Key Civil Rights Laws
advertisement

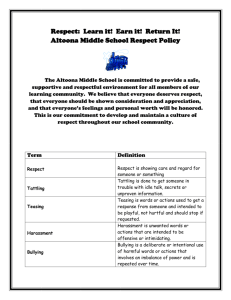
Hull Public Schools Annual Mandated Civil Rights Training August 27, 2012 Judith Kuehn Assistant Superintendent Learning Objectives • Participants Will Gain an Understanding of: – Key Civil Rights Laws – 504 Accommodation Plans – Behavior Restraint Procedures – Mc-Kinney Vento Act “Homeless” – Confidentiality – Bullying Civil Rights • Federal Laws Require: Full Compliance and Accountability District-Wide Coordinators Grievance Procedures Oversight by Office of Civil Rights Key Civil Rights Laws • Title VI: Title VI Civil Rights Act of 1964 – Prohibits discrimination, exclusion from participation and denial of benefits based on race, color or national origin in programs or activities receiving federal financial assistance. – Ms. Judith Kuehn Key Civil Rights Laws • Title IX: Title IX of the Education Amendments of 1972 regarding Sexual Harassment – Prohibits discrimination, exclusion from participation, and denial of benefits based on sex in educational programs and activities receiving federal financial assistance. • Ms. Rebecca MacDonald • Ms. Judith Kuehn Sexual Harassment Title IX • Sexual harassment of students is unwelcome conduct of sexual nature by: – school employees. – other students. – third parties. • Sexual harassment of a student can deny or limit participation in school programs therefore, a form of sex discrimination under Title IX. Key Civil Rights Laws Title I of the Americans Disabilities Act of 1990 • Prohibits: – Discrimination, exclusion from participation, and denial of benefits on the basis of disability in the areas of employment. • Ms. Judith Kuehn Key Civil Rights Laws • Title II of the Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990 • Prohibits discrimination, exclusion from participation, and denial of benefits on the basis of disability in the areas of educational programming and activities. • Ms. Judith Kuehn Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973 “No otherwise qualified handicapped individual shall, solely by reason of his handicap, be excluded from participation in, be denied the benefits of, or be subjected to discrimination in any program or activity receiving federal financial assistance.” Section 504 • Prohibits discrimination, exclusion from participation and denial of benefits based on disability in programs or activities receiving federal financial assistance. – – – – Ms. Ms. Ms. Ms. Philippa Young Andrea Centerrino Rebecca MacDonald Maureen Rosenplanter What Constitutes a 504 Evaluation? • 504 Team: Individuals Knowledgeable about: – The Student – Meaning of Evaluation Data – Potential Accommodations Options • Sample Evaluation Information – – – – Record Review; Student Observations Informational Inventories; Formal Assessments Teacher Reports; Student Work Samples Medical/Health Data/Diagnosis General Education Vs. 504 • General Education: –1st Consideration • Can student’s needs be met through General Education accommodations? • 504 Plan: –Does student’s disability substantially impact one or more of life’s major activities and require accommodations? • (Federal Eligibility Criteria) Key 504 Compliance: Staff Responsibilities • Make Programs and Activities Accessible within Least Restrictive Environment • Provide Reasonable Accommodations • Comply with Accommodations in Student’s 504 Plans Major Difference: 504 vs. Special Education Eligibility Requirements Student has a disability 504 Eligibility Including but not limited to: ADD, Emotional, Blindness, Visual Impairment, Hearing Impairment, Cerebral Palsy, Diabetes, Epilepsy, specific learning disability, etc. Student’s Disability impacts 1 or more of life’s major activities and requires Accommodation Plan Student’s Disability falls within Federal definition, impacts student’s ability to make effective progress in general curriculum and requires specialized instruction and/or related services Special Education Eligibility Including: Autism, Developmental Delay and Intellectual, Sensory, Neurological, Emotional, Communication, Physical, Health, Specific Impairments, Multiple Disabilities, specific learning disability, ADD Who is NOT Eligible for a 504 Plan? • A student is not automatically eligible for a 504 Plan just because he/she doesn’t qualify for an IEP. A 504 Plan is not a consolation prize. • A student that has a disability or medical diagnosis that does not substantially impact his/her ability to learn. What are Key 504 Liability Issues for Staff? • Failure by individual to make reasonable accommodations as required by law • Risk for district and personal liability for damages, attorney’s fees and compensatory services Discrimination/Harassment Connection ~Harassment could deny a student the right to an education free of discrimination and could threaten a student’s physical or emotional wellbeing, influence how well a student does in school and make it difficult for a student to achieve his or her career goals. Also, the courts have made it clear that, where harassment interferes with benefits protected by law, it creates a ‘hostile environment.’