The Land is Always Tougher In Russia
advertisement

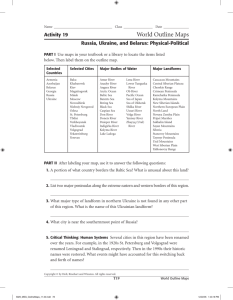
The Land is Always Tougher In Russia By, Alexander Cox & Anthony Li Introduction: Problems and Solutions Problems • Cold Climate: Very cold climate causes rivers to freeze and permafrost to Form • Ring Of Fire: a large ring of volcanoes on the Kamchatka Peninsula • Permafrost : a frost that forms in the winter months and stays permanently till Summer preventing Architecture and mining Solutions • Ice Breakers • Specific architecture (pilings) Landforms Of Russia Map Landforms: Mountains, Plateaus & Plains Ural Mountains: The mountain rage that is the border of Asia & Europe. Elevation:1000m Caucasus Mountains: The mountain range separating Russia and South East Asia. Mt. Elbrus: 5642m North European Plains: The Large plain west of the Ural Mountains Land Forms: Mountains, Plateaus & Plains Continued West Siberian Plain: The large plain just West of the Central Siberian Peninsula Central Siberian Plateau: a huge plateau in the center of Russia A few other mountain ranges in Russia are: Sayan Mts., Yablonovyy Range, Stanovoy Range, Verkhoyansk Range, & Kolyma Range Land Forms: Bodies of Water Kolyma River Ob River Yenisey River Volga River Don River Irtysh River Lena River Amur River Ural River Lake Baikal Landforms & Peninsula Russia’s largest peninsula is the Kamchatka. Russia has many landforms including the Ural mountains and the Siberian plain. Climate Introduction Climate The climates of Russia are Steppe, Humid continental, Subarctic and Tundra The annual precipitation is 2.9 in. The record high temperature of Russia is 98F The record low temperature is -44F Annual Snowfall About 160 to 200 days of snow annually Unique Features Taiga large evergreen forests that are in Siberia. Mostly found in humid subtropical. Permafrost not even hardy evergreens can grow there. Permanently frozen layers of soil. Covers 40% of Russia. CREDITS Written By: Anthony Li & Alexander Cox Illustrated By: Anthony Li & Alexander