Rise of Dictators
advertisement

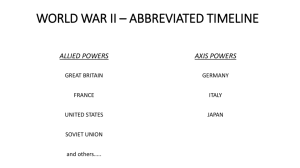
World War II: The Road to War (1931-1941) I. The Rise of Dictators: Stalin Warm-Up: What is Communism? ________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________________ How is it different than Democracy? ________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________________ I. The Rise of Dictators: Stalin Objective: Analyze how the Soviet Union was controlled by their leader Joseph Stalin Postwar Europe Every ___________________________________________________________________________________________ Destruction from trench warfare Our Great Depression spreads worldwide New governments aren’t working Totalitarian Rulers in Europe During the 1930s, totalitarian governments gained power in _______________________________________________________. These governments exerted total control over a nation, using terror to suppress individual rights and silence all opposition. Joseph Stalin Soviet Leader from 1922-1953 “We are fifty or a hundred years behind the advanced countries. We must make good this distance in ten years. Either we do it, or they will crush us.” "The Tasks of Economic Executives“- speech February 4th 1931 What is communism? It is an economic system ____________________________________________________________________________ The Government owns and controls everything. In “true communism,” there is no greed or competition. Each person _________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ In “true communism” there are no rich or poor people…everyone has what they need. In reality, everyone is poor in a communist system except for the government. You have no freedom to _____________________________________________________________________________ You have little choice in your profession. The quality and quantity of goods and services is terrible. There are no incentives to do better. You have no incentive to work hard or come up with new ideas because you are not rewarded. It is _____________________________________________________________________________________________ The goal is to spread communism worldwide. Soviet Union Joseph Stalin – ___________________________________________________ Communist Party Dictatorship Big Problem – ____________________________________________________ Solution – militarize, terrorize opponents. Stalin’s Soviet Union Joseph Stalin _________________________________________________________________________________ from the early 1920s to the 1940s. He gained popularity with working class individuals due to his socialist economic policies. ____________________________________________ - a political theory advocating collective or governmental ownership and administration of the means of production and distribution of goods. Stalin instituted a ________________________________________________________ in the Soviet Union during the late 1920s. Stalin’s Economic Plans Stalin’s state _______________________________________________________________ resulted in a dramatic fall in agricultural production as well as mass starvation. Stalin poured money and labor into industrialization rather than basic necessities such as housing and clothing. Due to Stalin’s policies, the Soviet Union soon became a modern industrial power, although one with a low standard of living. Stalin’s Reign of Terror To eliminate opposition, ________________________________________________________________, the removal of enemies and undesirable individuals from positions of power. Stalin’s purges extended to all levels of society. __________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ Nearly all of those purged by Stalin were innocent. However, these purges successfully eliminated all threats to Stalin’s power. Assessment 1. What was the name given to Stalin’s removal of all enemies? 2. A political theory advocating collective or governmental ownership and administration of the means of production and distribution of goods is called a. democracy b. capitalism c. socialism 3. In a communist government the people do not own any II. The Rise of Dictators: Mussolini Warm-Up: Respond to the following: “The liberty of a democracy is not safe if the people tolerate the growth of private power to a point where it comes stronger than their democratic state itself. That, in its essence, is fascism - ownership of government by an individual, by a group,” --Franklin D. Roosevelt ________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________________ II. The Rise of Dictators: Mussolini Objective: Analyze how Italy was controlled by their leader Benito Mussolini Italy Benito Mussolini Dictatorship ______________________ Party Main message- Italy is great, let’s restore the Roman Empire. Big problem- trains won’t run on time Solution- military will fix it. Benito Mussolini “Fascist education it moral, social, and military: it aims to create a complete and harmoniously developed human, a fascist one according to our views.” Fascism in Italy Benito Mussolini gained power in Italy both by advocating the popular idea of Italian conquest in East Africa _________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ Once appointed prime minister by the king, Mussolini, ___________________________________________, suspended elections, outlawed other political parties, and established a dictatorship. Mussolini’s rule improved the