Chapter 2 Physics Study Guide: Kinematics
advertisement
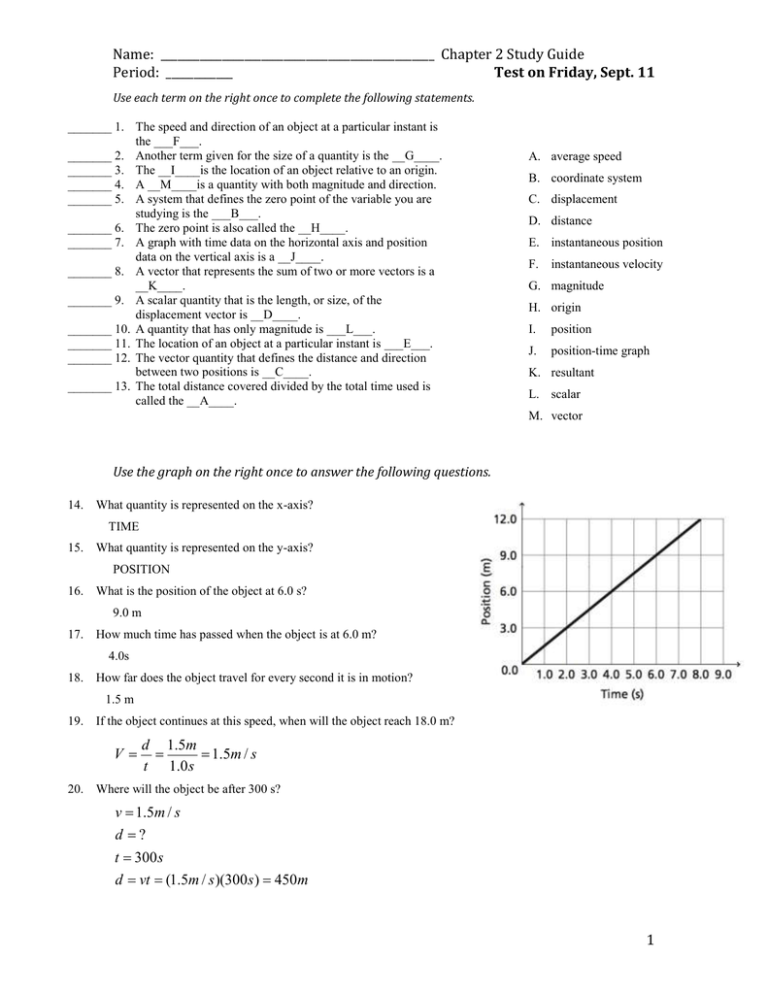
Name: _________________________________________________ Chapter 2 Study Guide Period: ____________ Test on Friday, Sept. 11 Use each term on the right once to complete the following statements. _______ 1. The speed and direction of an object at a particular instant is the ___F___. _______ 2. Another term given for the size of a quantity is the __G____. _______ 3. The __I____is the location of an object relative to an origin. _______ 4. A __M____is a quantity with both magnitude and direction. _______ 5. A system that defines the zero point of the variable you are studying is the ___B___. _______ 6. The zero point is also called the __H____. _______ 7. A graph with time data on the horizontal axis and position data on the vertical axis is a __J____. _______ 8. A vector that represents the sum of two or more vectors is a __K____. _______ 9. A scalar quantity that is the length, or size, of the displacement vector is __D____. _______ 10. A quantity that has only magnitude is ___L___. _______ 11. The location of an object at a particular instant is ___E___. _______ 12. The vector quantity that defines the distance and direction between two positions is __C____. _______ 13. The total distance covered divided by the total time used is called the __A____. A. average speed B. coordinate system C. displacement D. distance E. instantaneous position F. instantaneous velocity G. magnitude H. origin I. position J. position-time graph K. resultant L. scalar M. vector Use the graph on the right once to answer the following questions. 14. What quantity is represented on the x-axis? TIME 15. What quantity is represented on the y-axis? POSITION 16. What is the position of the object at 6.0 s? 9.0 m 17. How much time has passed when the object is at 6.0 m? 4.0s 18. How far does the object travel for every second it is in motion? 1.5 m 19. If the object continues at this speed, when will the object reach 18.0 m? V d 1.5m 1.5m / s t 1.0 s 20. Where will the object be after 300 s? v 1.5m / s d ? t 300 s d vt (1.5m / s )(300 s ) 450m 1 Calculate the answers to the following questions. Show your work and check for correct units and sig figs before circling your answers. 21. What is the average velocity (in m/s) of a car that travels 450 km in 9.0 hours? V= 14 m/s 22. How far (in meters) has a cyclist traveled if she has been moving at 30 m/s for 5.0 minutes? D= 9000m 23. A car travels at 55 km/h for 6.0 hours. How far (in meters) does it travel? D= 330,000m or 3.3x105m 24. A missile travels 2500 km in 2.2 hours. What is its velocity (in m/s)? V= 320m/s 25. How many minutes will it take a runner to finish an 11km race at 18 km/h? T= 37 min 26. A motorcyclist travels 350 km from home on the first day of a trip. The second day he travels at 75 km/h for 8.0 hours. How far (in km) is he from home at the end of the second day? D= 950 km 27. A businesswoman on a trip flies a total of 23,000 km. The first day she traveled 4000 km, the second day 11,000 km, and on the final day she was on a plane that could travel at 570 km/h. How long was she on the plane the final day? T= 10 hrs 2