Sports Medicine: Semester 1 Final Exam Study Guide Ch 1 – 2
advertisement

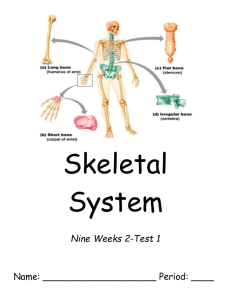
Sports Medicine: Semester 1 Final Exam Study Guide Ch 1 – 2 Athletic training chapter – Sports medicine and legal obligations Sports Medicine Negligence Assumption of Risk Proximate cause Informed Consent Gross Negligence Who sets the professional standards and code of ethics for the athletic training field? Who is part of the central sports medicine team? Ways to avoid legal problems are: HIPPA Law refers to what? Ch 4 Athletic training chapter – Basic Tissue Injuries Comminuted fracture Compound fracture Transverse fracture Pathological fracture Greenstick fracture Epiphyseal fracture Nonunion fracture Puncture wound Second impact syndrome All soft tissue injuries are known as wounds How are stress fractures diagnosed? What are the grades of sprains and strains and what do they mean Tendons connect _________________ to __________________ Ligaments connect ________________ to ___________________ What does the term concussion mean in Latin? Healing time of bones is usually __________ due to its vascular supply. The very first step when treating a wound is to _______________________________. This is also known as universal precautions. What are the risk factors if one fractures their epiphyseal plate? Ch 1 – Introduction to the human body Sagittal plane Frontal plane Transverse plane Proximal Distal Medial Anterior Superficial Deep Lateral Superior Know the body cavities and what organs are in those cavities? What structure separates the thoracic and abdominal cavities? What is anatomical position? What are the functions required in order for life? What is the correct sequence of the structural organization of life? Functions of the integumentary system Function of the respiratory system Function of the urinary system Positive feedback system Negative feedback system What is the stimulus, effector, control center, receptor in the feedback systems? The inguinal region is also commonly known as the _____________ Ch 3 – The cell and tissues Cell theory Endocrine glands Fibrosis Mitochondria Golgi apparatus Cytoplasm Rough endoplasmic reticulum Flagellum Cytoskeleton Smooth endoplasmic reticulum Ribosome Nucleus Avascular vs. vascular Parts of the nucleus Characteristics of the plasma membrane 4 types of tissues: What type of tissue is a tendon? A single layer of square shaped cells is called: What type of epithelium would be found in an area with a lot of friction/ wear and tear? 3 types of muscle Describe the 3 types of muscle as either striated or not striated and voluntary or involuntary Another name for fat tissue: Function of yellow marrow Connective tissues are usually vascular, but have 3 exceptions. What are these avascular connective tissues? List all types of connective tissues Ch 5 – The skeletal system Atlas Axis Rheumatoid arthritis Osteoarthritis Bursitis Pannus Rickets Fractures Gouty arthritis Bone spurs Crepitus Ankylosis Saddle joint Hinge joint Planar joint Ball and socket joint Condylar joint Pivot joint Fossa Appositional growth Ossification Osteoblasts Osteoclasts Fontanel Articular cartilage Fibrous joint Cartilaginous joint Synovial joint Synarthosis Amphiarthrosis Diarthrosis Why is the hyoid bone unique? Bones of the axial skeleton: Know the difference and examples of: short bones, long bones, flat bones and irregular bones The canal that runs through each osteon contains a blood supply and a nerve. What are the most important minerals stored in the bones? Know where the 4 sutures of the skull are located Another name for the tail bone: 3 bones of the sternum: What bones of the skull are paired and which only have the one bone? Hematopoiesis and what system does this happen in? What bones make the cheekbones? What group of bones make up the wrist? What type of joints are found in the vertebrae? What are true ribs and how many pairs of them do you have? What structure of the vertebrae does the spinal cord pass through? Know what bones fall into the following segments of the body: vertebrae, thoracic cage, upper extremity, pelvis, and lower extremities What happens at the epiphyseal plate? What are the differences of the male pelvis vs. the female pelvis? What part of the bone is stimulated by (PTH) Parathyroid Hormone? What factors determine when and where bone matrix is to be remodeled? Embryo skeleton is made of? Process of healing for fractures