Aims of Sentencing
advertisement

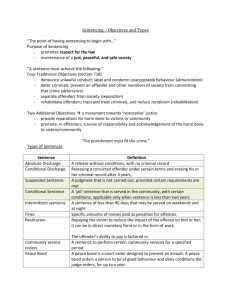
Role of the Courts • Court decides what sentence should be imposed on the offender. • The Judge or magistrates decide on an appropriate punishment in each case. • What restrictions are they subject to when deciding on a suitable sentence? Aims of Sentencing • The judge / magistrates will have to decide what they are trying to achieve by the punishment they give. • For example, should they simply punish D for what he’s done, or should they try and alter his future behaviour? Aims of Sentencing S.142 Criminal Justice Act 2003: • The punishment of offenders • The reduction of crime (inc. by deterrence) • Reform and rehabilitation of offenders • The protection of the public • Reparation by offenders to those affected by the crime Activity … Read the article and answer the questions on page 205 of “OCR Law for AS”. Retribution • “An eye for an eye…..” • Based on the idea of punishment because the offender deserves it. • No attempt to alter D’s future behaviour. • What types of sentences do you think achieve this aim? Denunciation • Society expressing its disapproval of criminal behaviour. • Can influence society’s views on what is acceptable / unacceptable conduct. • Examples: drink driving; enhanced sentencing for racist crime. Incapacitation • Offender is made incapable of re-offending. • Can be a short-term solution, however, depending on the sentence. • Think of some examples of sentences that reflect this aim of sentencing. Deterrence • Aimed at reducing future levels of crime. • Individual – to deter D from re-offending. • General- to deter other potential offenders from committing crimes. • Idea is to give a harsh punishment, e.g. prison sentence or heavy fine. What deters criminals? • Being caught? • A tough sentence? • The reaction of family / friends? • Theory assumes an offender will stop to consider consequences – but most crime is committed on the spur of the moment. Rehabilitation • Main aim is to reform the offender so that they do not re-offend in the future. • Usually involves community sentences. Criticisms: • Often discriminates against the underprivileged. • Leads to inconsistency in sentencing. Reparation • Aimed at compensating the victim of the crime. • Based on idea that criminals should pay compensation to their victims. • S.130 Powers of Criminal Courts (Sentencing) Act 2000 says courts are under a duty to give reasons if they do not make a compensation order. Activity… Read the article on page 212 of “OCR Law for AS” and answer the questions following it. Sentencing Practice Before passing sentence, the court will consider: • Any aggravating / mitigating factors • Pre-sentence reports (Probation service) • Any previous convictions • Medical Reports • Character Statements • D’s financial / domestic circumstances Pleading Guilty • Reduction in sentence for a guilty plea. • What reasons did the Sentencing Guidelines Council give for allowing reductions in sentences for guilty pleas? • Do you agree with this concept? Types of Sentence Draw a chart with 3 columns showing… 1) the different types of sentence available 2) an explanation of each sentence 3) the aims of each sentence Custodial Sentences S.152 Criminal Justice Act 2003: • Court must not pass a custodial sentence unless it is of the opinion that the offence was… “… so serious that neither a fine alone nor a community sentence can be justified”. Custodial Sentences • Range from intermittent (“weekend”) prison to life imprisonment. • Can be unfair on D’s family. • Can be very difficult for D to re-integrate into society on release (job, housing etc.) Community Sentences Criminal Justice Act 2003: • Created one community order under which the court can combine any requirements it thinks are necessary. • “Mix and match” approach to meet D’s needs Community Sentences s.177 Criminal Justice Act 2003 includes: • Unpaid work requirement • Curfew requirement • Exclusion requirement • Supervision requirement • Drug rehabilitation requirement Fines • Sum payable to the Crown – not compensation for the victim. • Most common sentence in Magistrates’ Court. • “Rich man, poor man” problems. • What happens if D cannot pay? Discharges and other orders… • Conditional discharge – often used for first time minor offenders. • Absolute discharge • Disqualification from driving • Compensation order Anti-Social Behaviour Orders • Civil orders that can be imposed where a person has behaved in an anti-social manner. • Breaking an ASBO is a criminal matter and the offender can then be sentenced for the breach. Young Offenders • At what age is a child criminally liable? • Different sentences available for those under 18, under 16, under 14 and under 12. • Main aim is reformation and rehabilitation