File - Grade 11 U Biology
advertisement

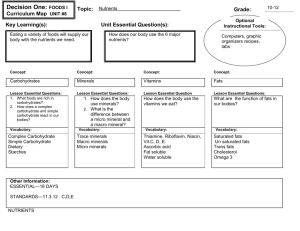
UNIT 3: Animals: Structure and Function WELCOME!! West Humber C.I. LOGO SBI3U1 Mr. Patel 2013-2014 Major Themes in Gr.11 Biology Grade 11 Biology covers a variety of different topics: Diversity of Living Things (Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes) Genetics (Mendelian Inheritance) Evolution (Darwin’s Theory) Animals: Structure and Function (Digestive, Circulatory, Respiratory Systems) Plants: Anatomy, Growth, and Function (Organs, Tissues, Cells) West Humber C.I. 2013-2014 How to Succeed and Survive! To best succeed in this unit, you will need to know and follow several important rules and you will need to have a few important items. I have several rules I would like you to follow to make life easier for you, me, and the rest of the class...most of the rules I have are a simple matter of politeness, responsibility, and just common courtesy... West Humber C.I. 2013-2014 How to Succeed and Survive! 1. If I am talking, please don’t talk...It will be disturbing to others as well as me. 2. If you have a question, please ask...I welcome questions and chances are, somebody else might have the same question, too! 3. Don’t make fun of people if they ask a question that you might think is stupid...it might be a valid question for them. 4. If I give an assignment or deskwork, I expect you to work on that work...if you waste time in our class, you will make up for it on your own time. 5. Assignments/labs/projects are to be handed in on the date due...If you are absent, make sure I get it the first day you are back. I want you to realize that I will not chase after you to get missed assignments...It is YOUR responsibility! West Humber C.I. 2013-2014 How to Succeed and Survive! Attendance & Promptness: I have a very high expectation when it comes to being in class on time...When you get in to class, you should open your books and be ready to start. If you miss a class, talk to another student or to me to find out what you have missed...you are still responsible for the work and it should be done on time. If you know you are going to be absent for a test, please make arrangements with me, before you are gone, to re-schedule a time to write it. West Humber C.I. 2013-2014 How to Succeed and Survive! General Stuff: I really believe that Biology does rule… We will be doing notes, labs, assignments, tests, and projects, watching videos, and also having some fun. You can find me in either of the Science Office or in our class or staff room. If you need to see me, please make prior arrangements in class. I am here to help you...So, if you need me to stay after school or during lunch to review for test or quiz, I’m more than willing to hold review sessions!!! West Humber C.I. 2013-2014 Units/Strands: Introduction Chapter 10: Digestive System Chapter 11: Circulatory System Chapter 12: Respiratory System Rat Dissection + Project + Unit Test West Humber C.I. 2013-2014 Evaluation Part 1: Your UNIT mark will be based on: Term Mark 70% 25% Knowledge/ Understanding West Humber C.I. 25% 10% 10% Thinking/ Inquiry Communication Application 2013-2014 Evaluation Part 1: Cardiovascular Fitness In-Lab + Report 15% [5% In-lab + 15% Lab Report] Weekly Chapter Quizzes 30% Home Work + In-class Activity 5% Rat Dissection In-Lab + Lab Report 15% [5% In-lab + 15% Lab Report] On-going Class Participation 5% Unit Test 30% TOTAL 100% West Humber C.I. Chapter 10: Digestive System UNIT D: Animals – Structure and Function West Humber C.I. LOGO Course: SBI3U1 TC: Mr. Patel 2013-2014 Agenda Video Activity 10.1 Nutrition and Digestion West Humber C.I. H.W 2013-2014 Video http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Nrjnebyzm2U West Humber C.I. 2013-2014 Question Why do we need to eat food? West Humber C.I. 2013-2014 Answer By eating, you’re providing your cells with the chemicals they need to live and grow! Food provides energy for all the work done by your cells and supplies over 40 substances that your body needs but cannot produce itself. West Humber C.I. 2013-2014 Agenda Video Activity 10.1 Nutrition and Digestion West Humber C.I. H.W 2013-2014 Major Themes 10.1 Nutrition and Digestion 1. It All Starts with a Healthy Diet Processing Molecules 2. Nutrients Carbohydrates Fibre from Plant Foods Proteins Fats Vitamins and Minerals Water West Humber C.I. 3. Food as Fuel Calories 4. Read Before You Eat Foods that May Fight Disease Probiotics 5. Canada’s Food Guide 2013-2014 Major