Land, Labor, Capital
advertisement
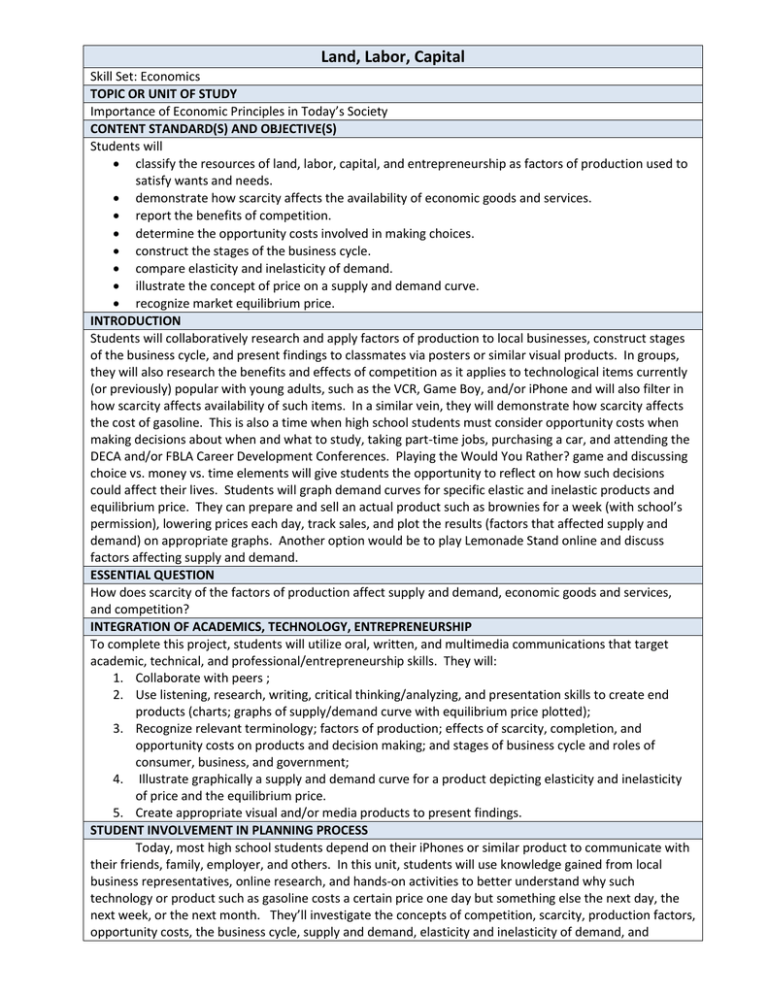
Land, Labor, Capital Skill Set: Economics TOPIC OR UNIT OF STUDY Importance of Economic Principles in Today’s Society CONTENT STANDARD(S) AND OBJECTIVE(S) Students will classify the resources of land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship as factors of production used to satisfy wants and needs. demonstrate how scarcity affects the availability of economic goods and services. report the benefits of competition. determine the opportunity costs involved in making choices. construct the stages of the business cycle. compare elasticity and inelasticity of demand. illustrate the concept of price on a supply and demand curve. recognize market equilibrium price. INTRODUCTION Students will collaboratively research and apply factors of production to local businesses, construct stages of the business cycle, and present findings to classmates via posters or similar visual products. In groups, they will also research the benefits and effects of competition as it applies to technological items currently (or previously) popular with young adults, such as the VCR, Game Boy, and/or iPhone and will also filter in how scarcity affects availability of such items. In a similar vein, they will demonstrate how scarcity affects the cost of gasoline. This is also a time when high school students must consider opportunity costs when making decisions about when and what to study, taking part-time jobs, purchasing a car, and attending the DECA and/or FBLA Career Development Conferences. Playing the Would You Rather? game and discussing choice vs. money vs. time elements will give students the opportunity to reflect on how such decisions could affect their lives. Students will graph demand curves for specific elastic and inelastic products and equilibrium price. They can prepare and sell an actual product such as brownies for a week (with school’s permission), lowering prices each day, track sales, and plot the results (factors that affected supply and demand) on appropriate graphs. Another option would be to play Lemonade Stand online and discuss factors affecting supply and demand. ESSENTIAL QUESTION How does scarcity of the factors of production affect supply and demand, economic goods and services, and competition? INTEGRATION OF ACADEMICS, TECHNOLOGY, ENTREPRENEURSHIP To complete this project, students will utilize oral, written, and multimedia communications that target academic, technical, and professional/entrepreneurship skills. They will: 1. Collaborate with peers ; 2. Use listening, research, writing, critical thinking/analyzing, and presentation skills to create end products (charts; graphs of supply/demand curve with equilibrium price plotted); 3. Recognize relevant terminology; factors of production; effects of scarcity, completion, and opportunity costs on products and decision making; and stages of business cycle and roles of consumer, business, and government; 4. Illustrate graphically a supply and demand curve for a product depicting elasticity and inelasticity of price and the equilibrium price. 5. Create appropriate visual and/or media products to present findings. STUDENT INVOLVEMENT IN PLANNING PROCESS Today, most high school students depend on their iPhones or similar product to communicate with their friends, family, employer, and others. In this unit, students will use knowledge gained from local business representatives, online research, and hands-on activities to better understand why such technology or product such as gasoline costs a certain price one day but something else the next day, the next week, or the next month. They’ll investigate the concepts of competition, scarcity, production factors, opportunity costs, the business cycle, supply and demand, elasticity and inelasticity of demand, and equilibrium price and how all affect costs of products and services. Relating these factors to costs of items they or their friends often purchase (designer jeans, Apple iPhone, gasoline, game Boy, graduation cap and gown, and less common insulin for diabetic) will help keep students focused. Those mathematically inclined can assist classmates in graphing supply and demand curves that plot equilibrium price and elasticity and elasticity of the price. Applying critical thinking, analyzing, and application skills and creating different visual and/or media products showing findings will keep students actively involved in the process from beginning to end. TASK(S) Become familiar with economic terminology. Classify the resources