Session two Microbiology intro
advertisement

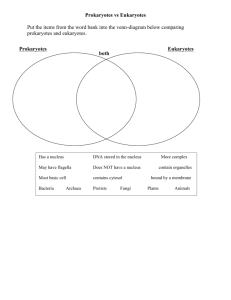
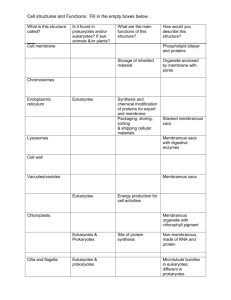
KAPLAN UNIVERSITY Microbiology 1 KAPLAN UNIVERSITY Cellular Characteristics 2 Prokaryotic cells and Eukaryotic cells are both similar and different in many ways. Prokaryotes are single celled organisms that do not have a nucleus (however they do have their own DNA) and also lack any membrane bound organelles (Pommerville 2010). Prokaryotes are typically bacteria. Prokaryotes have a circular DNA strand. They also have a cell membrane. Eukaryotes on the other hand do contain membrane bound organelles and a nucleus. They also have their own cytoskeleton which determines their individual shape and also aids in their own process of reproduction (Pommerville 2010). Eukaryotes can be unicellular or multicellular and their DNA consists of tightly bound chromosomes. Eukaryotes are found in protists, plants, animals, and fungus. Eukaryotes also have a cell membrane (just like prokaryotes) (Pommerville 2010). Some good examples of eukaryotes would be muscle cells or skin cells and plant cells. Prokaryotes usually come in one of three basic shapes; coccus (spherical), bacillus (rod-shaped), or spiral (midlandstetch.edu). The coccus shaped prokaryotes don’t always come out as perfect circles. They can be more oval or even flat looking. The bacillus prokaryotes can be seen as groups of single rods, multiple (chain-like) rods, or even sort of short and fat looking. The spiral prokaryotes look like curved rods that vary in length and number of twists (midlandstetch.edu). While these are the most common examples of the morphologies of prokaryote I came across some exceptions. Stella bacteria are a type of bacteria that are star shaped. They are found mostly in freshwater, soil and sewage. They are gram negative bacteria as well as flat and non-motile (Vasilyeva L.V. 1985). 3 Eukaryotes usually reproduce through mitosis which is a process where the chromosomes replicate within the cell and then divide to create two cells. Prokaryotes reproduce through binary fission, which is a process where the DNA is copied then the cells split (Pommerville 2010). Both eukaryotes and prokaryotes are able to move because of flagella. These are long thread-like structures that help them move around (Pommerville 2010). Prokaryotes and eukaryotes are both protected by their cell membranes. These membranes regulate what enters or leaves each cell (Pommerville 2010). Some prokaryotic bacteria secrete a substance known as Gycoclyx which consists of sugars and proteins. Glycoclyx can be thick (known as a capsule) or thin (known as a slime layer) and it serves as a buffer between the cell and the external environment. This substance protects the cell from desiccation and allows the cell to attach to surfaces (Pommerville 2010). An example of a cell that is really effective at protecting itself from our immune system is Streptococcus pneumonia (which often causes us to eventually get pneumonia). Our own cells seem to pull away from attacking it. Normally they would be eaten by our White blood cells but for some reason this task is very difficult. Scientists believe this could be due to the charges on the surface of the bacteria (Pommerville 2010). I found this cell particularly interesting as I have had pneumonia twice in my life. 4 References: Pommerville. (2010). Alcamo's Fundamentals of Microbiology, 9th edition . Jones and Bartlett. The Prokaryotic Cell. Retrieved on December 17,2013, From http://classes.midlandstech.edu/carterp/courses/bio225/chap04/lecture2.htm Vasilyeva L.V. Stella, a New Genus of Soil Prosthecobacteria, with Proposals for Stella Humosa sp. nov. and Stella vacuolata sp. nov. 1985. Journal of Systematic Bacteriology. Retrieved on December 17, 2013, From http://ijs.sgmjournals.org/content/35/4/518.full.pdf 5 6