PP Ch 12
advertisement

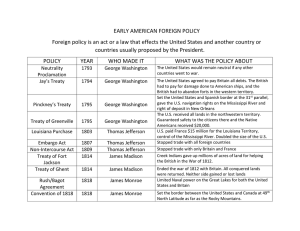
Army was ill prepared Supplemented by militias Canada Important battle ground British weakest there Americans not smart = offensive 3 pronged invasion U.S. fort captured Looked to the navy Skillfully handled Better gunners “Old Ironsides” The Constitution Thicker sides Heavier Firepower Larger crews Control of Great Lakes Oliver Hazard Perry Victory on lake Erie Captured a British fleet Infused new life into the Americans 1814 Americans grimly defending own soil Napoleon vanquished = Isle of Elba Americans faced it alone Redcoats pouring into Canada British prepare for an attack on N.Y. Using lake-river routes Lake Champlain waterway Thomas Macdonough Challenged the British = Sept. 11, 1814 Plattsburgh Floating slaughterhouses Snatched victory British army forced to retreat Saved the union from dissolution August 1814 4,000 redcoats = Chesapeake Bay Moving towards Washington 6,000 militiamen dispersed Washington Burned Set fire to most public buildings = Capital and White House Baltimore held strong Fort McHenry hit with cannon = Could not capture the city Francis Scott Key Detained American Wrote “The Star Spangled Banner” January 1815 Troops led by Andrew 7,000 Jackson British launched frontal assault 2,000 killed / wounded ½ hour U.S. victory 70 casualties Before battle peace agreement already signed Treaty of Ghent --- Christmas eve 1814 Treaty of Ghent Christmas Eve 1814 Armistice Restore conquered territory No mention of grievances previously fought for Virtual Draw 6,000 killed / wounded Led to end of Federalist Party Sectionalism / Hartford Convention Growth of American industries = Manufacture products Confirmed the status of the U.S. / free and independent nation Less dependent on Europe Canadian patriotism / nationalism Rush Bagot Agreement = 1817 Limited naval armament on the lakes December 15, 1814 Hartford Convention Federalist discontent Discuss grievances Compensation 2/3 vote Massachusetts called for convention Embargo Hartford Connecticut New state admission Mass, Conn, R.I. = Full delegations N.H. and Vermont = Partial 26 men = 3 weeks War declared 3/5 clause President = single term “Virginia Dynasty” Nationalism Most important by-product of War Emerged as one nation Writers to use American scenes / themes Nationalistic Spirit Revived Bank = 1816 School textbooks / magazines “North American Review” Army expanded Capital restored 1815 Madison moves U.S. toward economic independence Establishing a protective tariff Manufacturing would flourish Re-chartering the National Bank Credit Development of transportation Steamboat Erie Canal = N.Y. 1825 Madison / Clay James Monroe --- Elected in 1816 Secretary of State John Quincy Adams Foreign policy = Nationalism National interest placed ahead of regional concerns Era of Good feeling? Tariff, bank, land, sectionalism Over speculation in frontier lands Deflation depression / bankruptcies / bank failures Unemployment /soup kitchens “Wildcat Banks” Foreclosed mortgages 1818 Settlers in Missouri requested admission to the Union Free State or Slave State? 1820 -1821 Missouri Compromise Series of agreements passed 36˚30´ Line Henry Clay Expansion of territory Anglo-American Convention of 1818 Fixed the U.S. border at the 49th parallel Michigan west to the Rocky Mountains Agreed to jointly occupy Oregon territory with British 10 years 1818 Americans believed Florida was destined to be theirs Jackson sweeps into Florida Seizes 2 Spanish posts St. Marks / Pensacola Florida Purchase Treaty 1819 “Adams-Onis Treaty” Spain ceded Florida U.S. abandon claims in Texas Napoleon invaded Portugal and Spain Did not have money to maintain overseas colonies Napoleon defeated in 1815 Now wanted to reclaim their colonies Russians moving into Alaska Russo-American Treaty 1824 Establishing posts in California 1823 President Monroe = Message to Congress European powers not to interfere in the Western Hemisphere Do not attempt to create new colonies Do not try to over throw newly independent republics The U.S. would consider actions dangerous to peace and safety U.S. would not involve itself in European affairs Principles known as = Monroe Doctrine Foundation for future U.S. foreign policy