Chemistry 330
advertisement

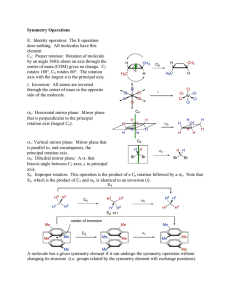
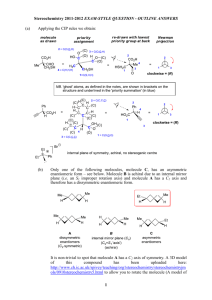
Chemistry 330 Symmetry Properties of Molecules Symmetry Elements Some of the symmetry elements of a cube. The twofold, threefold, and fourfold axes are labelled with the conventional symbols. Proper Rotations An NH3 molecule has a threefold (C3) axis An H2O molecule has a twofold (C2) axis. Mirror Planes An H2O molecule has two mirror planes. They are both vertical (that is, contain the principal axis) and so are denoted v and ‘v. Dihedral mirror planes Dihedral mirror planes (d) bisect the C2 axes perpendicular to the principal axis. The Inversion Centre A regular octahedron has a centre of inversion (i). Improper Rotation Axes A CH4 molecule has a fourfold improper rotation axis (S4) The staggered form of ethane has an S6 axis composed of a 60 rotation followed by a reflection. The Inversion Centre The presence of a twofold axis and a horizontal mirror plane jointly imply the presence of a centre of inversion in the molecule. The Dn Point Group A molecule with n twofold rotation axes perpendicular to an n-fold rotation axis belongs to the group Dn. The Dnh Point Group A molecule with a mirror plane perpendicular to a Cn axis, and with n twofold axes in the plane, belongs to the group Dnh. Cubic Point Groups Tetrahedral and octahedral molecules are drawn in a way that shows their relation to a cube: they belong to the cubic groups Td and Oh, respectively. The Point Group Flow Diagram A flow diagram for determining the point group of a molecule. Start at the top and answer the question posed in each diamond (Y = yes, N = no). Molecules and Point Groups A summary of the shapes corresponding to different point groups. Equivalent Elements Some symmetry elements are implied by the other symmetry elements in a group Presence of an inversion means at least an S2 element Hence, i and S2 are equivalent Characters of Rotations A rotation through 180 about the internuclear axis leaves the sign of a orbital unchanged but the sign of a orbital is changed. The characters of the C2 rotation are +1 and 1 for the and orbitals, respectively. Classes and Groups Symmetry operations in the same class are related to one another by the symmetry operations of the group. The px Orbitals and Symmetry A px orbital on the central atom of a C2v molecule and the symmetry elements of the group. Reflections The two orbitals shown here have different properties under reflection through the mirror plane: one changes sign (character -1), the other does not (character +1). SALC’s Two symmetryadapted linear combinations Each span a onedimensional irreducible representation, and their symmetry species are different. More SALC’s Typical symmetryadapted linear combinations of orbitals in a C3v molecule. Symmetry Species and Orbital Overlap Orbitals of the same symmetry species may have nonvanishing overlap The a1 and the two components of the doubly degenerate e orbitals