ailing Italian economy. Under Mussolini, the Italian army successfully conquered the African nation of Ethiopia in May 1936. Test Your Knowledge 1. Fascism was a policy of what nation? a. France b. Soviet Union c. Italy 2. The following quote came from who? "Fascist education is moral, physical, social, and military: it aims to create a complete and harmoniously developed human, a fascist one according to our views". a. Hitler b. Mussolini c. Stalin III. The Rise of Dictators: Germany and the Spanish Civil War Warm-up Baldur von Schirach, Head of the Hitler's Youth Describe the following quote : "He who serves our Fuhrer, Adolf Hitler, serves Germany and he who serves Germany, serves God." ________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________________ III. The Rise of Dictators: Hitler and the Spanish Civil War Objective: Describe the situation in Germany on the eve of WWII. Germany Adolf Hitler Dictatorship _________________Party Main message-Germans (Aryans) are superior Big problem- must completely rebuild the country. Solution – ________________________________________________________________________________________ Hitler’s Rise to Power - Hitler’s Rise to Power 1919–1934 Hitler’s Background: Adolf Hitler, _____________________________________________________, hated the way the Versailles Treaty humiliated Germany and stripped it of its wealth and land. The Nazi Party: Hitler joined and soon led the Nazi Party in Germany. Nazism, the philosophies and policies of this party, was a form of fascism shaped by Hitler’s fanatical ideas about German nationalism and racial superiority. ___________________________________: While imprisoned for trying to take over the government in November 1923, Hitler wrote Mein Kampf (“My Struggle”). In this book, he proposed that Germany defy the Versailles Treaty by rearming and reclaiming lost land. He also blamed minority groups, especially Jews, for Germany’s weaknesses. Hitler Becomes Chancellor: Between 1930 and 1934, _____________________________________________________ ______________________________________________, the lower house of the German parliament. Hitler became first chancellor and then president of Germany. He moved to suppress many German freedoms and gave himself the title Der Führer, or “the leader.” Adolf Hitler “I want war. To me all means will be right. My motto is not "Don't, whatever you do, annoy the enemy." My motto is "Destroy him by all and any means." I am the one who will wage the war!” Germany Rearms and Expands To boost the German economy and to prepare for territorial expansion, the Nazi Party began spending money on rearming Germany. ________________________________________________________, German troops entered the Rhineland, a region in western Germany that the Versailles Treaty explicitly banned them from occupying. However, neither Britain nor France took any action. Also in 1936, Hitler and Mussolini signed an agreement, beginning an alliance between the two nations. _____________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ In March 1938, Germany took over Austria. Several months later, Hitler demanded the Sudetenland, a region of Czechoslovakia. Following the policy of appeasement, or giving into a competitor’s demands in order to keep the peace, British Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain agreed to allow Hitler to occupy the Sudetenland. The Spanish Civil War In 1936, military rebels in Spain led by ________________________________________________________ attempted to take over the Spanish government. These rebels became known as the Nationalists. The resulting struggle between the ruling Republicans and the rebelling Nationalists led Spain into a civil war. _____________________________________________________________________________, while the Soviet Union supported the Republicans. In March 1939, the Nationalist army took over the _____________________________________________________ and ended the civil war, making Franco the ruler of Spain. Map of Europe during the 1930s Knowledge Check 1. What did Hitler write while he was in prison? 2. Which faction won the Spanish Civil War? a. Democrats b. Republicans c. Nationalist 3. Where was Hitler from and what was his first profession? IV. Japan Builds an Empire Warm-Up This map shows that Japan (much like Italy and Germany) was interested in expanding their influence throughout Asia. Why do you think that Japan wanted to expand? ________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________________ IV. Japan Builds an Empire Objective: Determine the effect of Japan’s growing military. Japan Geography presents __________________________________________________________ Small, mountainous island nation. They lack ___________________________________________________________ Their solution is to invade Manchuria to colonize and get them. Emperor ____________________________________ Military leaders Main message- “We are a world power.” Big problem – lack of natural resources. Growing Military Power During WWI Japan was a ____________________________________________________________________________ Although playing a limited role in WWI Japan was able to conquer several German possessions allowing the economy of Japan to prosper. After ____________________________________________________________________________________ system of government which allowed many more people