Short Story Notes
advertisement

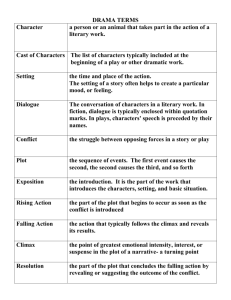
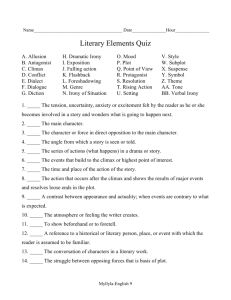
Get Excited! Fun! Fun! Fun! It’s Time for… Here it comes… Literary Terms Notes Oh…the suspense… yippy! Woooo-hoooo! Get Happy! Short Story • Not necessarily a “story that is short” • A short story by definition is a story that has one major conflict revolving around one major character. Character • Types: • Any noun that takes place in the action of a literary work – – – – – – round flat dynamic static antagonist protagonist Round Character • Has many different character traits…could theoretically be a real person. Wow…I didn’t know that… Flat Character • Has only one definable character trait. • Is completely one dimensional! Even more flat than THIS guy! Dynamic Character • A mini quiz: What was the nickname of Batman and Robin? The Dynamic Duo! A dynamic character is one that changes throughout the course of the plot (thoughts, feelings, etc.) Static Character • Hint: Think static cling… • This type of character sticks to his/her ideas throughout the plot. In other words, the character does not change. He/she stays the same during the course of action. Protagonist • This is your main character. • Usually the good guy. For example… Antagonist • Character who opposes the protagonist. • Usually the bad guy Who could an antagonist for our protagonist be? Point of View • The side from which the story is told • There are 3 different types of point of view (POV). • 1st person • 3rd person omniscient • 3rd person limited 1st person: told from the side of someone in the story; only get their thoughts and feelings. Key word in identifying 1st person is I. 3rd person omniscient: and outside voice that knows all the characters’ thoughts and feelings 3rd person limited: and outside voice that knows only one character’s thoughts and feelings . Setting • The time and place of the action. • Can be general or very specific • For example… • Summer afternoon (general); • Saturday, June 29, 2002 at 7:30 pm in Erlanger, KY (specific). Conflict Struggle between opposing forces; two types: external and internal • External conflicts: character struggles with something outside the self. • • • • • person v. person person v. nature person v. society person v. supernatural person v. machine • Internal Conflicts: character struggles with something within self • person v. self What type of conflicts do we see here? Freytag’s Pyramid The sequence of events in a literary work is called the plot. It follows Freytag’s Pyramid and involves characters and central conflict. 4 3 5 6 1 2 7 Decoding the Freytag 1. Exposition: beginning of work; introduces characters, setting, and basic situation 2. Inciting Incident: Thing that starts the central conflict 3. Rising Action: all events that lead up to the climax More Freytag… 4. Climax: the highest point of conflict/interest. The turning point. 5. Falling Action: all action that leads away from the climax to the resolution. 6. Resolution: end of central conflict. 7. Denouement: all action that takes place after the resolution; extra info. . . Other Stuff… • Surprise ending: ending that defies the expectations of the reader but is logical and believable. • Anticlimax: Takes place where the climax would be. Reader discovers that the story is not turning out the way expected. Terms You Need to Know… • • • • • Dialogue: Conversation between characters. Advances the plot and/or reveals something about the speaker. Foreshadowing: use of clues that suggest what is going to happen in the future of a literary work; creates suspense. Motivation: Why a character does what he does. Symbol: something that stands for something else Personification: giving non-human things human characteristics. (Think Disney) Irony • The general term for a literary technique that portrays the differences between appearances and reality. • There are three different types: • Verbal • Dramatic • Irony of situation Verbal Irony: . words used to suggest the opposite of what is meant. AKA sarcasm Dramatic Irony: The audience knows something that the characters do not know. Irony of Situation Event occurs that directly goes against the expectations of the characters, reader, or audience. Almost There… Theme The central idea or message in a literary work; may be directly stated or implied. It is not a summary!! Moral The lesson taught by a literary work. As Yakko, Wacko and Dot used to say… Wheel of morality turn, turn, turn…tell us the lesson that we should learn That about does it for your Literary Terms Notes Remember to look over them everyday…we will use them during each story, you will see them on a test, and on your final exam. Until then…