Religions of India
advertisement

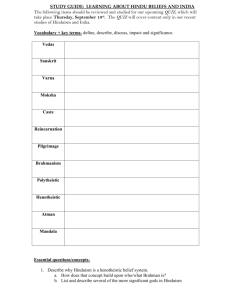
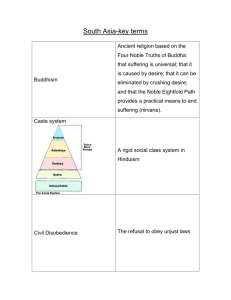
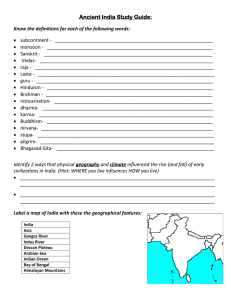
NOTES DISCUSSION One of the biggest concerns about any Social Studies class is the taking of notes. The ability to effectively take notes is a life long skill. It makes you question, and really focus on what is important in a conversation For instance, in college, the professor always lecture to us, the students. That was history for me in several classes. • Red: Instructions – Anything in red (STOP and pay close attention) it is critical information and should be copied exactly. – Pay attention and write down anything else that is said that you think might be important. • Yellow: – Anything written in yellow (SLOW down and pay attention) is useful information. You should write it in your notes IN YOUR OWN WORDS. – Pay attention and write down anything else that is said that you think might be important. • Green: – Anything in green (GO on to the next point) you do not have to write. – You do not have to write down anything that is said unless you want to or it helps clarify the subject Suggestions • Red: – Red contains the most important information of the subject matter. – Pay close attention to this section. – This would include: • Definitions • Explanations • Significances • Yellow: – Yellow contains the background information of subject. – It is important to understand but not as a crucial • Green: – Green usually contains anything extra, • Extra Stories • Other side information HINDUISM Religions of India Date: Topic: Essential Objective: Interaction: Summary: Notes: Topic: Hinduism Date: 3/4/15 Essential Questions: 1. How did the geography of India change religion? 2.Is Hinduism monotheistic or polytheistic? Explain. 3. How do Hindu beliefs of life and death differ from those of Christians, Jews and Muslims? Interaction Notes: ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS: How did the geography of India change religion? Is Hinduism monotheistic or polytheistic? Explain. How do Hindu beliefs of life and death differ from those of Christians, Jews and Muslims? WHO FOUNDED HINDUISM? There is no one single founder Developed slowly Combining old traditions and beliefs of Aryans WHERE DID IT COME FROM? Hinduism came from the mixture of Aryan and Indian cultures Aryans also introduced the caste system to India – an important aspect of Hinduism GOD … GODS? Brahman – one single spiritual power which lives in everything Though they worship many different gods and goddesses They stand for different parts of Brahman has no physical form “God is one, but wise people know it by many names” IMPORTANT GODS Gods take many different forms – called avatars Or a representation of a Hindu god or goddess in human or animal form Brahma – the Creator Vishnu – the Protector Shiva – the Destroyer SOUL Every person is born with a soul WHAT IS REINCARNATION? The rebirth of the soul If you are a faithful follower of Hinduism you will be born into a higher position in the next life If you are not you will be punished – born into a lower position REINCARNATION “As a man discards worn-out clothes to put on new ones, so the embodied self (soul) discards worn-out bodies to take on other new ones.” -Bhagavad Gita LAW OF KARMA Karma - The effect of your actions in this and previous lives Determines how a person is reborn Bad deeds = rebirth into lower caste, even as low as an animal Good deeds = rebirth into a higher caste 4 GOALS OF HINDUISM Goal 1 – dharma (duty) Do the jobs related to your caste, age or position in life Avoid harming living things (ahimsa) Goal 2 – strive for well-being Make a good living Raising a family Being honest, trust-worthy, honorable Materials do not bring true happiness Goal 3 – pleasure Physical - eating good foods, taking a hot bath Seeking nothing but pleasure can leave you feeling empty Goal 4 – moksha (freedom from reincarnation) Your soul is free from want, fear and pain Your soul becomes one with Brahman’s HOW TO ACHIEVE MOKSHA Knowledge To understand one’s soul and how it relates to Brahman Works Carry out religious rituals and duties to improve karma Do good deeds without expecting praise or recognition Devotions Path of love Devote yourself to loving God Worship one of Hindu god/goddesses Repeat name all day long Make offerings at temples Travel to holy sites IMPACT OF HINDUISM Spread 80% of today’s Indians are Hindu Growth In ancient times – many rulers, languages, religions Hinduism was flexible Accepted worship of new gods Didn’t have to give up old religion Kept old traditions IMPACT OF HINDUISM Appeal Didn’t require regular attendance at religious services Pray or make offerings at any time Keep a shrine in their homes Shrine – place of worship dedicated to sacred object or being Could practice wherever you were TRADITIONS, BELIEFS, SYMBOLS Ganges River Physical form of a goddess believe the waters can wash away bad karma and cure disease The Cow symbolizes all other creatures generous, taking nothing but water, grass and grain gives and gives and gives of its milk, as does the enlightened soul give of his spiritual knowledge vital to life, the sustainer of life, for many humans Diwali from the Sanskrit word Dīpãvali, meaning "row of lights“ lasting five days for many, Diwali is also New Year's Eve Topic: Hinduism Date: 3/4/15 Essential Questions: 1. How did the geography of India change religion? 2.Is Hinduism monotheistic or polytheistic? Explain. 3. How do Hindu beliefs of life and death differ from those of Christians, Jews and Muslims? Interaction Notes: Date: Topic: Essential Objective: Interaction: Summary: Notes: