Internal Coach
advertisement

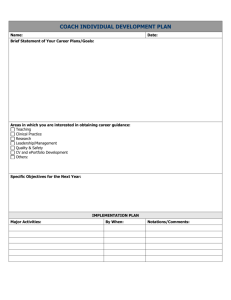
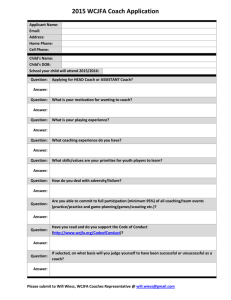
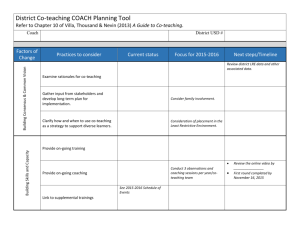
Building Trainer Competency for Coaches 2010 National PBIS Leadership Forum Session C3 Lori Newcomer (newcomerL@missouri.edu) Marla Dewhirst (marla.dewhirst@pbisillinois.com) Jane Nethercut and Semonti Basu Austin Public Schools Agenda • Roles and Responsibilities of Coaches • Self-Assessment of Skills and Competencies of Coaches • Organization and Training Model for Coaches at the State, District and Building Level • Sustainability Strategies Funding Visibility Political Support Policy SWPBS Implementation LEADERSHIP TEAM Blueprint (Coordination) www.pbis.org Training Coaching Evaluation Local School/District Implementation Demonstrations Behavioral Expertise Good to Great by Jim Collins Leadership First Who…Then What – Get the right people on the bus – Put the right people in the right seats – Start driving Coaching Defined • Coaching is the active and iterative delivery of: – (a) prompts that increase successful behavior, and – (b) corrections that decrease unsuccessful behavior. – Coaching is done by someone with credibility and experience with the target skill(s) – Coaching is done on-site, in real time – Coaching is done after initial training – Coaching is done repeatedly (e.g. monthly) – Coaching intensity is adjusted to need Outcomes of Coaching • Fluency with trained skills • Adaptation of trained concepts/skills to local contexts and challenges • And new challenges that arise • Rapid redirection from miss-applications • Increased fidelity of overall implementation • Improved sustainability • Most often due to ability to increase coaching intensity at critical points in time. What does research say about coaching? • Evidence exists that coaching increases student achievement. • Coaching increases teachers’ efficacy. • Coaching increases a teachers’ capacity to implement new instructional practices in the classroom. (Fullan, 2003; Costa and Garmston, 2002; Wong, 2008; Joyce and Showers, 2002) Training Outcomes Related to Training Components Training Outcomes Training Components Knowledge of Content Skill Implementation Presentation/ Lecture 10% 5% 0% Plus Demonstration 30% 20% 0% Plus Practice 60% 60% 5% Plus Coaching/ Admin Support Data Feedback 95% 95% Classroom Application 95% Joyce & Showers, 2002 Guiding Principles for Effective Coaching • Build local capacity – Become unnecessary…but remain available • Maximize current competence – Never change things that are working – Always make the smallest change that will have the biggest impact • Focus on valued outcomes – Tie all efforts to the benefits for children • Emphasize Accountability – Measure and report; measure and report; measure and report. • Build credibility through: – (a) consistency, (b) competence with behavioral principles/practices, (c) relationships, (d) time investment. • Precorrect for success Who should be a coach? Internal Coach External Coach Advantages Knowledge of school Staff relationships Regular access Independent Outside perspective Multiple schools experience Disadvantages Conflicting roles Narrow range of experiences Limited knowledge of school Limited relationships Less frequent access Who should be a coach Coaching Competencies Necessary Preferred Participate in team training Knowledge about SWPBS Able to attend team meetings at least monthly Knowledge about behavior support practices (targeted, individual) Effective working with adults Skilled in collection and use of data for decision-making. Knowledgeable about school operating systems Professional Commitment Coaching vs. Leading Coaching Team Leader Ensures the team meets regularly Sets the dates for meetings Offers tools to assist in record keeping, team evaluations, etc. Checks accuracy of records, directs team in evaluation Ensures equal distribution of roles and responsibilities Assumes the role of leader, delegates, assigns tasks Ensures the team is using data for decision making Refers the team to the data during team meetings Coaches Self-Assessment • Self-assess strengths • Determine professional development goals Level 1: Preliminary Internal Coach Data Systems •Facilitate team meetings •Consultation and technical assistance •Sustainability •ODR, SET, SWIS, BOQ,Surveys Achievement Scores •Data Decision Making Practices •Essential features •Instruction •Classroom Management •Increase/Decrease behaviors •ABA basics Level 2: Lead Coach/Facilitator External Coach Data Systems •Student Support Team Process •Consultation and technical assistance •Sustainability •Conduct SET & write report •DO / FBA •SWIS Facilitator •Analyze multiple data sets Practices •Brief & Full FBA •Function based Targeted -group •Social skills instruction •Advanced ABA •Academic modifications & accommodations Level 3: Coordinator District Region State Data Systems •Active leadership role •Resource for materials/experts/ exemplars •Assist with developing state policies •Evaluate multiple schools using multiple data sources •Identify needs within and across schools •Train teams on data use •District/Region/State evaluation reports Practices •Training & Professional Development Skills •District/region/state communication •Map policy to essential PBS features Brief Activity Take a quick look at the Self-Assessment • Does your coach training address the skills listed? If so put a + by them. • Does your coach training address the different levels listed? If so put a + by them. • Circle one thing you would like to learn about. Think about how you can move forward with that goal. Guiding Principles (“Requirements Review”) • • • • • • • • • • Coaching linked w/ school team Coaching training linked w/ team training Coaches participate in team training New teams added w/ increased fluency Coaching capacity integrated into existing personnel Supervisor approval given District agreements & support given Coaches experienced w/ school team implementation District/state coordination provided Coaches meet regularly for prompting, celebrating, problem solving, etc. The 7 Habits of Highly Effective People Stephen Covey • • • • • Be Proactive Begin with the End in Mind Put First Things First Think Win/Win Seek First to Understand, Then to be Understood • Synergize • Sharpen the Saw State Level Perspective Phases of Implementation Tool • Who? Internal Coach, with signatures of all others • What? Illinois’ assessment of implementation phases across the three tiers • Where? www.pbisillinois.org • When? Two times a year, October and March • Why? Provides the big picture view of PBIS to guide and direct teams toward full implementation • District IDM (Instructional Decision Making) Team • “Blueprint” • Monthly External Coach Meetings • Professional Development • Providing Individual Building Support • Data-Based Decision Making • Action Planning • Checklist • Self-Assessment • Provides Focus • Primary Tool Used for Recognition • Action Plan for Next Year • Discussion Between Team and External Coach Brief Activity Phases of Implementation • Quickly look at the document • Where would a building that you work with be on the rubric? • Turn to your shoulder partner and explain where the building you are thinking about is at and why. Discuss what support you need from the State and District to move forward. • Be prepared to share your thoughts if asked. Illinois Training Plan for Coaches • Full Day Workshops • On-Line Reviews • Network Meetings – Internal Coaches – External Coaches – Face to Face, Conference Calls, Go to Meetings • Annual Forum • Annual Leadership Conferences (2 per year) The Tipping Point: How Little Things Can Make a Big Difference Malcolm Gladwell • The point where the “new” becomes the expected • The Law of a Few – Connectors – know everyone – Mavens – Information specialists that want to help – Salesmen – can’t be resisted • Change and Radical Transformation is Possible How to Structure District Coaching Support to Ensure Maximum Effectiveness of Implementation Jane Nethercut PBS Administrative Supervisor Austin Independent School District (AISD) What Does It Look Like • Traditional Coaching Model (Before 09-10) District Team (15 external coaches for all AISD PBS campuses) • Administrative Supervisor • PBS External Coaches Campus Team • Principal (8-10 staff members on a • PBS Team Members specific AISD PBS campus) • Restructured Coaching Model District Team (15 external coaches for all AISD PBS campuses) • Administrative Supervisor • PBS External Coaches • Technical Assistance Facilitator • Schoolwide External Zone Team Coach (3 external coaches for • Classroom External a specific PBS Coach geographical location) • Student External Coach Campus Team (8-10 staff members on a specific AISD PBS campus) • Principal • PBS Team Members PBS Staff Structures School Wide Focus Group Classroom Focus Group Student Focus Group Zone 1 Team Coach 1 Coach 2 Coach 3 Zone 2 Team Coach 4 Coach 5 Coach 6 Zone 3 Team Coach 7 Coach 8 Coach 9 Zone 4 Team Coach 10 Coach 11 Coach 12 Zone 5 Team Coach 13 Coach 14 Coach 15 Coaching Responsibilities • One coach from each zone team serves as the coordinator for a campus • Functions of the coordinator – Work with the PBS team to establish and achieve campus PBS goals – Work with the PBS team and staff to implement PBS systems with fidelity – Review data trends to identify issues at each level of intervention – Review campus needs and facilitate access to training and other resources – Coordinate data collection for formative and summative evaluation Consulting Responsibilities At Each Level • Schoolwide level coach for – Active Supervision Training/PD – Increasing the 3:1 ratio in common area – Working on referrals coming from a particular common area – Increased support at the schoolwide level – Safety issues – Data based decision making to determine needs and resources at the schoolwide level Consulting Responsibilities At Each Level • Classroom level coach for – Classroom Management Training/Other PD – Working on classroom management issues identified by observation data – Individual classroom observations/support plans – Consultation requests from teachers/administrators – Book studies with targeted teacher groups – Data based decision making to determine needs and resources at the classroom level Consulting Responsibilities At Each Level • Student level coach for – CAPTURE/Other PD – Working on student issues identified by observation data – Individual student observations/support plans – Consultation requests from teachers/administrators – Collaboration with existing campus-based intensive needs resources (IMPACT, SPED and GenEd Behavior Specialists) – Access to mental health and other wraparound services How Does a Zone Team Coordinate Services? • Service coordination priorities determined as an entire district team • Service coordination priorities serve as guidelines for individual zone teams • Each zone team determines their training and support needs through weekly zone team meetings • Coordination is flexible within zones Using Data to Set Priorities Systems Identified for PBS Goals Discipline Data 1.2 6.3 1.6 1.5 6.2 6.8 2.1 1.7 2.1 11.8 47.1 11.8 6.1 75.0 5.9 23.5 7.8 12.5 6.7 6.9 37.5 58.8 64.7 56.3 92.7 47.1 23.5 A 90.1 91.7 91.1 37.5 11.8 B Team 91.8 68.8 47.1 41.2 92.2 C School-wide 6.3 D Classroom A B C D E Student Values indicate percentage of schools Tier1 (0-1ref) Tier2 (2-5 ref) E All District Tier3 (more than6) Values indicate percentage of students How Do We Maintain Fidelity? • • • • Centralized zone training Goal setting process Service Coordination and Planning Tool AISD PBS Benchmark Tool Goal Setting Process Goal: Data Indicators for Evidence of Need: Concerns: PBS System Impacted: System Structures to be Addressed: Action Steps: Data Indicators for Evidence of Progress: Centralized Zone Training • Training on common topics across all PBS campuses – Training on ‘Team Systems’ in January – Training on ‘Sustaining Momentum and Planning for Next Year’ in April/May • Training manuals to ensure access to same information – – – – – Volume 1: Introduction to PBS Volume 2: Team Systems Volume 3: Schoolwide Systems Volume 4: Classroom Systems Volume 5: Student Systems Service Coordination and Planning Tool AISD PBS Benchmark Tool • Measures fidelity across four PBS systems- Team, Schoolwide, Classroom, Student • Measures level of implementation for essential structures within each system • Allows for comparison across all campuses overall, and for each individual system PBS Quarterly Campus Report • Provides implementation status on system on which goal is based • Provides status of outcomes within a particular system • Summarizes campus priorities • Allows comparison of team systems status across all PBS schools Sustainability Strategies: The Flow in Illinois • Illinois PBIS Network Staff • District Leadership Team for School Improvement (Academic and Behavioral Early Intervention) • External Coaches for all Tiers • Building Leadership Team for School Improvement (Academic and Behavioral Early Intervention) • Internal Coaches for all tiers • Individual Building Teams • Teacher Performance • Student Outcomes Activity: Give 1 – Get 1 • Write one good idea that you have gotten in this session on the index card provided. • Follow next prompt… and smile. Thank you for your contribution to today and the future.