~ What is a “hostile environment”? – A “hostile environment” is created when conduct is “sufficiently severe, pervasive, or persistent so as to interfere with or limit a student’s ability to participate in or benefit from the services, activities, or opportunities offered by a school.” Dear Colleague Letter, SS IDELR 174 (OCR 2010) Bullying/Harassment • T.K. v. NYC: This will not be the last case that holds that tolerance of bullying can be a denial of FAPE. • NOTE: It is not BULLYING that denies FAPE, but TOLERANCE of it through DELIBERATE INDIFFERENCE. Harassment based on protected classes • Be aware of harassment based on other protected classes. • Aside from sexual harassment it is common to see harassment based on: Race Disability Sexual Orientation Age National Origin Religion Color Bullying generally refers to conduct that: • Adversely affects a student’s ability to participate in or • • benefit from the school’s educational programs or activities. Results from repeated negative actions by one or more students over time. Occurs in a relationship where there is an imbalance of power. – Some bullying incidents can be Harassment (capital “H”) and unlawful based on anti-discrimination laws. An Act Relative to Bullying in Schools • Chapter 92 Acts of 2010 • This law requires school districts to develop and adopt bullying prevention and intervention plans. • Intervention plan is available on the district website. What is Bullying? • Bullying is defined as the repeated use of a written, verbal, or electronic communication, or a physical act or gesture, or any combination thereof, by one or more students directed at another student that has the effect of: – causing physical or emotional harm to the other student or damage to his or her property; – placing the other student in reasonable fear of harm to him or herself or of damage to his or her property; – creating a hostile environment at school for the bullied student; – infringing on the rights of the other student at school; – Or materially and substantially disrupting the education process or the orderly operation of a school. The Law Prohibits Bullying: • At school and at all school facilities; • At school-sponsored or school-related functions, whether on or off school grounds; • On school buses and school bus stops; through the use of technology or an electronic device owned, licensed or used by a school; and • At non-school-related locations and through nonschool technology or electronic devices, if the bullying affects the school environment. District Bullying Intervention Plan Contains: • Procedures for responding to and investigating • • • • • reports of bullying. Strategies for protecting those who report bullying. Notice to the parents or guardians of students involved in bullying, including perpetrators and victims. Appropriate services for students who have been bullied or who are bullies. Annual staff training & professional development. Age appropriate instruction on bullying prevention in each grade. Forms of Bullying • Physical – Hitting, kicking, harming with a weapon, biting, spitting on, pushing/shoving • Verbal – Name calling, teasing, shaming, intimidating • Emotional or Social – Social isolation, subjecting another to ridicule, making up stories/events to embarrass a peer • Cyber – Email, facebook, cell phone, texting/sexting, Twitter, blogging, YouTube • Destruction of property – Defacing, destroying, hiding, stealing personal possessions Students Who Bully May: Control others. Lack empathy. View violence in a positive way. Associate with like peers. Be easily frustrated. May be popular and respected, and have good self-esteem. Is That Student Being Bullied? Student most likely won’t tell. Student feels ashamed. Look for behavioral signs. Trust your instincts – report. Targets of Bullying May Experience: Reluctance to go to school. Destroyed or missing belongings. Decreased success in class. Unexplained bruises or injuries. Lowered self-esteem. Complaints about feeling sick before school. Withdrawal and/or depression. Mandated Reporting & Responding • A staff member will report immediately to the principal or designee when he/she witnesses or becomes aware of conduct that may be bullying or retaliation. The requirement to report to the principal or designee does not limit the authority of the staff member to respond to behavioral or disciplinary incidents consistent with school or district policies and procedures for behavior management and discipline. • District incident reporting form INVESTIGATION The principal or designee will investigate promptly all reports of bullying or retaliation and, in doing so, will consider all available information known, including the nature of the allegation(s) and the ages of the students involved. Responses to Bullying • The principal or designee will notify parents of the target and the aggressor about the results of the investigation and, if bullying or retaliation is found, what action is being taken to prevent further acts of bullying or retaliation. • All notice to parents must comply with applicable state and federal privacy laws and regulations. Because of the legal