click - Uplift Education
advertisement
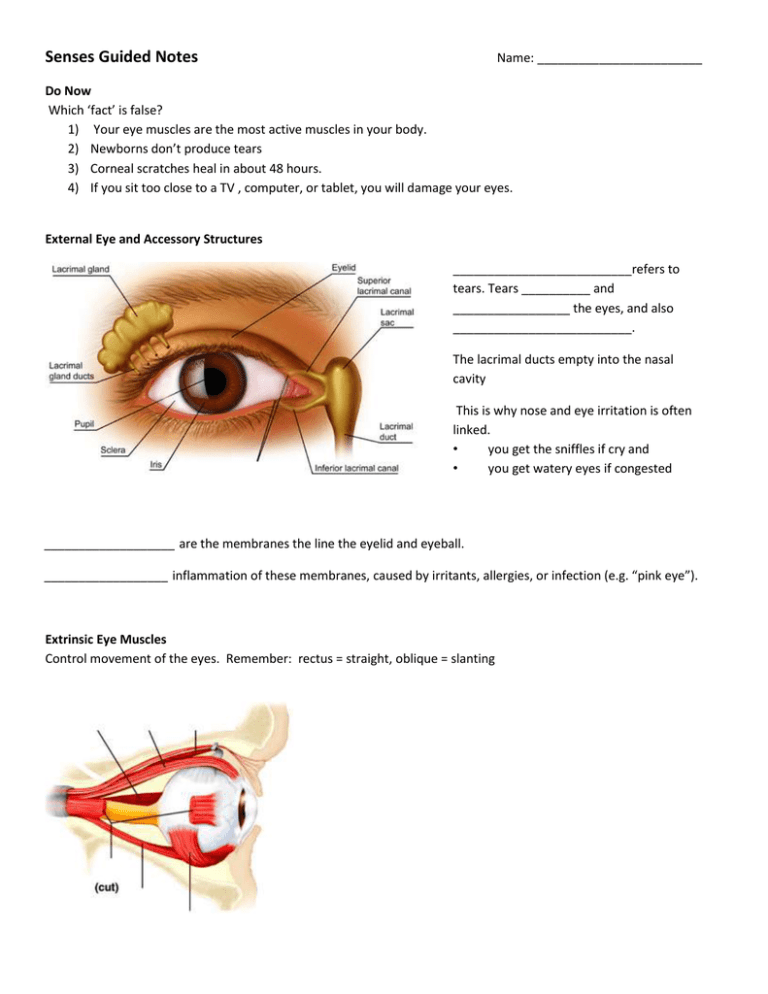
Senses Guided Notes Name: ________________________ Do Now Which ‘fact’ is false? 1) Your eye muscles are the most active muscles in your body. 2) Newborns don’t produce tears 3) Corneal scratches heal in about 48 hours. 4) If you sit too close to a TV , computer, or tablet, you will damage your eyes. External Eye and Accessory Structures __________________________refers to tears. Tears __________ and _________________ the eyes, and also __________________________. The lacrimal ducts empty into the nasal cavity This is why nose and eye irritation is often linked. • you get the sniffles if cry and • you get watery eyes if congested ___________________ are the membranes the line the eyelid and eyeball. __________________ inflammation of these membranes, caused by irritants, allergies, or infection (e.g. “pink eye”). Extrinsic Eye Muscles Control movement of the eyes. Remember: rectus = straight, oblique = slanting Eye muscle names and actions Name Action Lateral rectus Medial rectus Superior rectus Inferior rectus Inferior oblique Superior oblique Eyeball The eye has three ______________________, or coats. • _______________________ – “whites of the eye” , outermost, thick connective tissue. • _______________________ – has blood vessels, middle layer • _______________________ – contains the photoreceptors (rods & cones), inner layer The eye is divided into two fluid-filled chambers: • The anterior chamber is filled with ________________________________________ • The posterior chamber is filled with ______________________________________ • Both fluids ________________________________, and the aqueous humor _________________________________________. • _______________________________ occurs when the aqueous humor doesn’t drain properly, resulting in increased eye pressure and blindness Pathway of Light 1. Light enters the eye at the ________________________ – a clear, hard part of the sclera. Functions: protects eye and focuses light Fun fact: the cornea is responsible for ~70% of the eye’s focusing ability 2. Light passes through the ______________________ which is the opening in front of the lens. • • The size of the pupil is controlled by the muscles of the __________ (the the eye). colored part of The pupil dilates or contracts to vary the amount of light hitting the retina. 3. The light passes through the ______________which focuses the light onto the retina. • 4. The __________________________ are muscles which change the shape of the lens to focus on nearby items, a process called __________________________. The light passes through the _________________________ to land on the retina, which contains the photoreceptors. There are no photoreceptors on the _____________________________, which is where the optic nerve exits the eye – this causes a small blind spot. Photoreceptors Rods Responsible for night and peripheral vision – • more abundant that’s why colors seem to be lost in the dark. • sensitive to ______________________________ • do not discriminate _______________________________________________ Cones - ________________________________________ • 3 types, _______________________________________________________________________ • triggering of more than one cone is interpreted by brain as different colors e.g. if both red and green are activated, the brain will interpret the light as yellow or orange • ________________ than cones • mostly found in ___________________________________ Responsible for color and fine detail vision – including reading Color blindness is usually caused by the absence of one or more cones. • Occurs in ~5% of population • X-linked trait … much more common in men Refraction and Accommodation Light is bent – or __________________________– by nearly every eye structure that it passes through on the way to the retina. However the lens is the only structure that can vary how much the light is bent in order to allow us to focus on different objects – a process called __________________________. • At rest, our eyes naturally focus on far-away objects. • However, by contracting the ________________ ____________________, we can make the lens bulge so that it has greater refractive ability – allowing us to focus on close items. As we get older, our lens loses elasticity – making it harder to focus on nearby items. This condition is called _____________________________(old eyes) Refraction flips and reverses the light rays, forming an upside down and reversed image on the retina … but the brain learns to interpret visual information correctly. Refractive Errors Myopia Common name: Causes: Diagram: Why can myopic individuals see _______________ objects better? Because light from _____________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ to properly hit the retina Correction: _________________________corrective lenses / contacts magnify the image (make the light diverge more), before it enters the eye Lasik surgery to flatten cornea makes the light focus less so it can properly reach the retina. Hyperopia Common name: Causes: Diagram: Why can hyperopic individuals see _______________ objects better? Because light from _____________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ to properly hit the retina Correction: ________________________ corrective lenses / contacts Cornea surgery to make the cornea more ____________________ Both focus the light _______________ so that it properly reaches retina Astigmatism A-stigma = _________________________________ (light focuses unevenly on retina) Causes: Diagram: Signs of astigmatism: Fine details are blurry – whether ___________ or __________ “Halo”effects or glare from lights Correction Corrective lenses or contacts Shape of lens /contact __________________________________ to counteract irregular shape of the eye Contact lenses are often ___________________ so that they align properly with the eye Ortho-K / cornea surgery _________________ with special contact lenses worn at night or with laser surgery Ear Structure and Function Guided Notes Ear Anatomy Overview External Ear Middle Ear Inner Ear Structures: Structures: Structures: o o o Function: Function: Function: NOTE: Diagrams are misleading. The entire inner is bony, except for the labyrinth which is a series of cavities (spaces) within the bone. Outer Ear Function: __________________________________________________________ Pinna collect sound waves and direct to the tympanic membranes … but in humans, not very effectively. Cerumen (ear wax) lines the external auditory canal. ◦ Antibacterial ◦ Also discourages bugs, mold, etc. ◦ Lubricates ears ◦ Helps trap / remove foreign particles The tympanic membrane (ear drum) vibrates when sound waves hit it, transmitting the sound to the middle ear Disorders of the outer ear Ear Wax Blockage Ear wax can become impacted, usually from hear aid use or inappropriate methods of cleaning the ears Can cause temporary loss of hearing Otitis Externa (Swimmer’s Ear) Infection of external auditory ear canal, usually due to excess moisture in the ear canal (such as from swimming), though cuts and scrapes to the ear canal can also become infected. Middle Ear Function: _____________________________________________________________________________ How? The tympanic membrane transmits sound to the three ossicles. The ossicles act like levers, amplifying the sound and transmitting it to the oval window, a membrane-covered opening to the inner ear. Eustachian tubes Structure Tube that connects the middle ear to the nose and throat Mostly closed, but opens when we move our jaw Why do we have it? Equalize pressure in the middle ear Drain fluids to the throat Disorders of the middle ear Otitis media (middle ear inflammation / infection) – Inflammation (often with the buildup of infected fluids) within the middle ear Visible with an otoscope as a bulging eardrum Usually caused from a respiratory infection Babies who are allowed to drink bottles while lying down are also very likely to get ear infections Much more common in young children, because their Eustachian tubes are narrower and more horizontal Ear tubes are often recommended for children who experience chronic middle ear infections or fluid build-up The tube is placed in the ear drum, but