to vote. Japan pledged to resolve all conflict peacefully and condemned war. This would soon change. Manchurian Incident By 1930, Japan lacked the _____________________________________________________________________ to care for its growing population. Many Japanese saw the acquisition of neighboring Manchuria as a solution to these problems. ________________________________________________________________, a Japanese army stationed in Manchuria captured several cities. By February 1932, the army had seized all of Manchuria. This seizure came to be known as the Manchurian Incident. Puppet State Japan set up Manchuria as a puppet state, or a supposedly independent country under the control of a powerful neighbor. After ____________________________________________________________________, the military took a much stronger hand in governing Japan, especially in the area of foreign policy. War Against China In July 1937, __________________________________________________________________________. Although China had more manpower than Japan, Japan’s superior weapons allowed it to win control of major Chinese cities. The United States and other nations condemned Japan’s actions. The United States remained neutral, but the Soviet Union sent war equipment and military advisors to China. Later, Britain sent supplies to the Chinese over the Burma Road, a highway linking Burma to China. Battling political groups in _______________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________. While Japanese troops controlled the cities, Chinese guerrillas dominated the countryside. The war had reached a stalemate by 1939. Looking Beyond China - Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere In 1940, Japan announced a ________________________________________________________________, to be led by the Japanese, extending from Manchuria to the Dutch East Indies. Japan declared that this move would ___________________________________________________________________. However, the real reason was Japan’s additional need for natural resources. Alliances and Further Expansion In ______________________________________, Japan allied itself with Germany and Italy through the Tripartite Pact. Japan began to expand into French Indonesia and the oil-rich Dutch East Indies. In April 1941, Japan signed a _________________________________________________________________________ Japanese Expansion, 1931-1941 Blueprint for dictatorship Tell the people what they want to hear Do something! Get your foot in the ____________________________________________________ Eliminate opponents Eliminate political parties Control the _____________________ Use propaganda Eliminate elections Consolidate power Now it’s too late! Test Your Knowledge 1. Why did the Japanese military take over Manchuria in 1931? a. Because Germany and Italy requested that they do so b. To gain land and raw materials for Japan c. To expand the Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere d. Because Chinese manpower outnumbered the Japanese forces 2. In September 1940 Japan allied itself with Italy and Germany, forming the 3. After the Japanese invasion of China the U.S. a. joined the war on the side of the allies b. remained neutral c. declared war on Japan V. German Aggression in Europe Warm-Up Picture Description What does this photograph tell us about the situation in Europe in 1940? ________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________________ V. German Aggression in Europe Objective: Explain the impact of German policies during the late 1930s. German Aggression, 1939-1941 Germany After taking control of Germany, Adolf Hitler immediately _________________________________________________ They stop paying reparations. They mobilize the military. This gives __________________________________________________________________________, either by having them join the military or working in industries making military supplies. As soon as the treaty was broken, someone should have stepped in. Who? Why didn’t they? What does this mean? _______________________________________________________________________________________ should have stepped in. The United States was geographically too far away. Each of these countries had their own problems that prevented them from acting. This meant that Hitler would push forward with more aggressive expansion plans. Hitler says ________________________________________________________________ He sees that the League of Nations didn’t help Ethiopia. He sees that no one did anything when Germany broke the _________________________________________________ He’s ready for a greater test. One of Hitler’s biggest themes was “___________________________________________________________________ The idea was that the German people needed more room to live. There were millions of Germans forced to live outside Germany, according to Hitler. These people had to be brought back to the fatherland. The Rhineland is “remilitarized” in 1936. Nothing is done about it. Next, _______________________________________________________________________. Nothing is done about it. Hitler says these places wanted to return to Germany. Hitler is now ready for an even bigger test. The _________________________________________________________. It is the western section of Czechoslovakia. This is a big deal because both Great Britain and France have a treaty of mutual