The brain
advertisement

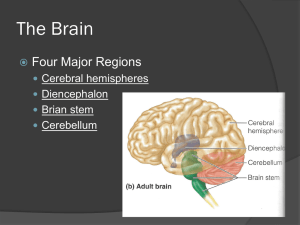
Anatomy & Physiology right & left connected by large fiber tract: corpus callosum cover most of other 3 parts surface: elevated ridges = gyri separated by shallow grooves = sulci Fissures deeper grooves separate regions of brain separates cerebral hemispheres other fissures separate brain into lobes spaces in brain filled with CSF connected to subarachnoid space (around brain & spinal cord) and central canal of spinal cord parietal lobe posterior to central sulcus receives impulses from sensory receptors (not special senses), interprets them ◦ pain recognition ◦ temperature ◦ light touch anterior to central sulcus in frontal lobe major voluntary motor tract visual area auditory & olfactory areas Brocca’s Area: ability to speak ◦ @ base of precentral gyrus (usually only on left side) ◦ injury inability to correctly vocalize words http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_0aNILW6 ILk http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=c6kRP41y grI anterior frontal lobe: higher intellectual reasoning complex memories: frontal/ temporal lobe all facets of speech: occipital/temporal/parietal lobes gray matter in brain that is NOT in cerebral cortex functions: help regulate voluntary motor activity by modifying instructions sent to skeletal muscle by primary motor cortex Parkinson’s Huntington’s sits atop brain stem enclosed by cerebral hemispheres major parts: ◦ Thalamus ◦ Hypothalamus ◦ Limbic system ◦ Epithalamus relay station for sensory impulses passing thru to sensory cortex ANS center role in: ◦ temperature control ◦ water balance ◦ metabolism regulates autonomic & endocrine functions in response to emotional stimuli (“reacting” brain vs. cerebral cortex being “thinking” brain) ◦ set level of arousal ◦ motivation ◦ reinforcing behaviors ◦ rage, love, memory, empathy ~size of thumb in diameter & ~ 3 inches long 3 parts: 1. midbrain 2. pons 3. medulla oblongata knots of capillaries w/in each ventricle produce & secrete CSF (cerebral spinal fluid) smallest, uppermost part of brain stem cerebral aquaduct: tiny canal that runs thru midbrain connecting 3rd & 4th ventricles contains reflex centers for vision, hearing “bridge” rounded structure that protrudes below midbrain contains apneustic (produces deep, prolonged inspirations) & pneumotatic center (inhibits inspiration) most inferior part of brain stem inferior border merges into spinal cord centers: heart rate, BP, breathing, swallowing, vomiting large, cauliflower-like projects dorsally from under occipital lobe 2 hemispheres convoluted surface provides precise timing for skeletal muscle activity controls balance & equilibrium Head injuries are leading cause of accidental death in USA. Concussion: dizziness, “see stars”, briefly lose consciousness; No permanent brain damage Contusion: result of marked tissue damage. Cerebrum: may maintain consciousness Brainstem: coma Cerebral Edema: swelling of brain due to inflammatory response to injury/ initially conscious neuro signs deteriorate (think edema or hemorrhage) stroke 3rd leading cause of death in USA occur when blood circulation to brain is interrupted ◦ vessel could be blocked (temporary or permanent) or hemorrhaging characterized by: ◦ abrupt onset of persisting neurological symptoms that arise from destruction of brain tissue common causes: ◦ intracerebral hemorrhage ◦ emboli ◦ atherosclerosis of cerebral arteries 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. hypertension hypercholesterolnemia heart disease narrowed carotid arteries hx of TIAs (transient ischemic attacks) diabetes smoking obesity excessive alcohol intake Thrombolytic: ◦ clot-dissolving drug: tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA) greatly improved prognosis for CVA ◦ aspirin (makes plts slippery fewer clots) ◦ blood thinners Aphasia: from damage to left side cerebrum where language centers are Motor Aphasia: ◦ damage to Broca’s area ◦ loss of ability to speak Sensory Aphasia: ◦ loss of ability to understand written or spoken word Transient Ischemic Attack “mini-stroke” due to temporary restriction of blood flow symptoms last 5 – 50 minutes “red flags” that warn impending & more serious CVAs most common type of dementia >10% population > age 65 4th leading cause of death in US characterized by progressive loss of reasoning & ability to care for oneself cause of most cases unknown but… ◦ genetic factors ◦ environmental or lifestyle factors ◦ normal aging process