Limited Government Types
advertisement

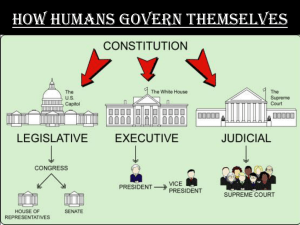
Limited Government Types Republic A republic is a government without a king or queen. Often people in a republic choose representatives to make decisions. The United States, for example, is a republic. A republic might also be group of hereditary nobles such as the Republics of Venice and Genoa once were. Additionally, before Ancient Rome became an Empire they were once a republic where people made decisions as citizens. Democracy In a democracy, government authority is based on the will of the people. People either vote directly on issues (direct democracy) or they elect representatives who make government decisions for them. In a democracy, people also enjoy certain basic rights. This allows them to openly question or criticize the government. Today many nations such as Mexico, United States, and India have democratic governments. *The very first democracy arose in Ancient Greece in the 5th Century B.C. In fact the word DEMOCRACY in Greek means- “people power”. Ancient Greece had a direct democracy where people voted directly on the decisions. Constitutional Monarchy In a constitutional monarchy the king/queen shares their power with an elected legislature. Great Britain is an example of a constitutional monarchy. Britain used to have a hereditary monarch where the king or queen made all of the decisions, however, now the monarchy serves as a symbol of power while the people who really have the power are the elected members of Parliament (legislature). Theocracy A theocracy is a government run by religious leaders. This type of government is an extremely old form of government. In a theocracy the government claims to be directed by God, or divinely blessed. There is no legal separation between church and state, and citizens of other faiths/beliefs are often expelled or persecuted. Ancient Egypt is an example of a theocracy in which the Pharaohs claimed to be gods. A modern example of a theocracy can be found in Iran in which the Supreme Leader is an Islamic cleric who is appointed for life. Totalitarian/Dictator A dictatorship is a system of government where a single person exercises complete power over the citizens. Usually, the dictator or leader seizes power by force or is placed into authority by others. Dictators are free to do as they please, while other citizens have very little rights or influence over government decisions. Totalitarian dictators such as Adolf Hitler, Saddam Hussein, or Kim Jong-Un use their power to control every aspect of individuals lives. Oligarchy In an oligarchy a small group of people has all the power. Oligarchy is the Greek word that means ‘rule by few’. Sometimes this means that only a certain groups of people has political rights and power. For example, from 1962-2011 Myanmar was ruled by a military junta. A junta is a small group of people-usually military officers- who rule a country after taking it over by force. Today, China is ruled by an oligarchy through the Communist Party. Monarchy Monarchy is probably one of the oldest forms of government. The ruler in a monarchy inherits their power. When the ruler dies, power is automatically passed to one of the ruler’s children or close relatives. A few examples of monarch titles include king, queen, emperor, or sultan. The monarch rules with complete authority. In older forms of monarchy the king or queen often claimed ‘divine right’ or that they were ruling over the people because it was ‘God’s will’. Ordinary people have no rights or freedoms in a monarchy.