defense with Czechoslovakia. What does that mean? This means that if one country is attacked, the others have already agreed to help. Hitler knows about the treaty. Before either country can act, he invites the leaders _____________________________________________ to Germany to talk it over. The Munich Conference Hitler tells Britain and France that if they let him keep Sudetenland, he will ____________________________________ They agree. This is called ____________________________________________ – giving in to aggression to prevent further conflict. This was a lie. __________________________________________________________________________________ announced he had secured “peace for our time” Why would Hitler bother? It buys some time Gives the element of surprise Makes the leaders of ________________________________________________________________________________ He plays mind games Assessment ______________ was annexed in 1938. a. France b. Austria c. Poland 2. ______________ and France had a treaty of mutual defense with Czechoslovakia. 3. Hitler broke the Treaty of a. Versailles. b. Paris. c. Nuremberg. VI. Germany Invades Poland Warm-Up Interpret this political cartoon (one to two sentences) ________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________________ VI. Germany Invades Poland Objective - Describe the German invasion of Poland and the ramifications this action caused. What next? England and France must act They reach out to the ___________________________________ Joseph Stalin does not want to ally with England and France. They are weak ___________________________ comes calling. Nazi-soviet pact _________________________________________________________________________ agree not to fight each other. They secretly agree to split Poland. Why would each side do this? Hitler is a liar! Why? Nazis gain time to get stronger and focus on the __________________________________________________________ Soviet get free land and time. Appeasement Fails Prime Minister ____________________________________________________________________________________ toward Germany was not the right approach for many: “That is the deep difference between the Prime Minister and myself throughout these days. The Prime Minister believed in addressing Herr Hitler through the language of sweet reasonableness. I have believed that he was more open to the language of the mailed [armored] fist.” - Alfred Duff Cooper, First Lord of the Admiralty, 1938 __________________________________________________________ (who succeeded Chamberlain as Prime Minister in 1940) agreed and believed that Hitler had no intention of stopping. German Invasion of Poland After Hitler ________________________________________________________________________________, Britain and France ended their policy of appeasement. They warned Hitler that an invasion of Poland would mean war. Hitler, however, had stopped believing _________________________________________________. On September 1, 1939, Germany invaded Poland. Britain and France declared war on Germany two days later. Germany quickly overran Poland using a new military tactic called blitzkrieg, or _______________________________ Blitzkrieg tactics involved a fast, concentrated attack that took the enemy by surprise. To avoid war on two fronts, Germany signed a __________________________________________________________. In a secret addition to this pact, the two nations agreed to divide between them the independent states of Eastern Europe. “Phony War” & The Maginot Line “Phony War” and the Maginot Line: After Poland fell, the war entered a quiet period. The American press called this __________________________________________________________________ France prepared a massive string of fortifications, known as the Maginot Line, along its border with Germany. French fortification along the Maginot Line What does this cartoon indicate about the thoughts of Hitler's advisors? Germany Moves West In April and May 1940, Germany attacked and quickly ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________, Belgium, and Luxembourg. British and French troops tried to hold of the Germans but arrived too late. The German army quickly controlled __________________________________________________________________ The Fall of France Dunkirk: When Germany advanced on France, British and French forces retreated to the French coastal city of Dunkirk. From there, hundreds of thousands of soldiers were ferried to Great Britain in one of the greatest rescues in the history of warfare. On June 22, 1940, France officially ____________________________________________________________________ In accordance with the surrender terms, Germany occupied most of France, while the French government controlled an area known as Vichy France in the south. Vichy France adopted a policy of ___________________________________ _______________________________________________, with Germany. The Fall of France continued… ________________________________________________________________________, supported by the Free French government in exile in Britain, sought to undermine German occupation. By the summer of 1940, Hitler had conquered most of _________________________________________________ and seemed on the verge of conquering the Allies, the group of countries that opposed the Axis Powers. Britain alone stood against the Axis. The Battle of Britain