Themes 10.1 Nutrition and Digestion It All Starts with a Healthy Diet Processing Molecules Nutrients Carbohydrates Fibre from Plant Foods Proteins Fats Vitamins and Minerals Water West Humber C.I. Food as Fuel Calories Read Before You Eat Foods that May Fight Disease Probiotics Canada’s Food Guide 2013-2014 Healthy Diet Nutrients are the chemicals in the food you eat that help your body perform all its functions. There are six types of nutrients in food: Carbohydrates Proteins Fats Vitamins Minerals Water West Humber C.I. 2013-2014 Healthy Diet Macronutrients (needs so much of them): Carbohydrates Proteins Fats Water Micronutrients (need less of it daily): Vitamins Minerals West Humber C.I. 2013-2014 Processing Molecules Food you eat are usually large molecules, which are too big to pass through your cell membranes into your cells. Your digestive system must disassemble the food you eat into smaller molecules. Then, these molecules are used as a source of energy to help build and maintain cell structure and function. West Humber C.I. 2013-2014 Major Themes 10.1 Nutrition and Digestion It All Starts with a Healthy Diet Processing Molecules Nutrients Carbohydrates Fibre from Plant Foods Proteins Fats Vitamins and Minerals Water West Humber C.I. Food as Fuel Calories Read Before You Eat Foods that May Fight Disease Probiotics Canada’s Food Guide 2013-2014 Nutrients: Carbohydrates Carbohydrates: Compounds made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms Major source of energy for your body Use just minutes after a meal or store them for later use Simple Carbohydrates (include sugars): • Fruit, Honey, and milk. • Glucose: Main fuel supply for the work done by your cells. – Cells break down glucose molecules and extract their stored energy Complex Carbohydrates: • Starches, such as from whole-grain cereals and bread, rice, and potatoes • Broken down by digestive system into simple sugars West Humber C.I. 2013-2014 Nutrients Carbohydrates: Complex Carbohydrates: • Simple sugars are absorbed into the blood and carried to cells • Excess blood sugar is converted into glycogen in the liver and in muscle and fat cells to be used later. Cellulose is a complex carbohydrate that is often called fibre. • Help your muscles to move food and waste through your digestive system. West Humber C.I. 2013-2014 Nutrients: Proteins Proteins: Protein is a complex molecule that is constructed from 20 kinds of smaller molecules called amino acids. Proteins contribute to almost all your day-to-day functions For example: • Form hair and muscles • Circulate in the blood and defend the body from harmful micro-organisms • Convey messages from one cell to another “8” Essential amino acids: • Your cells cannot make from other molecules • If you lack even one essential amino acid, your body cannot make protein properly • Meat, Milk, Eggs, Cheese provide all 8 essential amino acids West Humber C.I. 2013-2014 Nutrients: Proteins Proteins: “8” Essential amino acids: • If you’re vegetarian (combinations): – corn and beans, rice and lentils, and hummus with pita bread. West Humber C.I. 2013-2014 Nutrients: Fats Fats: Also called lipids, are molecules formed from fatty acids and glycerol. They store energy in your body. Fatty tissues cushion your organs and provide your body with insulation. Saturated fats: • Have only single bonds between carbon atoms • Carbon atoms has the maximum number of hydrogen atoms • Example: Lard and butter • Promote the build-up of fat deposits within the walls of blood vessels, reducing blood flow causing heart disease. • Should be only small % of daily intake of fats West Humber C.I. 2013-2014 Nutrients: Fats Fats: Unsaturated fats: • Have one double bond in a fatty acid chain • Fats in fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, and fish • Usually liquids at room temperature Trans fats: • Some unsaturated fats have been partially hydrogenated, which means they have been processed to accept more hydrogen atoms. • Are solid at room temperature, and have a longer shelf life than other unsaturated fats. • For example, margarine. Trans fats are used in frying fast foods. • AVOID Trans fats Contribute to heart disease and other health problems. West Humber C.I. 2013-2014 Nutrients: Vitamins and Minerals Vitamins: Are organic nutrients that you need in small amounts to regulate your body processes and perform chemical reactions. Water-soluble vitamins: • Vitamin C and B (cannot be stored in your body, so should be included in your