Subculture
advertisement

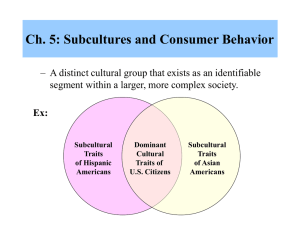
Consumer Behavior, Eighth Edition SCHIFFMAN & KANUK Chapter 13 Subcultures and Consumer Behavior 13-1 Subculture 13-2 A distinct cultural group that exists as an identifiable segment within a larger, more complex society. Figure 13.1 Relationship Between Culture and Subculture Subcultural Traits Of 13-3 Dominant Cultural Traits of U.S. Citizens Subcultural Traits Table 13.1 Examples of Major Subcultural Categories CATEGORIES EXAMPLES Jamaican, Vietnamese, French Religion Mormon, Baptist, Catholic Geographic region Northeast, Southwest, Midwestern Pacific Islander, Native American, Caucasian Senior citizen, teenager, Xers Gender Female, Male Occupation Bus driver, mechanic, engineer Lower, middle, upper 13-4 Hispanic Subculture Demographics • Median age is 10 years younger than the population • Concentrated in which cities? • 12 Hispanic subgroups • 4 major subgroups: • Mexicans: 64% • Puerto Ricans: 12% • Cubans: 4-5% • Dominicans: own 13-5 Issues in Studying Hispanic American Subcultures • Hispanic Consumer Behavior – Stronger preference for well-established brands – Some are shifting food shopping to non-ethnic American-style supermarkets – Youths are more fashion-conscious 13-6 Table 13.2 Traditional Characteristics of the Hispanic American Market Prefer well-known or familiar brands Buy Are fashion-conscious Historically prefer to shop at smaller personal stores Buy brands advertised by their ethnic-group stores Tend not to be impulse buyers (i.e., are deliberate) Increasingly clipping and using cents-off coupons Likely to buy Prefer Tend to be negative about marketing practices 13-7 Table 13.3 Traditional “Hispanic”Variables • Spanish Surname • Country of Origin • Country of family ancestry 13-8 • Spanish spoken at home • Self-identification • Degree of identification Marketplace behaviors • Heavy users and buyers of cosmetics and toiletries • Family shopping is a weekend outing • tend to be loyal to firms that are socially responsible • …….. brand loyal than the average American • Prefer using cash - why? • Event marketing is highly recommended by marketers - why? 13-9 Figure 13.4 Hispanic Linguistic Challenge Bilingual/ prefer Spanish Bilingual/ no preference Bilingual/ prefer English Spanish only English only 13-10 Religious Subcultures • 200+ organized religious groups in the U.S. • Primary organized faiths include: – Protestant denominations – Roman Catholicism – Judaism • Consumer Behavior is directly affected by religion in terms of 13-11 Geographic Subcultures • Regional identification is used as a way of describing others • Geographic subcultures even at the neighborhood level • why the interest in researching geographic subcultures? 13-12 Regional Subcultures • Many regional differences exist in consumption behavior – Westerners have a mug of black coffee – Easterners have a cup of coffee with milk and sugar – White bread is preferred in the South and Midwest – Rye and whole wheat are preferred on the East and West coasts 13-13 Major Racial Subcultures • The African-American Consumer – Largest racial minority in U.S. – Purchasing power estimated at $572 billion • Asian-American Consumers – Currently about 12 million in size – Estimated at 13 million in 2005 – Gain of 54% since 1990 13-14 Reaching the AfricanAmerican Audience • Two Alternate Strategies – Running all the advertising in general mass media – Running additional advertising at special advertising in selected media directed exclusively to African-Americans 13-15 Major Racial Subcultures • Asian-American Consumers – Median age is 27, highest median income, highest rate of completing college. – Currently about 10 million in size – Estimated at 10.9 million in 2001 – Gain of almost 50% since 1990 • • • • • • 13-16 Chinese 23% Filipinos 19% Japanese 12% Asian Indian 11% Korean 11% Vietnamese 14% Asian-American Consumers • Where Are the Asian-Americans? • Asian-Americans As Consumers – Buying power of $110 billion annually – Attracted to retailers who welcome Asian-American patronage 13-17 Major Racial Subcultures • Value quality - well known brands • generally male oriented decision making • VERY diverse cultural backgrounds – Japanese Americans buy quality products and have the money to spend – Asian Indians are usually vegetarians – Koreans prefer shopping in person – Chinese will pay cash for a car, Japanese will finance it 13-18 Major Age Subcultures 13-19 Generation X Market Generation Y Market Seniors Market Baby Boomer Market Generation Y 13-20 Born between 1977 and 1994; also called and millennium generation 3 Subsegments of Gen Y • Gen Y Adults • Gen Y Teens • Gen Y Tweens 13-21 Generation X 13-22 Born between 1965 and 1979; post baby boomer segment (also referred to as ). Baby Boomers 13-23 Individuals born between 1946 and 1964 (approximately 45% of the adult population). Baby Boomers • Frequently make important consumer purchase decisions • Include a small subsegment of trendsetting consumers ( ) who influence consumer tastes of other age segments 13-24 Seniors 13-25 Generally older consumers. Consist of subcultures, including the 50-plus market and the “elderly consumers” market. Three Senior Subsegments • The Young-Old (65-74) • The Old (75-84) • The Old-Old (85 and older) 13-26 Table 13.12 Comparison of New-Age and Traditional Elderly NEW-AGE ELDERLY • Perceive themselves to be different in outlook from other people their age • Age is seen as a state of mind • See themselves as younger than their chronological age TRADITIONAL/STEREOTYPICAL ELDERLY • Perceive all older people to be about the same in outlook • See age as more of a physical state • See themselves at or near their chronological age • Feel younger, think younger, and “do” younger • Tend to feel, think, and do things that they feel match their chronological age • Have a genuinely youthful outlook • Feel that one should act one’s age • Feel there is a considerable adventure to living 13-27 Issues in Understanding Sex as a Subculture • Sex Roles and Consumer Behavior – Masculine vs. Feminine Traits • The Working Woman – Segmentation Issues – Shopping Patterns 13-28 Segmenting the Female Market • Four Segments: – Stay-at-Home Housewives – Plan-to-Work Housewives – Career-Oriented Working Women 13-29 Table 13.10 How Women Control the Purse Strings Women control or influence… 80% of all purchase decisions 80% of new vehicle purchases 46% of menswear purchases 82% of supermarket purchases 53% of investment decisions 70% of appliance choices Women also… handle 75% of family finances constitute 40% of business travel are 43% of the persons with assets over $500,000 13-30