requirements regarding the confidentiality of student records, the principal or designee cannot report specific information to the target’s parent or guardian about the disciplinary action. Notice to Law Enforcement • At any point after receiving a report of bullying or retaliation, including after an investigation, if the principal or designee has a reasonable basis to believe that criminal charges may be pursued against the aggressor, the principal will notify the local law enforcement agency. How Does This Affect Special Education? • Special education students may be more likely to be subjected to acts of bullying and harassment. Bullying & Special Education When the IEP Team determines the student has a disability that affects social skills development or the student may participate in or is vulnerable to bullying, harassment, or teasing because of his/her disability, the Team will consider what should be included in the IEP to develop the student's skills and proficiencies to avoid and respond to bullying, harassment, or teasing. M.G.L. c. 71B, § 3, as amended by Chapter 92 of the Acts of 2010 Complaint Procedures • Issues of bullying, discrimination and harassment are particularly sensitive for adults and students. • If a teacher or student receives a report of harassment and discrimination, such reports should be taken seriously. • Always report information to the proper school authority. Safety • Regardless of what type of harassment occurs, a school must take immediate and appropriate steps to stop or prevent it from happening again. The judgment and common sense of teachers and administrators are important elements of any response. Bullying/Harassment Court Cases • Courts are trying to draw a clear line between bullying vs. the normal give and take of adolescent life - tough thing to do. • Courts continue to follow the general rule that schools are not liable for what others do (other students, third parties) but only for their own deliberate indifference to obvious harm. CASE STUDY # 1 Shore Reg’l. High Sch. Bd. Of Educ. V. P.S., 41 IDELR 234 (3d Cir. 2004) 1. Middle school boy with depression and labeled 2. 3. 4. ED Years of bullying due to his perceived sexual orientation Attempted suicide in the 8th grade Request by parents to transfer to neighboring LEA so that the boy would not matriculate to high school with the gang of bullies What Did the Court Say? A. Bullying due to sexual orientation is not related to the boy’s disability. B. Forcing the boy to attend high school with the gang of boys who had bullied him for years would constitute a denial of FAPE. C. Placement at the LEA high school with a behavior plan that called for weekly counseling and selfreporting satisfied the FAPE obligation. D. None of the above. The Correct Answer is.. B. Forcing the boy to attend high school with the gang of boys who had bullied him for years would constitute a denial of FAPE. CASE STUDY # 2 R.R. v. Kinsport City sch. Dist., 45 IDELR 212 (SEA TN 2005) 1. 9th grade boy with an LD in written expression and 2. 3. 4. 5. ADHD was involved in 5 altercations (verbal and physical) with peers over a 7-month period. Parents complained to administrators about bullying. LEA developed and implemented a BIP (counseling; self-reporting of bullying; social skills training). LEA placed an adult escort with the boy throughout the school day. Boy was beaten up again—parents withdrew him and sued for denial of FAPE. What Did the Court Say? A. Administrators took every action necessary in response to allegations of bullying. B. Student was denied FAPE because the school failed to prevent attacks after the parents’ report of bullying. C. Getting into a fight with peers does not constitute bullying per se. D. None of the above. The Correct Answer is.. A. Administrators took very action necessary in response to the allegations of bullying. AND C. Getting into a fight with peers does not constitute bullying per se. CASE STUDY # 3 M.P. v. Indep. Sch. Dist. No. 721, 38 IDELR 262 (8th Cir. 2003) 1. A school health paraprofessional divulged to 2. 3. 4. the school community that a 16-year-old student had been diagnosed with schizophrenia. Student was teased and physically harassed by peers. Student’s grades declined, and his mental health condition deteriorated. Is this bullying? Disability-based harassment? What Did the Court Say? A. No, this is not bullying or disability-based harassment. B. Yes, this constitutes disability-based harassment. C. The school district could be found liable for money damages. D. The paraprofessional could be found to have acted with bad faith or gross misjudgment. The Correct Answer is.. B. Yes, this constitutes disability-based harassment. C. D. AND The school district could be found liable for money damages. AND The paraprofessional could be found to have acted with bad faith or gross misjudgment. CASE STUDY # 4 P.R. v. Metro. Sch. Dist. Of Washington Twp., 55 IDELR 199 (S.D. Ind. 2010) 1. Middle school girl confided to her BFF that she 2. 3. 4. 