of land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship as factors of production used to satisfy wants and needs – research online or interview local business representative regarding how they use factors of production. Demonstrate how scarcity affects the availability of economic goods and services. Report the benefits of competition. Determine the opportunity costs involved in making choices – utilize Would You Rather? Game. Construct the stages of the business cycle. Compare elasticity and inelasticity of demand--prepare and sell actual product such as brownies ( or WVDE/school approved product) for a week, lowering prices each day, track sales, and plot results graphically OR play Lemonade Stand online and discuss factors that affect supply and demand. Illustrate the concept of price on a supply and demand curve. Recognize market equilibrium price. RESOURCES “1.1 What is the economic problem?” Web. 24 July 2011. http://www.pearsonschoolsandfecolleges.co.uk/Secondary/BusinessAndEconomics/1416/OCRGCSEEconomics/Samples/Samplechapters/GCSEOCREconomicsChapter1.pdf. Buffa, Chris, Editor in chief. “PlayStation Vita Release Will Result in 3DS Price Drop.” Web. 2011. Modojo. 24 July 2011. http://useconomy.about.com/od/tradepolicy/tp/How-Jobs-Outsourcing-Affects-USEconomy.htm. Chyung, Jin. “New Rules for Setting Standards in Today’s Hi-Tech market: Lessons Learned from the VHS – Betamax War.” Web. 24 July 2011. http://besser.tsoa.nyu.edu/impact/f96/Projects/jchyung/. “Factors of Production.” 2000-2011. AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia. AmosWEBLLC. 24 July 2011. http://www.amosweb.com/cgi-bin/awb_nav.pl?s=wpd&c=dsp&k=factors+of+production or http://www.AmosWEB.com. Farese, Lois S., G. Kimbrell, and C. A. Woloszyk, Ph.D. Marketing Essentials: The DECA Connection. Columbus, OH: Glencoe, 2006. Print. (See Chapter 3 Political and Economic Analysis, pp. 50-71.) Herman, R. Paul. “Why Is Business Blind to the Potential Profits from Sustainability?” Huffpost Business. Web. 2011. TheHuffingtonPost.com, Inc. 24 July 2011. http://www.huffingtonpost.com/r-paulherman/post_2140_b_881528.html. (Interesting comments about labor factor) http://glencoe.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0078612578/student_view0/unit2/chapter3/. (Chapter 3 Home Site Listing Activities) http://glencoe.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0078612578/student_view0/unit2/chapter3/chapter_summaries.html. (Chapter 3 Summaries) http://glencoe.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/dl/free/0078612578/287023/ch03_student_study_organizers.pdf. (Chapter3 Study Organizers: What Is an Economy? and Understanding the Economy (Economic Measurements) http://glencoe.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0078612578/student_view0/unit2/chapter3/figures_online_action.html. (Chapter 3 Figures Online Action) http://glencoe.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0078612578/student_view0/unit2/chapter4/. (Chapter 4) http://glencoe.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0078612578/student_view0/unit2/chapter4/chapter_summaries.html. (Chapter 4 Summaries) http://glencoe.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0078612578/student_view0/unit8/chapter25/. (Chapter 25 Home Site) http://glencoe.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0078612578/student_view0/unit8/chapter25/chapter_summaries.html. (Chapter 25 Summaries) http://wvde.state.wv.us/teach21/All-PurposeRubrics.html . http://wvde.state.wv.us/teach21/PBLRubrics.html. “Inside the Vault – Oil. Demand and Supply – It’s What Economics Is About! Lesson Plan.” Web. 2005. 24 July 2011. http://www.stlouisfed.org/education_resources/assets/lesson_plans/05ITV_OilPrices.pdf. (Use ideas from this plan!) Iraki, XN. “Is it time for the fifth factor of production?” Standard Group. Web. 2011. 24 July 2011. http://www.standardmedia.co.ke/columnists/InsidePage.php?id=2000037503&cid=497&. Local business representative – use of factors of production Romer, Christina D. “Business Cycles.” Liberty Fund, Inc. Concise Encyclopedia of Economics, The. Library of Economics and Liberty. Web. 2008. Econlib.org. 24 July 2011. http://www.econlib.org/library/Enc/BusinessCycles.html. Schrock, Kathleen. “Poster Rubric.” Kathy Schrock’s Guide for Educators. Web. 1995-2011. Discovery Education. 