for speech END.