5. was HIV+. The BFF passed this information on to others. The girl was teased and harassed for two years at school. LEA responded to each incident of bullying by meeting with alleged harassers, informing parents, and punishing the perpetrators. Was this enough to escape liability? What Did the Court Say? A. Yes, the LEA acted appropriately. B. No, the LEA should have offered a private school placement to remove the girl from her tormentors. C. No, the LEA is responsible for preventing this type of bullying/harassment. D. Yes, because LEA are not responsible for stopping all acts of bullying/harassment in schools. The Correct Answer is.. A. Yes, the LEA acted appropriately. AND D. Yes, because LEA are not responsible for stopping all acts of bullying/harassment in schools. CASE STUDY # 5 1. 7th grade girl with ADHD and a 504 plan loves 2. 3. 4. Lady Gaga. Girl wears shirts with Lady Gaga’s photo to school, has a Lady Gaga lunch box, Lady Gaga stickers on her backpack, etc. Other students subject girl to daily ridicule (calling her “Monster Girl”) because of her devotion to Lady Gaga and have defaced her notebook sticker. The girl’s parents are threatening to file an OCR complaint. What will OCR say? What Did the Court Say? A. There is no evidence of disability-based discrimination because the teasing has nothing to do with the girl’s disability. B. There is evidence of disability-based discrimination because the girl has a 504 plan and a disability. C. Students with disabilities under 504 are protected against all forms of bullying/harassment by virtue of their protected-class status. D. None of the above. The Correct Answer is.. A. There is no evidence of disability-based discrimination because the teasing has nothing to do with the girl’s disability. CASE STUDY # 6 J.E. v. Boyertown Area Sch. Dist., 56 IDELR 38 (E.D. Pa. 2011, aff’d, 57 IDELR 273 (3d Cir. 2011) 1. Elementary school boy has Asperger’s 2. 3. 4. Syndrome. Mother requested placement in private school due to her fears that the boy would be subjected to bullying due to his disability. LEA proposed placement in a special education classroom with a transition plan and counseling services. Mother withdrew the child and sued seeking funding for private school. What Did the Court Say? A. The LEA was ordered to fund the private school placement because it was reasonably foreseeable that the boy would be subjected to bullying in the public school environment. B. Fears about possible future acts of bullying do not constitute a denial of FAPE. C. The LEA’s offer of placement and support services satisfied its obligation to provide FAPE. The Correct Answer is.. C. The LEA’s offer of placement and support services satisfied its obligation to provide FAPE. CASE STUDY # 7 Mathers v. Wright, 56 IDELR 188 (8th Cir. 2011) 1. An elementary teacher refused to instruct a 2. 3. 4. student with intellectual disabilities who was placed in her general education classroom. Teacher excluded the child from recess and fire drills, and allegedly forced her to crawl on the floor in the classroom. Do the teacher’s actions constitute “bullying?” Could the teacher be liable for money damages? What Did the Court Say? A. This teacher is in BIG TROUBLE! B. No, the teacher cannot be personally liable because she is protected by “qualified immunity.” C. No, because teachers have the discretion to exclude students from certain activities. D. This teacher needs to get a lawyer. The Correct Answer is.. D. This teacher needs to get a lawyer. And FAST! Bullying and Personal Liability • Can an individual teacher or administrator be personally liable for bullying a student with disabilities? What Must We Do To Avoid Liability? • Maintain anti-bullying policies and programs in • • • • • our school district. Train staff to spot/stop bullying. Take ALL reports of bullying/harassment seriously. Meet with parents and students to hear complaints of bullying/harassment. Investigate, interview, and document. Punish the perpetrators (NOT the victim)! Remember… • School districts are NOT liable for ALL acts of bullying or harassment. • School districts are liable ONLY for acts of bullying/harassment when they are aware of this activity and fail to act reasonably. • The law does not hold schools to a 100% standard of perfection—you cannot ensure that NO bullying or harassment will occur! DESE Physical Restraint Requirements • Annual Review Requirement, for ALL staff • District Restraint Policy and Procedures – Alternative Strategies to Restraint – Required Staff Training – Trained Teams as Resources – Types of Restraint and Related Safety Issues – Required Reporting & Documentation District Procedures Physical Restraint • Use reasonable force as necessary to protect a • • • • student or other persons from assault, or imminent physical harm. Only trained persons to administer restraint. Staff submits written report by the next day. Principal/Designee to inform parents. Principal/Designee submits complaints about restraint procedures to Director of Student Services. When may Physical Restraint be Necessary? When other, non-physical, interventions have been tried and failed or are judged to be inadequate to the circumstances. A student’s behavior poses a threat of IMMINENT, SERIOUS, PHYSICAL