23 July 2011. http://school.discoveryeducation.com/schrockguide/assess.html. School personnel: business and marketing teachers “Supply and Demand.” http://www.schools.manatee.k12.fl.us/072JGALINDO/supplyanddemand/models_and_curves.html ; http://www.schools.manatee.k12.fl.us/072JGALINDO/supplyanddemand/one_man_s_story.html; http://www.schools.manatee.k12.fl.us/072JGALINDO/supplyanddemand/quantity_supplied_and_d emanded.html. “Supply and Demand Curves: Understanding Price and Quantity in the Marketplace.” Mind Tools Ltd. Web 1996-2011. Mindtools.com. 24 July 2011. http://www.mindtools.com/pages/article/newSTR_69.htm. U. S. Department of State. “A Mixed Economy: The Role of the Market.” Web. 2011. About.com. 24 July 2011. http://economics.about.com/od/howtheuseconomyworks/a/mixed_economy.htm. “Understanding Demand Curves. Tutorial 1 – Elastic and Inelastic Demand.” Web. Dogsbody.psych. 24 July 2011. http://dogsbody.psych.mun.ca/~bmckim/2800/demand/demtut.html. (Simple explanation with examples) Valentine, Gregory P. “Economics and Entrepreneurship – Making It Happen.” 2006. Web. 24 July 2011. http://www.usi.edu/business/econed/acte-conf-paper.doc. “Would You Rather?” 24 July 2011. http://www.zobmondo.com/ or http://www.zobmondo.com/play/game. Zeitler, Gerd. “Factors of Production: Efficient Economic Allocation of Labor, Natural Resources and Capital.” Web. 2009. Google. 24 July 2011. http://knol.google.com/k/gerd-zeitler/factors-ofproduction/2otpq9c0cx6bo/79#. Materials: Computer lab and software; Internet; Glencoe study organizers and other interactive materials; Would You Rather? Game; poster board and art supplies; graph paper and/or graphing calculators; rubrics. TECHNOLOGY USE Computer lab, Internet, Glencoe interactive activities, graphing calculators EVALUATION 1. Glencoe online interactive activities, including quiz and Concentration (relevant terminology) 2. Business cycle chart or poster 3. Product (such as VCR, iPhone) Report -benefits/effects of competition – findings presented via visual aid 4. Chart or graph reflecting how scarcity affects cost of gasoline 5. Discussion – opportunity costs 6. Sales Project (i.e., brownies or WVDE/school-approved produce): Results of week’s sale with variable prices; results graphically plotted (supply and demand, elasticity and inelasticity, equilibrium price) 7. General Rubric (below) with respective hyperlinks to individual rubrics (adjust points as necessary) TIMELINE This project will take at least three weeks. CONCLUSION Using knowledge gleaned from local business representatives, online research, and during hands-on activities and other student projects (individual and collaborative), students will have a better understanding of the business cycle, the factors of production used to satisfy wants and needs, and the effects of competition and scarcity on availability and costs of products and services. Students will realize opportunity costs affect the decisions they make—their lives! Creating graphs related to products of interest to young adults will help the students understand the concepts of supply and demand, elasticity and inelasticity, and price equilibrium. Overall, they will realize economic principles are important in today’s society and in the future. Importance of Economic Principles Components (See previous PBL rubric hyperlinks.) Glencoe online activities/terminology: quiz, organizer, and Concentration game Local business’s use of factors of production chart and/or poster: o Land o Labor o Capital o Entrepreneurship o Presentation – discussion Findings – how scarcity affects cost of gasoline (graph, chart, or other visual display of findings) Online product research: competition’s effect on product (VCR, DVD player, Game Boy, etc.) o Findings o Presentation o Modern Marvels episode/s discussion Opportunity costs – discussion (money/choices – what students give up) Would You Rather? Game participation Stages of business cycle (chart, PowerPoint, brochure, or other tool) – w/ actions of consumers, businesses, and government (75 pts): o Expansion o Recession o Trough o Recovery o Stage today (back us view with facts, statistics, etc.) o Presentation followed by discussion Product analysis (120 points) o Name of product o Whether price is elastic or inelastic justify o Demand curve graph for elastic price o Demand curve graph for inelastic price o Equilibrium price o Presentation: compare, contrast, and discuss resulting graph o Class discussion Product sale o Product approved o Schedule of workers o Weekly sales documentation – prices lowered each day o Effect of price on demand o Presentation of results (see previous rubric hyperlinks) Points Possible 25 10 10 10 10 10 25 25 25 25 20 20 10 10 10 10 15 25 10 10 20 20 20 20 20 10 10 20 10 20 400 Points Earned Comments