Stock Crash to Depression
advertisement

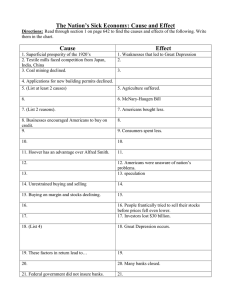
BELLWORK 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. List three factors that contributed to economic growth in the 1920’s. What is consumerism? What are the pros/cons of buying on credit? Explain Lassiez-Faire economic policies. Why would the government support this? THINKER: How do stocks work? THINKER2: Do you have a savings account? Why do banks pay interest on savings? Buying on Credit How do stocks work? Companies are made up of stocks Stocks (shares): small portions of the company that can be bought and sold for a given amount of money. When a company does well (makes a profit), the stock increases in value. When a company does poorly (loses money), the stocks decrease in value. The Stock Market: the place where stocks are bought and sold. Current Share Prices AT&T: $35.17 Visa: $211.43 Chevron: $116.58 McDonalds: $94.83 Nike: $89.39 Apple: $99.78 Google: $575.51 These share prices are constantly changing……why? STOCK VOCABULARY Speculation - Making high risk investments with the hope of huge returns. “Have to bet big to win big” THE CASE OF CIRCUIT CITY Opened in 1949 as a retailer of brand-name electronics, computers, and entertainment systems. Joined the stock market in 1984 – fairly successful 2003: eliminated commission sales, 4000 employees laid off As of 2005, Circuit City held $1 billion in investments 2007: Management Turnover, 3500 more jobs lost 2008: CEO resigned, closed 155 stores, laid off 17% of workers 11/10/08: filed for Bankruptcy, $2.32 billion in debt 1/16/09: announced they were closing all stores •Roller coaster notes! •Coincides with page 182 in your HOA textbook Discuss: What contributed to economic growth in the 1920’s? BELLWORK 10/7 What was the problem with large investors buying a huge portion of stock? What could go wrong? What is the purpose of the Federal Reserve Bank? Why did it fail in the year prior to the Stock Market Crash? List three factors leading to the Crash that showed signs of economic trouble ahead. Signs of an “unsound economy” Uneven Prosperity Tax cuts to wealthy Rich get richer & poor get poorer Personal Debt Luxury items seem affordable with credit Not everyone could pay it off Playing the Stock Market Speculation: high risk investments for a big return Buying on margin: bought portion of stock & borrowed the rest High interest rates Overproduction Originally high demand, but now, too much product Companies lost a lot of product and money All these factors combined until October 29, 1929 when. . . . . . THE STOCK MARKET CRASHED!!!! BLACK TUESDAY Inflated stock prices began to fall at a rapid rate. 16.4 million shares were immediately sold Sold at much lower prices than for what they were bought= huge financial losses for sellers. Sends economy into a downfall. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RJpLMvgUXe8 Make a prediction…….. Now that the STOCK MARKET has crashed… Think about what effects this event might have on: People buying goods People producing goods Employment IMMEDIATE RESULTS #1 - Massive selling of stocks All sold for low prices. Many investors lost tons of money. IMMEDIATE EFFECTS #2- Lack of BuyingPeople begin to worry about their money. Stop buying manufactured goods- try to hold onto what money they have left. IMMEDIATE EFFECTS #3- Lack of productionSince people stopped buying goods, companies stop producing goods. Economy is at a stand-still. IMMEDIATE EFFECTS #4 UnemploymentSince people are not buying goods, people have to stop making goods Workers begin to lose their jobs. Many workers have no income. In 1929, America’s population was 120 million, but only 4 million held stocks. If this was such a small number, how and why did EVERYONE become affected by the Great Crash? Ripple Effect of the Crash 1. 2. 3. 4. The Great Crash spread to the rest of Americans through the combination of 4 factors: Risky loans hurt banks: business and consumer borrowing Cuts in production: output of goods dropped, no longer affordable Rise in unemployment: at height, 25% Bank runs: fearful that banks would run out of money, people rushed to make withdrawals from their accounts. This eventually wiped out people’s savings and created bank failures. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EOzMdEwYmDU BELLWORK 1. Even days before Black Tuesday, the stock market seemed stable, so what went wrong? Why did the Stock Market crash? 2. In six words or less, explain how the Great Crash impacted Americans who didn’t own stock. 3. What is a bank run? Why did this happen? 4. THINKER: Could this have been avoided? List two things that might have prevented the stock market from crashing. These results of the Great Crash triggered the most severe economic downturn in history. The Great Depression: lasted from 1929 until the U.S. entered WWII in 1941. Impact on Farmers and Workers As production fell and unemployment increased, factories began to close. Ford shut down his Detroit factories – 75,000 people were laid off. Farm prices began to fall – In 1929 wheat was $1.18, in 1932 it was $0.49. 12 million unemployed (1/4 of labor force) GNP: 1929 - $103 billion; 1933 - $56 billion Discussion If the Great Depression started in the U.S., how did this become a global economic depression? Impact on the World Countries in the Americas and Europe depended on the U.S. markets for goods, investments and loans. Global economic system crumbled. U.S. couldn’t invest in European/American goods Stop providing loans German banks failed suspended reparation payments Allies stopped paying debts Industrial production fell = FAILURE OF GLOBAL ECONOMY! Reading: Failures of Hoover and the Federal Reserve For the rest of class and homework, read page 187 and finish the rest of the gold worksheet. CLOSURE What factors lead to an unsound economy? What four factors involved all Americans in the Great Depression? Out of those four, which do YOU feel had the biggest effect on America’s economy? Explain! How did America’s depression send the world into a global economic crisis?