HARM to self and/or others. Proper Administration of Physical Restraint • Have an adult witness if possible. • Use only the amount of force necessary to protect the student or others. • Use the safest method. Do not use floor or prone restraints unless you have received in-depth training. • Discontinue restraint as soon as possible. Do NOT Use Physical Restraint • When non-physical interventions could be used. • As a means of punishment. Regulation 46.04(3) • As a response to property destruction, school disruption, refusal to comply, or verbal threats. Key Reporting Requirements • Report all restraints to principal. • Log required for restraints over 5 minutes or in • any case of an injury (to student or staff). Notify School Administration: – Notify school administration as soon as possible & provide written report by the next school working day. • Notify Parents: – The principal or designee notifies the parent, verbally as soon as possible, and by written report. Content of Written Report • Who participated in the restraint? – Observers? – Who was informed and when? • When did the restraint occur? – (Date/Time) • What was happening before, during, and after the restraint? – Describe alternative efforts attempted and the outcomes of those efforts. – Describe the restraint. • Documentation of any injury to students or staff. • Has the school taken, or will it take, any further actions, including disciplinary consequences? Special Circumstances For students with disabilities (w/IEP’s or 504 plans), physical restraint can be used for different reasons (other than danger) of reasons are detailed and part of the IEP or 504. Certain limits and requirements will still apply. Parents may agree to a waiver of reporting requirements in individual circumstances. However, the school cannot require parental consent to a waiver. Mc-Kinney Vento Act Students in Transition • Eligibility – Student has lost permanent residence. – Student has temporary residence (home/shelter). • Homeless students may: – – – – – – Attend school in Hull. Attend school in new community. Receive free transportation to school. Receive free breakfast and lunch. Enroll immediately. Be eligible for Title I services. What is Homeless? • Students who lack a fixed, regular and adequate nighttime residence are considered homeless. It may include students who: – – – – – – Live in shelters. Live in hotels, campgrounds, parks, cars, public buildings. Double up with friends or relatives. Are awaiting foster care or abandoned in a hospital. Are unaccompanied youth. Are migratory. McKinney Vento Act Staff Responsibilities • Notify principal if you become aware of a student living in temporary residence. • Principal will follow-up to verify eligibility for services and to verify residency status. Student Records & Confidentiality • Authorized School Personnel – School administrators, teachers, counselors and other professional working directly with a students in an administrative, teaching, counseling or diagnostic capacity – Administrative office staff and clerical personnel – Evaluation Teams Student Record • Temporary Record – Kept 7 Years After Graduation – Information in the records not contained in the transcript. • e.g., standardized test scores, extra-curricular activities, special education records, evaluations by teachers, counselors, and other staff. • Transcript –Begins at H.S. – Kept 60 Years – Minimum data necessary to reflect student’s educational progress. Access Log • Used to track access to the student’s record. • Authorized school personnel are not required to log their access. Student/Parent Access • Parents (or students 14 or older) have access to complete student records. • Parents/students may also have school records inspected by a third party. • A third party must have written consent. Additional Third Party Access • Court order/lawfully issued subpoena – School shall attempt to notify parent in advance of compliance. • First responders in emergency situations • Any school to which a student plans to transfer • Department of Children & Families (DCF) (51A) Non-Custodial Parents • Access Allowed UNLESS – Parent has been denied legal custody or visitation rights. – Supervised visitation has been ordered based on a threat to student’s safety. – Access to student has been restricted by temporary or permanent restraining order. – A judge’s order prohibits distribution. • Documents in student records will indicate limited or restricted access. “Sole Possession” Records • Records kept “in sole possession of the maker” are not considered part of educational records. • Once these records are shared with others (via email, for example,) they are considered educational records. Staff Reminders Be sure to keep confidential information in a secure location. Do not discuss confidential information in a public space (hallway, cafeteria, faculty room). Do not use email to communicate confidential information. Great TOWN Hull Pride Great SCHOOLS




![Bullying and Harassment Advisor role des[...]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006976953_1-320eb77689e1209d082c9ec2464350ee-300x300.png)