AS Level Law
advertisement

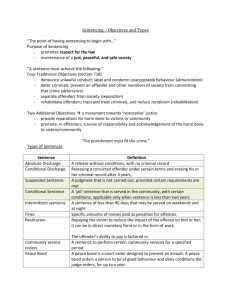
AS Level Law Machinery of Justice Sentencing AS Level Law What you need to know and discuss: •the need for a criminal justice system •the main aims of punishment •key concepts in effective punishment •the current approach to sentencing of both adult and young offenders •the effectiveness of the system in achieving its aims AS Level Law Introduction • 2 main reasons for criminal justice system: discourage anti-social conduct satisfy moral sense in society AS Level Law Aims of sentencing • CJA 2003, s.142 identifies five purposes of sentencing: punishment of offenders crime reduction, including through deterrence reform and rehabilitation of offenders protection of the public reparation by offenders to those affected by their offences AS Level Law Objective Sentences available Retribution (punishment) – society’s revenge on the offender Custodial sentences have a significant retributive element. Also serve public protection by incapacitating the offender Deterrence – aim to deter offender from re-offending (individual) and others by example (general) Again, custodial sentences are seen as having a strong deterrent element – questionable? Rehabilitation – discourage reoffending by rehabilitating offender into mainstream society Rehabilitation is a major objective of community sentences Reparation (restorative justice) – offender makes good the harm they have caused Again, reparation is largely concerned with community sentences (e.g. unpaid work requirement, activity requirement) AS Level Law Key concepts in effective punishment • proportionality (punishment fits the crime) • certainty (enhances deterrence) • publicity (again, deterrence) • promptness (again, deterrence) AS Level Law Sentencing in the English courts • major reforms in CJA 2003 following Halliday Report • adult offenders - three options: custodial (see s.152 and s.153) community (new generic Community Order, allowing courts to mix and match different requirements, e.g. unpaid work, drug rehabilitation, alcohol treatment etc - see s.147, 148 and 177) fines (see s.164) AS Level Law Also new types of sentence: • ‘Custody Plus’ – short prison sentence followed by community supervision – see s.181 • ‘Custody Minus’ (suspended sentence) – Community supervision with custodial element suspended (activated if community requirements not met) – see s.189 • ‘Intermittent Custody’ – Community supervision with short periods of custody - preserve family and community ties (currently 43% of convicted prisoners and 48% of remand prisoners lose contact with their families, and 125,000 children per year have a parent imprisoned) AS Level Law Minimum, Indeterminate, and Extended Sentences: • Minimum – 3rd Class A Drug Trafficking (7 yrs – PCC(S)A 2000, s. 110), 3rd Domestic Burglary (3 yrs – PCC(S)A 2000, S.111), unlawful possession of firearm (5 yrs – CJA 2003, s.287) • criticised for limiting judge’s discretion and being contrary to proportionality - highlights conflict between policy and principle - see R v Offen and others [2000] AS Level Law • Indeterminate – where convicted of a serious offence, and significant risk of further serious offences, court must either: (a) impose life sentence if available for that offence; or (b) impose a sentence of imprisonment for public protection (a sentence of imprisonment for an indeterminate period) – CJA 2003, s.225 – justifiable? • Extended – where convicted of a ‘specified’ violent or sexual offence (other than a ‘serious’ offence) and significant risk of serious harm to the public from further such offences, court must impose an extended sentence – appropriate custodial term plus max 5 yrs (violent) or 8 yrs (sexual) – CJA 2003, s.227 AS Level Law • miscellaneous sanctions - e.g. Confiscation Orders, Compensation Orders • special provision for young offenders: Pre-court orders: Acceptable Behaviour Contracts, Anti-Social Behaviour Orders, Local Child Curfews, Child Safety Orders – also Reprimands and Final Warnings Court orders: Detention & Training; Supervision; Community Rehabilitation; Community Punishment; Action Plan; Attendance Centre; Referral; Reparation; Curfew; Drug Treatment & Testing; Parenting AS Level Law Many of these orders require the offender to work with the local Youth Offending Team (Police, Probation, Social Services, Education reps etc) AS Level Law The effectiveness of the system • ‘Justice Gap’ – in 2000-1, 5.17 million recorded crimes, but only 19.8% resulted in a conviction • custody - 58% re-convicted within 2 years • weaknesses in rehabiltation? Poor support on release? • community sentences - no more effective but much cheaper + lower social costs • focus too much on consequences of crime and not enough on causes – link between offending and social exclusion? AS Level Law • Public confidence? See Confidence in the Criminal Justice System: Findings from the 2000 British Crime Survey AS Level Law Conclusion • sentencing (type & severity) should be closely linked to fault • must maintain public confidence while sentencing appropriately in each case - difficult balance • custody sometimes the only option, but better use should be made of community alternatives - see Home Affairs Select Committee report (1998) • proposed reforms a move in the right direction? AS Level Law Revision Headings: C&P - Intro (need for system) C&P - Aims of Punishment C&P - Key Concepts C&P - Custodial Sentences C&P - Other Sentences C&P - Minimum and Mandatory Sentences C&P - Effectiveness of System C&P - Reforms C&P - Conclusion AS Level Law Test Questions: Using your cards, you should now be able to write a short paragraph in response to each of the following questions: •Why do we need a criminal justice system? •What aims and objectives may a judge be pursuing when sentencing an offender? •What elements should be present in an effective system of punishment? •Describe the approach to sentencing under the Powers of Criminal Courts (Sentencing) Act 2000 and Criminal Justice Act 2003. •Discuss the use of minimum and mandatory sentences. •How effective is the system in achieving its aims? AS Level Law Useful Websites: Criminal Justice System website (a portal site with links to other relevant sites) Youth Justice Board The Home Office HM Prison Service The Halliday Report ‘Justice for All’: Responses to Auld and Halliday British Crime Survey 2000 Powers of Criminal Courts (Sentencing) Act 2000 Criminal Justice Act 2003 ‘Narrowing the Justice Gap’ ‘Reducing Re-offending’ (Social Exclusion Unit)