CH 22 Lower Respiratory Tract Anatomy
advertisement

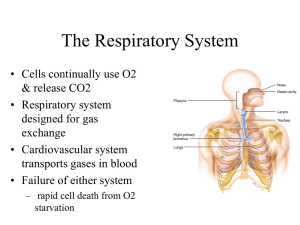
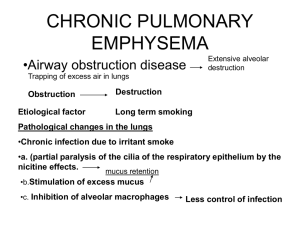
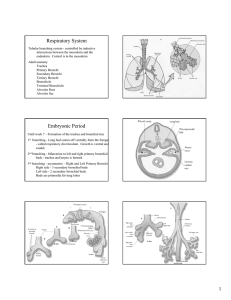
CH 22 Lower Respiratory Anatomy James F. Thompson, Ph.D. The Lungs apex cardiac notch • Apex, base base • Left lung has cardiac notch • R lung thicker, broader, shorter than L The Lobes of the Lungs Lobes are separated by fissures • Each lobe has a secondary bronchus and tertiary bronchi – 10 tertiary bronchi/lung – tertiary bronchi supply each bronchopulmonary (BP) segment • Tumors, infections or abscesses initially localized The Lobules of the Lungs • Each bronchopulmonary segment has elastic connective tissue around a lymphatic vessel, an arteriole, a venule, and the terminal bronchiole • Terminal bronchiole continues to branch – Respiratory bronchiole Alveolar duct Alveolar sac Alveoli The Alveoli of the Lungs • Alveolar ducts open into alveolar sacs & alveoli • Alveolar sacs - 2 or more alveoli • Thin walls – simple squamous epithelium – thin elastic basement membrane – capillary endothelium • ~300 million alveoli • Total surface area 1/2 to 2/3’s of a tennis court covered by ~1 liter of blood! The Alveolus • 2 cell types in walls – type I alveolar pulmonary epithelial (squamous) cells • Make ACE – type II alveolar or septal cells • secrete surfactant alveolar fluid • (detergent-like substance) • Alveolar macrophages (“dust cells”) patrol the alveolar walls The Alveolar Wall • Capillaries (endothelial cells) surround alveoli for gas exchange • Smooth muscle controls airway resistance Alveolarcapillary (respiratory) interface The Alveolar Wall Alveolar-capillary (respiratory) interface O2 • Interface consists of: 1. 2. 3. 4. CO2 • Alveolar epithelium Epithelial basement membrane Capillary basement membrane Endothelial cells of capillary Total thickness – 0.5 µm – short diffusion distance The Alveolar Space • Alveolar fluid – Surface tension – Attraction of water to other water molecules • Surfactant: phospholipids decrease surface tension • Respiratory distress syndrome Blood Supply for the Resp. System • Pulmonary circulation – blood for gas exchange – low pressure system - 25/6 mm Hg • Bronchial (systemic) circulation – – – – a small supply from the aorta for nutrients and O2 supplies entire lung (except alveoli) high pressure system bronchial arteries to bronchial capillaries, then to both pulmonary veins and bronchial veins • Pulmonary plexus – Area of root where nerve fibers enter lung – Sympathetic/parasympathetic/visceral sensory The Pleura • Lungs – housed in the bony thorax – Two pleural membranes with pleural cavity between • outer - parietal pleura • inner - visceral pleura • pleural cavity – lowered intraplural pressure is normal – Rib cage • protective and flexible End CH 22: Lower Respiratory Anatomy