Diffusion and osmosis
advertisement

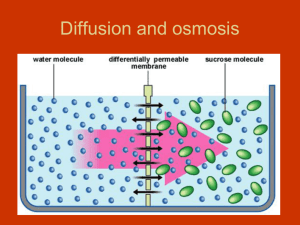
Diffusion and osmosis Describing Solutions Sucrose Solution – Solution: One or more substances distributed uniformly in another substance. – Solute: The substance dissolved in a solution. – Solvent: The substance in which the solute is dissolved. • Concentration: the measurement of the solute in a fixed amount of solvent. – Ex: 2% sugar solution = 2 grams sugar + 100 ml water. Passive Transport • Molecules moving across the plasma membrane without use of cell’s energy. Think: how does the membrane act as a barrier?? Concentration gradient – Molecules are always moving. – They move from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration. – Equilibrium is reached when concentrations are equal. (No concentration gradient) Diffusion • The movement of any molecule in solution from high concentration to low concentration – Membranes allow some molecules to pass others not to pass. • Ability to pass through the membrane depends on: – Size – Lipid soluble. – Appropriate pore Think: what happens when you put a drop of dye in water? Passive Transport:Osmosis • Osmosis – Movement of water molecules through a membrane from high concentration area to low concentration. Terms relating to osmosis. – Hypertonic; high solutes - low water. – Hypotonic; low solutes - high water. – Isotonic; equal solutes - equal water. Which way is the WATER moving in each of the pictures? How Cells Deal With Osmosis • Freshwater single cell organisms: • Water moves in due to osmosis. • Excess water collected by contractile vacuole. • Water is expelled from organism. Contractile vacuole collecting water in a paramecium. How Plant Cells Deal With Osmosis • Plant cells have turgor pressure due to water wanting to move into the cell. • Central water vacuole fills. • Pressure against the cell wall is turgor pressure. Filled water vacuole due to hypotonic environment. Think: why do plants “droop” when they need water? How Cells Deal With hypertonic solution • Plasmolysis is loss of turgor pressure. • Water leaves cell due to hypertonic solution. • Cytoplasm and organelles move to center of cell. • The cell wall helps the cell keep its shape. Elodea cell in hypertonic solution. How Animal Cells Deal With Osmosis • Animal cells must be in isotonic solution. • Animal cells in a hypotonic solution gain water. – Cytolysis results( they burst apart) • Animal cells in hypertonic solution lose water ( they shrivel up and die) Relate the Latin roots “iso”, ‘hypo’ and ‘hyper’ to these solutions RBCs in Isotonic solution. (RBC= red blood cell) RBCs in hypotonic solution. RBCs in hypertonic solution. Summary paragraph • 1. What is the difference between a solute and a solvent? • 2. How is osmosis a type of diffusion? • 3. Meat can be kept without refrigeration by salting it. What would happen to a bacteria if it was in a super salty solution?