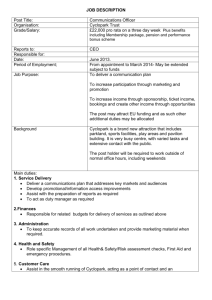
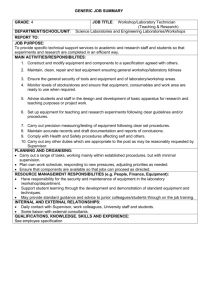
Job Analysis
advertisement

HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT Zanete Garanti Lecturer University of Mediterranean Karpasia STRATEGIC PLANNING– HR PLANNING MISSION OBJECTIVES EVALUATE existing people STRATEGY STRUCTURE COMPARE demand and supply PEOPLE HIRE new people, FIRE existing ones Research shows, that managers mostly are concerned about 2 “main” things– HIRE AND FIRE Personnel planning is the key element for successful HRM, and include more than HIRE AND FIRE HR PLANNING DEFINITIONS Human resource planning is the term used to describe how companies ensure that their staff are the right staff to do the jobs. Sub topics include planning for staff retention, planning for candidate search, training and skills analysis and much more. Process, by which an organization ensures that it has the right number and right kind of people at the right place and right time, capable of effectively and efficiently completing those tasks that help the organization achieve its overall objectives PURPOSES OF HRP Each organization needs personnel with necessary skills, qualifications, knowledge, experience etc. Need for replacement of personnel Meet manpower shortages due to labor turnover Meet needs of expansion/ downsizing Cater to future of personnel needs- avoid surplus or deficiency of labor Nature of present workforce in relation with changing environment METHODS OF PERSONNEL PLANNING APPROCHES QUANTITATIVE planning How many people do we need? QUALIFICATION planning What qualifications do we need? TIME planning PLACE planning Long term/ short term planning Changes in structure (new branches etc.) QUALIFICATION PLANNING What kind of personnel do we need? What are the skills, qualifications, knowledge we look for? Do we have it already inside of organization? Do we need to train people? HUMAN RESOURCE INFORMATION SYSTEMS (software)! QUANTITATIVE PLANNING Demand planning: Trend Analysis Ratio Analysis Regression Analysis Supply planning: How many current employees will remain in their positions during the planning period? How many will move to another position (e.g., through transfer, promotion, or demotion)? How many will leave the organization? 1. TREND ANALYSIS Trend analysis- future demand for human resources is projected on the basis of past business trends regarding a business factor Example: YEAR 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 Sales volume (€) 110 000 120 000 95 000 70 000 50 000 100 000 Number of people 30 33 28 25 20 ? 2. RATIO ANALYSIS Ratio analysis- the process of determining future HR demand by calculating an exact ratio between the specific business factor and the number of employees needed. It thus provides a more precise estimate than trend analysis Example: University has 10,000 students and 500 professors Calculating ratio: how many students for each professor? If the university plans a student enrollment increase of 1,000 for next year, how many new professors it would need? 3. REGRESSION ANALYSIS Regression analysis- similar to both trend and ratio analyses in that forecasts are based on the relationship between a business factor and workforce size 35 Workforce 30 25 20 15 10 5000 7000 9000 Sales 11000 13000 PERSONNEL PLANNING DOCUMENTS JOB ANALYSIS Job analysis is a process to identify and determine in detail the particular job duties and requirements and the relative importance of these duties for a given job Job analysis can be used in selection procedures to identify or develop: job duties that should be included in advertisements of vacant positions appropriate salary level for the position minimum requirements for screening applicants interview questions selection tests/instruments applicant appraisal/evaluation forms STEPS IN JOB ANALYSIS Collection of Organizational Structure Information Selection of Representative Position to be Analysed Collection of Job Analysis Data Developing Job Description Developing Job Specification WHO, WHAT, HOW? WHO? Employees, supervisors, managers, consultants WHAT? Skill and education factor needed for job Each task that is essential to achieve overall result Physical and metal activity involved in achieving result HOW? Checklist, interviews, observation, participation, diary method etc. Job Analysis Process of obtaining all pertinent job facts Job Description A proper definition and design of work. It contains: Job Title Location Job summary Duties and responsibilities Materials, tools and equipment used Forms and reports handled Supervision given and received Working conditions Hazards and safety precautions Job Specification A statement of human qualifications necessary to do the job. It contains: Education and qualifications Experience and training Knowledge and skills Communication skills Physical requirements like height, weight, age Personality requirements like appearance, judgment, initiative, emotional stability JOB DESCRIPTION Job Description Job descriptions are required for recruitment so that managers and the applicants can understand the role Job descriptions are necessary for all people in work A job description defines a person's role and accountability Without a job description it is not possible for a person to properly commit to, or be held accountable for, a role Job Specification Logical outgrow of job description Summarizes the human characteristics needed for satisfactory job completion It describes key qualifications someone needs to perform job successfully PURPOSE OF JOB DESCRIPTION AND SPECIFICATION Clarifies employer expectations for employee Provides basis of measuring job performance Provides clear description of role for job candidates Eneables pay and grading systems to be structured fairly and logically Essential reference tool for discipline issues Enables formulation of skill set and behavior set requirements per role THANK YOU!