Using Outcomes to Plan Your Course and Your Assessments
advertisement

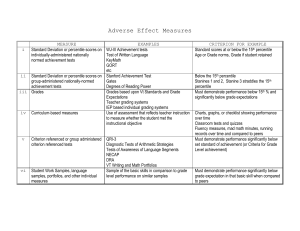
Assessment of Student Learning Outcomes by Kirby Hayes August 15th 2007 Why assess student learning outcomes? Improve learning Deliberate use of evidence of student learning to inform curricular improvements Respond to accreditation requirements University-level regional accreditation Discipline-level accreditation e.g. ABET August 15th 2007 Outline North Central Association Created the Higher Learning Commission Changes in process since 1999/2000 Emphasis on assessment of student learning Purdue Preparation 3-Step Process Examples Timeline August 15th 2007 North Central Association Northwest Western North Central Southern Middle States New England North Central region – 19 states, 980 colleges/universities August 15th 2007 North Central Association Review occurs every ten years Purdue continually accredited since 1913 Last review in 1999/2000 August 15th 2007 North Central Association Timing for 2009/10 review Fall 06: HLC notified Purdue to “get ready” Spring 07: SLOAW Organized Fall 07: Purdue identifies self-study coordinator Fall 07/Summer 09: Campus conducts self-study and prepares report. Fall 09: Site visit by review team. Spring 10: Team report and university response reviewed by HLC panel. Spring 10: Final decision by HLC. (Monitoring reports have been common since 2005) August 15th 2007 Higher Learning Commission NCA created the Higher Learning Commission (HLC) in 2005 The process/focus of accreditation was changed in 2005, to an evidence-based evaluative (vs. descriptive) report demonstrating compliance with five basic criteria. August 15th 2007 The Five Criteria Student Learning and Effective Teaching Preparation for the Future Mission & Integrity Acquisition, Discovery, Application of Knowledge August 15th 2007 Engagement & Service Student Learning and Effective Teaching 3a - The organization’s goals for student learning outcomes are clearly stated for each educational program and make effective assessment possible. 4b - The organization demonstrates that acquisition of a breadth of knowledge and skills and the exercise of intellectual inquiry are integral to its educational programs. 4c - The organization assesses the usefulness of its curricula to students who will live and work in a global, diverse, and technological society. “Shared responsibility” and high faculty involvement August 15th 2007 Student Learning and Effective Teaching 3a - The organization’s goals for student learning outcomes are clearly stated for each educational program and make effective assessment possible. 4b - The organization demonstrates that acquisition of a breadth of knowledge and skills and the exercise of intellectual inquiry are integral to its educational programs. 4c - The organization assesses the usefulness of its curricula to students who will live and work in a global, diverse, and technological society. “Shared responsibility” and high faculty involvement August 15th 2007 Student Learning and Effective Teaching 3a - The organization’s goals for student learning outcomes are clearly stated for each educational program and make effective assessment possible. 4b - The organization demonstrates that acquisition of a breadth of knowledge and skills and the exercise of intellectual inquiry are integral to its educational programs. 4c - The organization assesses the usefulness of its curricula to students who will live and work in a global, diverse, and technological society. “Shared responsibility” and high faculty involvement August 15th 2007 Student Learning and Effective Teaching 3a - The organization’s goals for student learning outcomes are clearly stated for each educational program and make effective assessment possible. 4b - The organization demonstrates that acquisition of a breadth of knowledge and skills and the exercise of intellectual inquiry are integral to its educational programs. 