West Africa - Lee County Schools
advertisement

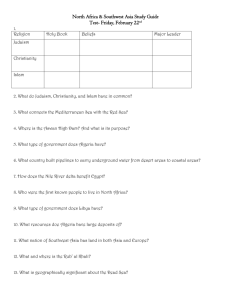
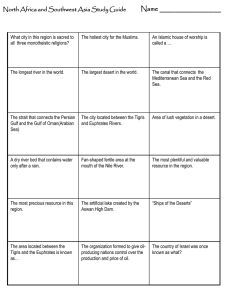
7th Grade UBD - Unit 3 - Middle East Location and Landforms- The region has several landforms. Its rivers are a vital resource. Surrounding seas serve as transportation routes. Climate and Resources-The region is dry except for the fertile valleys of Turkey and the Middle East. Oil is a major resource. Water is scarce. Society and Culture- Three of the world’s religions- Judaism, Christianity, and Islam have their roots in Southwest Asia. Today, as in ancient times, Southwest Asia is an important region. It is the crossroad of three continents- Europe, Africa, and Asia. The region has several landforms. Its rivers are a vital resource. Surrounding seas serve as transportation routes. Unlike Africa, Southwest Asia is not a separate continent. It is the corner of the enormous continent Asia. There are a wide number of religions that are practiced in this region of the world. Southwest Asia links Europe, Africa, and Asia. In ancient times, many people migrated there. Traders crossed the region spreading goods and ideas. Modern Southwest Asia is still a crossroads of world trade. It controls vital sea and land routes. Key Term Strait- A narrow waterway that connects two larger bodies of water. Many Americans think of Southwest Asia as one large desert. In fact, the region has a variety of landforms. Mountains affect movement and communication. Traders, invaders, and modern-road builders had to find a way around or through the mountains. Mountains also influence Southwest Asia’s environment. The region’s high peaks affect rainfall. The area has severe earthquakes that sometimes kill thousands of people. Video- Earthquakes Some parts of the region has a climate suitable for growing crops. While other areas are large deserts. Like mountains, deserts discourage the movement of people because they have little or no water. 1. What three continents cross to give Southwest Asia its relative location? 2. Why is Southwest Asia considered to be a crossroads of world trade? What three continents cross to give 1. Southwest Asia its relative location? Southwest Asia links Europe, Africa, and Asia. Why is Southwest Asia considered to be a 2. crossroads of world trade? It controls vital sea and land routes. Oil and water are unevenly distributed in the region. Much of the world’s supply of oil is from Southwest Asia. Even though many people are farmers, the region has to import food because of lack of enough fertile land and moisture. Water, like oil, is a valuable commodity. Which do you think is more valuable to the people of Southwest Asia? Why? (5 minutes) Work with a neighbor and compare your answer with theirs. What things are the same and what things are different? (3 minutes) The majority of the Persian Gulf Oil Fields are located in the Persian Gulf Basin. The top five future oil fields in the world all reside in the Middle East. Much of the world’s supply of oil is from Southwest Asia. This one region is thought to have most of the world’s supply of oil. Yet only a few nations in Southwest Asia have large oil reserves. Although continents such as North America and Europe use the most oil currently, countries such as China and India are rapidly growing, thus increasing their need for oil. The burning of fossil fuels creates greenhouse gases. Water pollution through oil spills have can very adverse affects the animals and plant life of the surrounding spill. Although there are large reserves of oil in and around the Persian Gulf, new sources of energy are eventually going to be required to replace these oil fields. Lack of moisture has made fresh water, especially from rivers, enormously important to the region. The Fertile Crescent, an area of green land, is a key agricultural region due to the availability of water. Key Term The Fertile Crescent- Is located in the Middle East, a crescent-shaped area where agriculture and civilizations evolved first. The Persian Gulf is important to the world’s economy. The Suez Canal is a key link in world trade routes running between Europe and Asia. Key Term Aquifers-An underground reservoir of water which can be extracted for use. Because of the arid climate, water is a scarce and valuable resource in Southwest Asia. As population grows so does the demand for water. Today there are often tensions among nations that share water supplies. Key Term Wadis-Are dry streambeds found throughout the desert region. Key Term Depleted- Is when natural resources become exhausted over centuries of use. Modern scientists have invented methods to help people adapt to the arid climate. Two ways are desalination and fertigation. Key Term Fertigation- Is feeding water and fertilizer directly to the roots of crops. Key Term DesalinationInvolves changing salty water into fresh water that can be used for drinking and irrigation. Video- Desalination Myths and Misconceptions Three of the world’s religions- Judaism, Christianity, and Islam have their roots in Southwest Asia. Islam is viewed by many Muslims not simply as a religion, but also as a cultural identity and heritage. Arabs serve coffee or tea to honor guests. Refusing it is a refusal of generosity. The public display of intimacy between men and women is considered offensive. This code also applies to husbands and wives . The maintenance of family honor is one of the highest values. In Middle Eastern cultures, promiscuous behavior can be more damaging to family honor. Most Middle Easterners still prefer an arranged marriage. Women’s status vary depending on the country involved. In the Persian Gulf States, most women do not work. Those who do, work only in all-female environments such as schools for women. Key Term Hijab- A head covering worn in public by some Muslim women. Video- Islam History and Teachings Arabs are people in different countries who share a common culture and language. About 90 percent of the people in Southwest Asia are Muslim. They are divided into two main groups the Sunni and Shiite. Religion is an important part of culture. Like Jews and Christians, Muslims believe in one God. Monotheism is the belief that there is one God Allah is the Arabic word for God. The sacred book of Islam is the Quran. Besides teaching about God, the Quran provides a guide to life. Like the Bible, the Quran forbids lying, stealing, and murder. It also prohibits gambling, eating pork, and drinking alcohol. Islam unifies the people of Southwest Asia. Islamic law governs all aspects of life, including family life, business practices, banking and government. Key Term Allah- The Arabic word for God. Key Term Mosque- A Muslim place of worship. 1. Faith: Belief in one god and that Muhammad is his prophet. 2. Prayer: Five times a day – facing Mecca. 3. Alms: Giving money to the poor is REQUIRED, not optional. 4. Fasting: During the month of Ramadan, Muslims cannot eat or drink anything during the daylight hours. 5. Pilgrimage: Once in their lives – if they can afford it, Muslims make a pilgrimage to Mecca. Islam is an important religion, which shares many beliefs and practices with Christianity and Judaism. Muslims live in many different countries. Islam is especially widespread in Africa, Asia, and southeastern Europe (the Balkans). 1. What are the Five Pillars of Islam? 2. The two main sects or groups of Muslims are what? 3. What three religions have their roots in Southwest Asia? What are the Five Pillars of Islam? 1. Faith, Prayer, Alms, Fasting, and Pilgrimage are the Five Pillars of Islam. The two main sects or groups of Muslims are what? 2. The two main groups the Sunni and Shiite. What three religions have their roots in Southwest 3. Asia? Judaism, Christianity, and Islam have their roots in Southwest Asia. Do you think it is easy for three religions to share a holy city? Why or why not? (10 minutes) What has been the “muddiest” point so far in this lesson? That is, what topic remains the least clear to you? (4 minutes) Work with a neighbor and compare your muddiest point with theirs. Compare what things are the same and what things are different? (3 minutes)