diet everyday) Fat-soluble vitamins: • Vitamin A, D, E, and K can be stored in the fatty tissue of your body for future use. Minerals: Are inorganic nutrients and do not contain carbon. Example: Calcium, iron, phosphorus, copper, sodium, and zinc. West Humber C.I. 2013-2014 Nutrients: Vitamins and Minerals Minerals: You use calcium to make bones and teeth. Consume food rich in minerals each day to replace the minerals you lose in sweat, urine, and digestive wastes. Vitamins and minerals are found naturally in many foods: meat, eggs dairy products whole-grain products Tofu green leafy vegetables and some fruits. West Humber C.I. 2013-2014 Nutrients: Water Water: Every one of your cells needs water to complete its processes Water makes up the bulk of blood Suggested: Drinking at least 1 L of water each day West Humber C.I. 2013-2014 Major Themes 10.1 Nutrition and Digestion It All Starts with a Healthy Diet Processing Molecules Nutrients Carbohydrates Fibre from Plant Foods Proteins Fats Vitamins and Minerals Water West Humber C.I. Food as Fuel Calories Read Before You Eat Foods that May Fight Disease Probiotics Canada’s Food Guide 2013-2014 Food As Fuel Cells convert about 40% of the energy from food into energy for performing cell functions. 60% of energy is converted to thermal energy, which radiates from your body in the form of heat. Calories: Is the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1 g of water by 1oC. 1 dietary calorie = 1000 calories. Must consume a minimum number of calories every day just to sustain life. • Female teenagers: 2200 calories • Male teenagers: 2500 calories At least 30 mint. exercise helps burn excess calories West Humber C.I. 2013-2014 Food As Fuel Calories: West Humber C.I. Nutrient % of Total Daily Calories Carbohydrates 45-65 Proteins 10-30 Fats 25-35 2013-2014 Major Themes 10.1 Nutrition and Digestion It All Starts with a Healthy Diet Processing Molecules Nutrients Carbohydrates Fibre from Plant Foods Proteins Fats Vitamins and Minerals Water West Humber C.I. Food as Fuel Calories Read Before You Eat Foods that May Fight Disease Probiotics Canada’s Food Guide 2013-2014 Read Before You Eat Reading food labels can help you track if you are meeting your daily requirement for important nutrients such as: Dietary fibre Protein Vitamins Healthy Fats Labels also identify ingredients such as: Unhealthy fats Sugars Sodium West Humber C.I. 2013-2014 Read Before You Eat West Humber C.I. 2013-2014 Foods that May Fight Disease Nutraceutical: is a substance that is purified from foods and taken like a medicine to provide health benefits including disease prevention. Example: An omega-3 fish oil pill taken as a supplement Functional Food: is a food that has health benefits, including disease prevention, that are beyond the normal nutritional benefit of the food. Fruits and vegetables that contain vitamins such as A, C, E and beta-carotene Foods such as garlic, cabbage, carrots, licorice, soy, and ginger as possible cancer-fighters. West Humber C.I. 2013-2014 Probiotics Probiotics: Which are foods that contain substances that support health and that may help to strengthen the body’s natural defence against disease. Antibiotics kill bacteria in the body, including some of helpful intestinal bacteria. Probiotic products, such as probiotic yogurt, help to add beneficial bacteria back into the large intestine. West Humber C.I. 2013-2014 Major Themes 10.1 Nutrition and Digestion It All Starts with a Healthy Diet Processing Molecules Nutrients Carbohydrates Fibre from Plant Foods Proteins Fats Vitamins and Minerals Water West Humber C.I. Food as Fuel Calories Read Before You Eat Foods that May Fight Disease Probiotics Canada’s Food Guide 2013-2014 Canada’s Food Guide One way to get the information you need to make healthy choices is to use Canada’s Food Guide to Healthy Eating: (Refer to Pg. 283) West Humber C.I. 2013-2014 Agenda Video Activity 10.1 Nutrition and Digestion West Humber C.I. H.W 2013-2014 Exit Card ANSWER ANY OF THE FOLLOWING: What are 3 things you learned today? What are you still unsure about? Something I still don’t understand is... What was one thing you enjoyed in class today? West Humber C.I. 2013-2014 Agenda Video Activity 10.1 Nutrition and Digestion West Humber C.I. H.W 2013-2014 Homework Question on Pg. 285: 1, 2, 7, 10, 14, 20, 22 and 23. I/we (as a class) will mark only “selective questions”. So, be aware to frame your answers correctly... Spend sometime working on it!!! West Humber C.I.