4c - The organization assesses the usefulness of its curricula to students who will live and work in a global, diverse, and technological society. “Shared responsibility” and high faculty involvement August 15th 2007 Preparation for 2009/10 Fall 2007: appoint leadership team and develop plan for self-study. Determine theme for self-study. Develop campus plan for assessment of student learning activities (SLOAW). Join HLC Assessment Academy (SLOAW). Learn from Purdue faculty serving as HLC peer reviewers. Learn from recent reviews of Big 10/peer institutions. Inform and engage campus in review activities. August 15th 2007 Assessment “Assessment is the process of gathering and discussing information from multiple and diverse sources in order to develop a deep understanding of what students know, understand, and can do with their knowledge as a result of their educational experiences; the process culminates when assessment results are used to improve subsequent learning.” (Huba and Freed, 2000) August 15th 2007 Basic Assessment Model Student Learning Outcomes Instructional Assessment August 15th 2007 Instructional Activities Basic Assessment Model Student Learning Outcomes Instructional Assessment Instructional Activities Program student learning outcomes define what a student will be able to know AND do upon completion of the program. August 15th 2007 Basic Assessment Model Student Learning Outcomes Instructional Assessment Instructional Activities Instructional activities provide students with meaningful opportunities to achieve a stated learning outcome. August 15th 2007 Basic Assessment Model Student Learning Outcomes Instructional Assessment Instructional Activities Instructional assessments allow you to monitor student learning and provides you feedback about the effectiveness of your instructional activities for supporting students achievement of a stated learning outcome. August 15th 2007 Purdue's Plan August 15th 2007 Scope of Assessment For each undergraduate, graduate and postbaccalaureate program (broadly defined as major), the HLC review team will want to see evidence of: student learning outcomes and how they are addressed, assessment of student learning outcomes, and ongoing efforts to help improve student learning based on these assessments. To meet the requirements stated in subsections 3a, 4b, and 4c, the following steps need to be completed for each program (undergraduate, graduate, and postbaccalaureate) and answers to the related topic questions should be provided. August 15th 2007 3-Step Plan Step 1: Identification of and Activities for Achieving Student Learning Outcomes Step 2: Assessment of Student Learning Outcomes Step 3: Ongoing Efforts to Improve Student Learning August 15th 2007 3-Step Plan Step 1: Identification of and Activities for Achieving Student Learning Outcomes Outcomes: What are the student learning outcomes and their sources for this program? Activities: In what activities are students involved to help achieve these learning outcomes? August 15th 2007 3-Step Plan Step 2: Assessment of Student Learning Outcomes Evidence: What assessment evidence is collected to determine students’ achievement of the learning outcomes? (show multiple measures and frequency of measures) Findings: Based on your assessment evidence, to what extent have students achieved the learning outcomes? August 15th 2007 3-Step Plan Step 3: Ongoing Efforts to Improve Student Learning Reviews: To help inform improvement of student learning, what processes do you use to review the assessment evidence? Changes: As a result of reviewing the assessment evidence, what did or will you change (if anything) to help students achieve an acceptable or higher level of the learning outcome? Impacts: If any changes were made, what impacts did they have on the extent to which students achieved the learning outcome? August 15th 2007 3-Step Plan Shared Responsibility How did you ensure broad faculty involvement in these three steps? August 15th 2007 Template See Handout August 15th 2007 2007/2009 Timeline Thru December 2007 Develop/Implement process (SLOAW) Develop web-based template (SLOAW) Thru May 2008 All programs populate template with one outcome (establish review process) Thru May 2009 All programs populate template with all outcomes August 15th 2007 Beyond 2009/10 Assessment of student learning must become a routine part of the work we do. We can begin to accomplish this by embedding the learning outcomes initiative into our next strategic plan. August 15th 2007 Assessment Resources University of Central Florida - Assessment Document http://iaaweb.ucf.edu/oeas2/pdf/acad_prog ram_assessment_handbook_rev022704.p df American Psychological Association – Assessment Strategy http://www.apa.org/ed/eval_strategies.html August 15th 2007 Books and Articles Angelo, T. A. & Cross, K. P. (1993). Classroom assessment techniques. (2nd ed.). San Francisco: Jossey-Bass. Huba, M. E. & Freed, J. E. (2000). Learnercentered assessment on college campuses. Boston: Allyn & Bacon. Walvoord, B.E. (2004). Assessment clear and simple. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass. August 15th 2007 Assessment of Student Learning Outcomes by Kirby Hayes August 15th 2007