Relentless Attack Before attempting to invade Great Britain, ______________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ In August 1940, Germany launched an air assault on Britain, called the Battle of Britain, which continued well into September. At first, Germany only attacked ____________________________________________________________. However, it later began bombing London and other cities to decrease British morale. Courageous Defense Although greatly outnumbered, _______________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ German bombers. Despite massive losses, the British people kept their will to fight. __________________________________________________________________________________, British scientists cracked the German secret communication code. This enabled Britain to get a general idea of Hitler’s battle plans. “We shall fight on the beaches” The British Empire and the French Republic, linked together in their cause and in their need, will defend to the death their native soil, aiding each other like good comrades to the utmost of their strength. Even though large tracts of Europe and many old and famous States have fallen or may fall into the grip of the Gestapo and all the odious apparatus of Nazi rule, we shall not flag or fail. We shall go on to the end, we shall fight in France, we shall fight on the seas and oceans, we shall fight with growing confidence and growing strength in the air, we shall defend our Island, whatever the cost may be, we shall fight on the beaches, we shall fight on the landing grounds, we shall fight in the fields and in the streets, we shall fight in the hills; we shall never surrender Instructions to British Assessment 1. How did Britain and France react to Hitler’s invasion of Poland? a. They declared war on Germany. b. They continued their policy of appeasement. c. They signed a nonaggression pact with the Soviet Union. d. They surrendered to Germany. 2. Which nation began a resistance movement against Germany? a. Poland b. Britain c. France d. Belgium 3. Who did Winston Churchill Replace? VII. From Isolationism to War: Neutrality Acts & Lend-Lease Act Warm-up: Words to Remember Reflect (one sentence) on the message that FDR was trying to send with these words "We defend and we build a way of life, not for America alone, but for all of mankind” - Franklin D. Roosevelt ________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________________ VII. From Isolationism to War: Neutrality Acts & Lend-Lease Act Objective: Describe how cash and carry and the Lend-Lease Act moved the U.S. away from neutrality. The United States Chooses Neutrality Rather than addressing foreign concerns, _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ surrounding the Great Depression during the 1930s. Congress further prevented international involvement by passing a series of Neutrality Acts. -The ________________________________ prevented the United States from providing weapons to nations at war. -The second act banned loans to nations at war. -The third act permitted trade of ________________________________________________________________, as long as those nations paid cash and transported the cargo themselves. This policy became known as cash and carry. The Neutrality Acts prevented the United States from selling arms even to those nations that were trying to defend themselves from aggression. American Involvement Grows Debating the American Role: After the German _________________________________________________________, many Americans began to feel that the United States shared the Allies’ interests. Roosevelt asked Congress to revise the __________________________________________ to make them more flexible. Isolationists formed the ____________________________________________________ to protest increasing American aid to Britain. During the election of 1940 FDR said the following in response to questions about the U.S. involvement in the war: - “Your boys are not going to be sent into any foreign wars.” American Involvement Grows Lend Lease Act: ____________________________________________________, Britain confessed its inability to pay cash for supplies. In response, Roosevelt announced a new plan to provide war supplies to Britain without any payment in return. Despite protest from the America First Committee, Congress passed _________________________________________ ____________________________________________________. This act authorized the President to aid any nation whose defense he believed was vital to American security. F.D.R. Quote on the Lend-Lease Act "Suppose my neighbor's home catches fire, and I have a length of garden hose four or five hundred feet away. If he can take my garden hose and connect it up with his hydrant, I may help him to put out his fire...I don't say to him before that operation, "Neighbor, my garden hose cost me $15; you have to pay me $15 for it."... I don't want $15--I want my garden hose back after the fire is over." Franklin Roosevelt's Press Conference December 17, 1940 Test Your Knowledge 1. Which of the following did the Lend-Lease Act provide? (A) Trade in nonmilitary goods to fighting nations (B) An end to loans to nations at war (C) Aid to nations deemed vital to American security 2. What did the America First Committee advocate? (A) More American aid to Britain (B) Less American aid to Britain (C) More American spending on the military