WHO governs China? - Education Scotland
advertisement

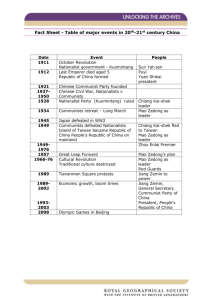
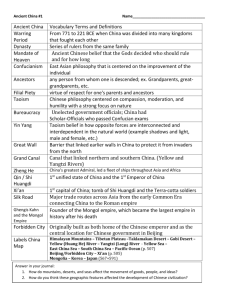
A BRIEF History of China Perth High School Confucius Classroom Introductory Presentation 2 A Brief History of China In the Beginning… • China is a very ancient civilisation • The kingdom from which China grew was established for many centuries BC • The first emperor, Shi Huangdi, established the Qn Empire in 221 BC Ancient Dynasties • • • • • • • • • Shang: c.1600 - c.1100 BC Zhou: c.1100 BC - 256 BC Qin: 256 BC - 206 BC Han: 206 BC - 220 AD 3 Kingdoms: 220 - 265 Six dynasties: 265 - 589 Sui: 589 - 618 Tang: 618 - 907 5 dynasties & 10 kingdoms: 907980 • Song: 980 - 1279 Later Dynasties • Yuan: 1279 - 1368 (the Mongol Empire) • Ming: 1368 - 1644 (the first Ming emperor drove out the Mongols and re-established the Chinese Empire) • Qing: 1644 - 1912 The Chinese Empire survived for 2133 years. In comparison, the Roman Empire survived for about 500 years and the British Empire for about 350. The Modern Era • • • • • • • The Boxer Rebellion (1899-1901: against European and US control of China) is defeated in 1901. Chinese Republic proclaimed in 1912 after the abdication of the child-emperor Yuan Shikai (a warlord) seizes power from 1912 to 1916 Dr Sun Yat-Sen, leader of the Kuomintang Party, attempts to establish the republic despite feuding warlords but dies in 1925 In 1928 Chang Kai-shek seizes Beijing for the Kuomintang Civil war with Mao Zedong’s Communist Party begins in 1929. The 6000-mile Long March sees Mao’s army escape the Kuomintang forces in 1934-35 (Mao Zedong, Zhou Enlai and Deng Xiaoping are all comrades on the March) The 2nd Sino-Japanese War • • • • • • The Empire of Japan begins attacks on China in 1937 and quickly seizes many northern and coastal areas The US gunboat Panay is sunk by Japanese bombers whilst peace still exists between the US and Japan With the attack on Pearl Harbour on Dec. 7, 1941, Japan captures European and US territories in China e.g. Hong Kong and Macau The Chinese capital is moved far up the Yangzi river to Chongqing but comes under attack Chinese, US and British forces fight back from western and central China, with supplies carried by the Burma Road to Kunming The Japanese are eventually defeated in 1945 but many areas of northern, southern and eastern China are devastated by the war The Civil War and Revolution • • • • • Despite partial alliances against the Japanese, a state of war exists between the Kuomintang and Communist forces for over 20 years from 1926 The Civil War fully breaks out in 1946 The Communist Party of China seizes power on October 1st, 1949 (although some parts of China are not captured until 1950) Various offshore islands stay loyal to the Kuomintang and Chang Kai-Shek reestablishes the Chinese Republic on Taiwan Several offshore islands are captured by the Communists between 1949 and 1960 Leaps Forward (and Back) • The Great Leap Forward (1958-60) saw Mao attempt to turn China from an agrarian economy to an industrialised society. Between 14 and 43 million Chinese starved to death. • The Cultural Revolution (1966-69) saw Mao Zedong unleash the Red Guards to stamp out liberal economic and political thought. • Death of Mao Zedong in September 1976 • In October 1976, The pro-Mao Gang of Four - led by Mao’s wife, Jiang Qing were arrested by the new Party chairman, Hua Guofeng. The Making of Modern China • • • • Deng Xiaoping was restored to Party positions he had lost during the Cultural Revolution. He quickly removed Hua Guofeng from power but allowed him to retire peacefully. Deng stayed as the most influential Chinese leader until the mid 90s. The Tiananmen Square protests in 1989 highlighted China’s growing clamour for liberalisation Third Generation leaders, under President Jiang Zemin, took power in the 90s and introduced economic liberalisation. Fourth Generation leaders, under President Hu Jintao, took power early in the 21st century and now control China.