THE LIVER ENZYME LAB
advertisement

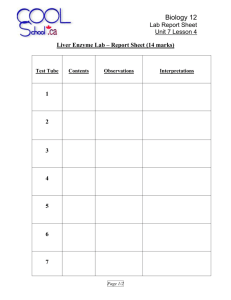
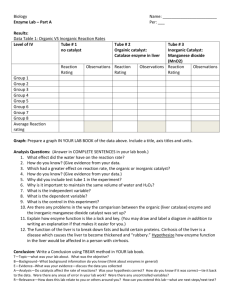
Name: __________________________________ Block: ____________ Lab Partners: __________________ __________________ ____________________ ____________________ Honors Biology The Liver Lab Introduction to Enzymes In each individual cell of a human there are many chemical reactions taking place, performing the necessary functions for being a large, complex, multicellular organism. This is relatively easy to understand. How do these reactions occur? This is not so easy to understand. Chemical reactions involve the breaking and reforming of chemical bonds between molecules (substrate(s) of the reaction), which are transformed into different molecules (product(s) of the reaction). Chemical reactions can occur spontaneously (without added energy or intervention), and indeed many of the chemical reactions necessary for life processes are spontaneous; some however, are not. Metabolic pathways are processes, which involve many chemical reactions that occur in a specific order. For example, to get energy out of a molecule of glucose, a series of reactions must take place in a specific order to break the bonds between the carbons of the glucose molecule. In addition, you have to rely on a series of chemical reactions that break down stored glycogen into glucose molecules to have glucose molecules in the first place. If you had to rely on these reactions to take place spontaneously, you would wait a very long time -- you wouldn't be here! Enzymes catalyze chemical reactions so that they occur in a timely and sequential manner to produce a product. Enzymes are biological catalysts. They help to increase the rate of chemical reactions. Enzymes are most often proteins and their three-dimensional shape is important to their catalytic activity. Because of their 3-D shape, enzymes are highly specific for the reactions that they catalyze. In other words, they are highly specific for the substrates that they will act upon. So any one "function", such as getting energy from a glucose molecule, actually involves many reactions, each with a specific enzyme. Enzyme activity is influenced by many factors. You will conduct a series of experiments and observe the reaction that takes place in several test tubes. The reaction that we will be studying is the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen gas. This reaction will be catalyzed by the catalase enzyme found in liver. Catalase is an enzyme, which is found in many cells, but in highest levels in the liver because the liver often functions to break down toxins present in the blood. PRELAB #: 1. What is an enzyme? 2. What do enzymes do? 3. Define catalyst. 4. Complete the following sentence: a. All enzymes are _______________________ but not all _____________________ are enzymes. 5. Do a little research and determine THREE (3) factors that will effect the effectiveness of enzymes: a. b. c. 6. Highlight the reactant(s) in the equation above yellow. Highlight the product(s) in the equation above green. 7. What is our substrate in this lab? 8. What is our enzyme in this lab? 9. How will we know that the enzyme is working? (HINT: Look at the products, what would having these together LOOK like?) MATERIALS: 100 mL beaker test tube holders 5 test tubes 1 test tube rack Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) dropper Liver Samples (raw, boiled, base, acid, iced) splints goggles matches PROCEDURE: 1. You will prepare the contents as outlined below for each corresponding test tube: a. Test tube #1 – Raw Liver & *H2O2 b. Test tube #2 – Liver (that has been soaked in ammonia overnight), & *H2O2 c. Test tube #3 – Liver (that has been boiled for several minutes) & *H2O2 d. Test tube #4 – Liver (that has been cooled on ice for several minutes) & *H2O2 e. Test tube #5 – Liver (that has been soaked in lemon juice overnight) & *H2O2 * VERY IMPORTANT: DO NOT ADD THE H2O2 until you are running the experiment for that test tube. 2. Record a hypothesis for EACH test tube set-up BEFORE beginning the lab. (space below) 3. Test ONE test tube at a time. a. Test Tube #1: i. Place piece of raw liver in test tube, add 10 drops of H2O2 and record results. b. Test Tube #2: i. Place piece of liver soaked in ammonia in test tube, add 10 drops of H2O2 and record results. c. Test Tube #3: i. Place piece of boiled liver in test tube and add 10 drops of H2O2 and record results. d. Test Tube #4: i. Place piece of cooled liver in test tube and add 10 drops of H2O2 and record results. e. Test Tube #5: i. Place piece of lemon-soaked liver in test tube, add 10 drops of H2O2 and record results. 4. Record observations of each experiment for ~3 minutes. 5. Interpret what you think has happened to the enzyme. 6. CLEAN UP; CLEAN UP; EVERYBODY, EVERYWHERE!!!! CLEAN UP, CLEAN UP, EVERYBODY DO YOUR SHARE!!! DATA: TUBE # CONTENTS HYPOTHESIS OBSERVATION INTERPRETATIONS ANALYSIS: 1. What effect do you think water would have on enzyme function? a. How do you know? 2. What effect did the ice have on enzyme function? a. How do you know? 3. What effect did the heat have on enzyme function? a. How do you know? b. Explain why you think this happened? 4. What effect did the lemon juice have on enzyme function? a. How do you know? 5. Why is it important to use the same size liver piece and volume of H2O2 in every experimental setup? 6. Explain how enzyme function is like a lock and key. (You may draw and label a diagram in addition to writing an explanation if that makes it easier for you.) 7. The function of the liver is to break down fats and build certain proteins. Cirrhosis of the liver is a disease which causes the liver to become thickened and “rubbery.” Though it has many causes, one of the most common is due to constant exposure to harmful substances such as alcohol. Hypothesize how enzyme function in the liver would be affected in a person with cirrhosis. 8. Write a CONCLUSION on your lab experiment.