Biology and Behavior The Brain
advertisement

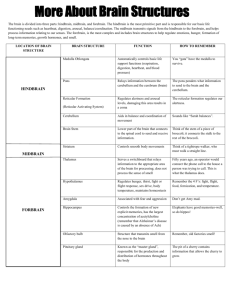
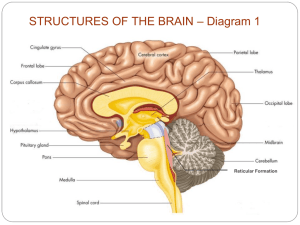
BIOLOGY AND BEHAVIOR The Brain OBJECTIVE Identify the major structures of the brain, and explain the functions of each structure. TODAY’S GOALS Notes on the brain THE BRAIN The brain is the center for all thought processes and nearly all regulatory function in the human body. The brain directly or indirectly controls every aspect of the living body such as voluntary and involuntary motor control, enzyme and hormone production, and immune system responses. Much of what we know today about the function of the brain comes from the imaging technologies that use scanning instruments to look at brain structure and function. THE BRAIN– IN HISTORY People did not attribute human psychological processes such as thinking to the working of the brain Creative thought, art, and analytical abilities– Not Biological– the body was inhabited by souls or demons. Ancient Egyptians– little person dwelled within the skull and regulated behavior Aristotle– the soul had set up living quarters in the hear BF Skinner (1987)– English language still reflects the belief in the heart as the seat of will, though, hunger, and joy. What are some expressions that we use about the heart that should be attributed to the brain? PARTS OF THE BRAIN PARTS OF THE BRAIN The Hindbrain: Medulla Pons Cerebellum The Midbrain: Reticular Activating System The Forebrain: Thalamus Hypothalamus Limbic System Cerebrum-cerebral cortex- surface of the cerebrum THE FOREBRAIN Thalamus– Latin word meaning “inner chamber” Relay station for sensory stimulation Most of the messages coming from the sense organs go through the thalamus on the way to the higher levels of the brain (thinking and reasoning) Also relays information from the eyes and ears to the appropriate parts of the brain for interpretation. Hypothalamus – Greek “under” – Lies below the thalamus Involved in many aspects of behavior and physiological functions. Regulates body temperature, storage of nutrients and various aspects of motivation and emotion. Involved in hunger, thirst, sexual behavior, caring for offspring, and aggression. Limbic System– Learning and memory, emotion, hunger, sex, and aggression If limbic system is damaged people can recall old memories but do not create new memories. THE MIDBRAIN Involved in vision and hearing Eye-movement Part of the Reticular activating system Attention, sleep, and arousal Increases heart rate and blood pressure and increases brain activity. Alcohol reduces the activity of the reticular Sudden noises will activate the reticular THE HINDBRAIN The Medulla– Vital functions such as hear rate, blood pressue and breathing Pons— In front of the medulla Regulates body movement, attention, sleep, and alertness Cerebellum— Latin for “little brain” Balance and coordination Damage to the cerebellum– have trouble with coordination CEREBRUM Go to other slide show