L 4 Growth Hormone
advertisement

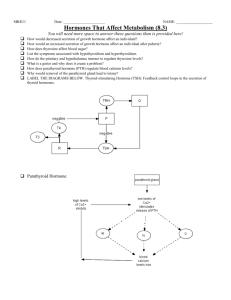
GROWTH HORMONE Dr. Amel Eassawi OBJECTIVES The student should be able to: Identify the factors that affect growth beside the growth hormone. Identify the hormones that affect growth beside the growth hormone. Describe the metabolic effect of growth hormone. Identify the relationship between growth hormone and insulin-like growth factors. Explain the functions of the growth hormone. Define the factors that influence the growth hormone secretion. Describe the growth hormone abnormalities. Describe the functions of melatonin hormone. Explain the biological effect of melatonin hormone. 2 FACTORS AFFECT GROWTH Growth depends on growth hormone but is influenced by other factors as well: – Genetic determination of an individual’s maximum growth capacity. – An adequate diet. – Freedom from chronic disease and stressful environmental conditions. – Normal levels of growth-influencing hormones 3 HORMONES REGULATING GROWTH • • • • • Thyroid Hormone Insulin: Stimulates IGF-1 (Somatomedin) Prolactin: Stimulates IGF-1 Testosterone Estrogen 4 HORMONES REGULATING GROWTH • Other hormones besides growth hormone are essential for normal growth – Thyroid hormone • Growth severely stunted in hypothyroid children • Hypersecretion does not cause excessive growth – Insulin • Deficiency often blocks growth • Hyperinsulinism often stimulate excessive growth – Androgens • Play role in pubertal growth surge, stimulate protein synthesis in many organs – Estrogens • Effects of estrogen on growth prior to bone maturation are not well understood. 5 GROWTH RATE • Not continuous • Factors responsible for promoting growth are not the same throughout growth period • Fetal growth – Promoted largely by hormones from placenta – GH plays no role in fetal development • Postnatal growth spurt – Displayed during first two years of life • Pubertal growth spurt – Occurs during adolescence 6 Growth Hormone 7 GROWTH HORMONE FUNCTIONS DIRECT EFFECT • Growth hormone binds directly to its target cells: – bones & muscles • Stimulates growth – Hypertrophy: increase in size/volume of cells – Example: increase in bone thickness • Stimulates cell reproduction – Increased rate of mitosis – Hyperplasia: increase in the number of cells, proliferation rate – Example: increase in bone length • Stimulates cell metabolism – Increase protein synthesis – Increase fat breakdown for energy – Increase glycogen breakdown so that there is an increase in blood glucose levels to fuel cell growth 8 BONE GROWTH AT THE EPIPHYSEAL PLATE 9 GROWTH HORMONE FUNCTIONS INDIRECT EFFECT • Most growth occurs through the indirect method. • GH acts as a tropic hormone. • stimulating liver’s production of somatomedins – Primary somatomedin is insulin-like growth factor (IGF-1) • Acts directly on bone and soft tissues to bring about most growth-promoting actions • Stimulates protein synthesis, cell division, and lengthening and thickening of bones 10 GROWTH HORMONE REGULATION hypothalamus growth hormone releasing hormone (GHRH) growth hormone inhibiting hormone Somatostatin (GHIH) anterior pituitary growth hormone (GH) GH half-life is 20 – 30 min liver Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) 11 12 GROWTH HORMONE SECRETION • Secreted in bursts (not continuous) • GH released mostly during sleep – optimal at night time – Changing sleeping pattern affects GH release • GH production declines with age Increased Growth Hormone Secretion: • Exercise regularly • 8 hours of sleep • Protein-rich diet • Avoid Stress 13 GH ASSOCIATED DISORDERS • Dwarfism • Gigantism • Acromegaly 14 DWARFISM • Deficiency in GH • Short stature – Adult 4'10" or shorter • Proportional body • Affects 1/10 000 • Occurs in children – GH absent during child’s development 15 GIGANTISM • Excessive growth and height • Continuous secretion of GH • Open epiphyseal plate – Affects bone growth length • Occurs during childhood 16 Robert Wadlow the world’s Tallest Man (1918-1940) 8 feet 11 inches and 439 pounds when he died 17 TALLEST PERSON ALIVE • Sultan Kosen • born in Turkey • 8 feet 1 inch http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ODFHC2XCtjU http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Rf-lcBzZwC4 18 COMPARING GROWTHS 19 GIGANTISM • Pituitary Adenoma – Tumour formed by pituitary gland – Secretes excessive GH / IGF-1 – Non cancerous • Average brain size – Skull grows but brain size stays the same, thus the brain function is unchanged 20 GIGANTISM PROBLEMS • Poor blood flow due to large body • Increased muscle mass but weaker muscle – Excess GH produces salt in muscle tissues – Muscles swell with water – Results in disproportional muscle growth weaker muscles 21 ACROMEGALY • Increased GH secretion in adults • Closed epiphyseal plate – Bone lengthening stopped • Bone width increases • Slow progression Effect of Acromegaly: Soft tissue harden – Deeper voice because larynx enlarges – Bigger tongue and lips that affects breathing – Cartilage in nose enlarges making nose broader 22 ACROMEGALY: PHYSICAL EFFECTS • Bone thickens – Forehead expands – Eyebrow ridges bulge outwards – Cheekbones more prominent – Mandible enlarges and pushes lower teeth outwards and become widely space 23 ACROMEGALY: EFFECT ON MUSCLES • Impaired Movements – Enlargement of bones crushes peroneal nerve in knee – Nerve carries messages to move foot and lower leg – Nerve cannot send messages to leg to trigger walking motion • Also cause muscle numbness • Leads to early death 24 ACROMEGALY: HEART DEFECTS • Heart tissue stiffen – heart cannot contract and relax – Ventricle harder to fill up • Heart grows bigger in order to pump out sufficient blood 25 ACROMEGALY: LUNG DEFECT • As bones grow, rib cage expands • Diaphragm is stretched thin and loses elasticity • Breathing is reduced 26 PINEAL GLAND • The pineal gland is a small, cone – shaped structure located in the center of the brain, diencephalon. • The pineal gland is composed of pinealocytes and glial cells. • Connects endocrine with nervous system 27 PINEAL GLAND Functions: • Secretion of the Hormone Melatonin • Regulation of Endocrine Functions • Conversion of Nervous System Signals to Endocrine Signals • Causes Feeling of Sleepiness • Influences Sexual Development Precursor of melatonin is serotonin. Synthesis and secretion of melatonin is affected by light exposure to the eyes. 28 BIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF MELATONIN • Helps keep body’s circadian rhythms in synchrony with light-dark cycle • Effects on Reproductive Function • Anti-gonadotropic • Effects on Sleep and Activity • Acts as antioxidant to remove free radicals • Alterations in melanin pigment distribution 29 REFERENCES Human physiology, Lauralee Sherwood, seventh edition. Text book physiology by Guyton &Hall,11th edition. Physiology by Berne and Levy, sixth edition. 30