performs the functions of a eustachian tube – ventilating and draining the middle ear. Hearing and the inner ear Hearing takes place within the cochlea of the inner ear. Cochlea is a long, curled cavity with three layers ◦ 2 layers of _______________ – a plasma-like fluid ◦ In-between: a system of membranes that contain the ______________________ and the ______________________ _______________________ that create the nerve impulse The top diagram is a cross-section of the cochlear cavity. Take a moment to figure out … ◦ What fills the scala vestibuli? ◦ The scala tympani? ◦ The cochlear duct? When the stapes beats against the oval window, it causes pressure waves within the perilymph The movement of the perilymph disturbs the cilia (receptors) of the Organ of Corti, generating a nerve impulse Different frequencies (pitch) vibrate the membrane in different locations. High pitches are heard that the front, low at the back. The round window is a membrane-covered opening just below the oval window. It bulges to keep the pressure waves from bouncing back. Balance and Aging Guided Notes How do we maintain balance? Cerebellum monitors and controls balance. It receives input from four main sources: __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ Static vs Dynamic Equilibrium Static equilibrium has to do with our ____________________________________________________________ e.g. upside down, tilted to the left, slowing down, etc. Sensed by the _________________________ of the _____________________ Dynamic equilibrium has do to with ________________________________________________________ E.g. spinning, roller coasters, boat rides Sensed by the _____________________________ of the ______________________________ Static Equilibrium The ___________________contains hair cells surrounded by an _______________________________ (a jellylike material) that contains ________________________________ (tiny calcium stones) The otolithic membrane slides due to gravity or linear acceleration, bending the hairs When the hairs are bent, the hair cell generates a nerve impulse Dynamic Equilibrium 3 canals, oriented in the three planes of space At the base of each is a receptor region called the _____________________________, which consists of hair cells covered with a gelatinous cap called the __________________. During angular / rotational movements, the _____________________________ in one or more canals will move, pushing against the hair cells When the hair cells are bent, they generate a nerve impulse. Types of Receptors Sense Type of Sensor Name Location Vision ______________ & ___________ Retina of eye Hearing ____________ ( on organ of Corti) Cochlea of ear Balance ____________________ (on crista ampullaris) Vestibule of ear Semicircular canals of ear Tendons, muscles, joints _____________________ Smell Olfactory receptor Top of nasal cavity Taste Taste buds Papillae of tongue Pain nocioreceptors Skin, muscles, bladder, digestive system, mucus membranes, cornea Temp Thermoreceptors Skin Pressure Pacinian corpuscle Skin & internal organs Touch Meissner’s corpuscle Skin Senses and Aging Vision Develops slowly in babies Kids are far-sighted until around 6 because the eye needs to grow In old age _________________________________, causing _________________ – an inability to accommodate and focus on near items Other factors which reduce visual acuity include ___________________, inability to fully dilate pupil, loss of photoreceptors Many diseases more common with age: cataracts, glaucoma, macular degeneration, etc. Hearing ___________________ – a loss of hearing, especially speech sounds and high pitches – due to damage to the organ of Corti A type of __________________________l hearing loss Associated with age and noise exposure ____________________ hearing loss Anything that prevents sound from getting to the inner ear, including fusion of ossicles Smell & Taste Very sharp at birth Declines starting around age 40 Most people over 80 have poor taste sensation and almost no ability to smell Balance, Touch, Pain Begin to decline around age 50 Leads to increased risk of falls Inability to recognize injury