Cellulose
advertisement

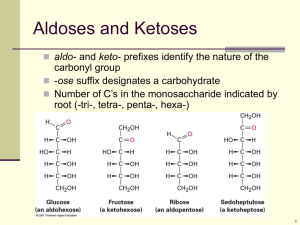
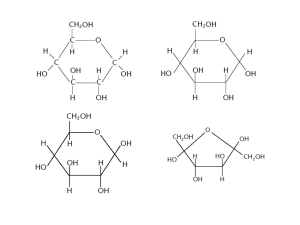
Carbohydrates & Lipids KEY WORDS Dehydration Synthesis (Condensation) Polymer Monomer Carbohydrate Simple sugar Complex carbohydrate Starch Glycogen Cellulose Lipid Triglyceride Saturated fatty acid Unsaturated fatty acid Steroid Cholesterol The synthesis and breakdown of polymers CARBOHYDRATES Carbohydrate Types 1. SIMPLE SUGARS Monosaccharides - one sugar molecule • Hexose = 6 carbons Glucose –cell energy Fructose - honey Galactose – milk • Pentose = 5 carbons Ribose - RNA Deoxyribose - DNA Linear and ring forms of glucose Carbohydrate Types 2. SIMPLE SUGARS Disaccharides - two sugar molecule Sucrose (sugar) Glucose + Fructose Lactose (milk) Glucose + Galactose Maltose (grains) Glucose + Glucose How are disaccharides made? Dehydration synthesis: Examples of disaccharide synthesis Carbohydrate Types COMPLEX CARBOHYDRATES POLYSACCHARIDES: Long chains of monosaccharides EXAMPLES Starch (amylose) Glycogen Fiber (cellulose) Chitin Starch • Long-term energy storage of glucose for plants (roots, seeds) • < 500,000 glucoses Glycogen Short term storage polysaccharide for animals • ~300g carbs stored in body • 72g liver (glycogen) • 245g muscle (glycogen) • 10g blood (glucose) Storage polysaccharides Chitin String of modified glucose Structural component of: Insects, Arthropods, fungi Cellulose •Polymer of glucose •Structural material in plants - Fiber •Why indigestible? •Monomers linked together differently than in starch •Starch •Cellulose Starch verses Cellulose • Glucose linked differently • Cellulose is not recognized by our digestive enzymes • Some organisms (microbes) in the guts of cows and termites do make enzymes that can digest cellulose Starch and cellulose structures Starch and cellulose structures QUESTION When you eat a starchy food, an enzyme in your mouth breaks it down into maltose. Maltose enters your small intestine, where it is broken down into glucose. The starch is a _________, the maltose is a ________, and the glucose is a(n):_________. a) Protein b) Monosaccharide c) Triglyceride d) Amino acid e) Polysaccharide dipeptide disaccharide fatty acid dipeptide disaccharide amino acid polysaccharide glycerol protein monosaccharide Question • Which of the following terms includes all others in the list? A. B. C. D. E. Monosaccharide Disaccharide Starch Carbohydrate Polysaccharide Question • The molecular formula for glucose is C6H12O6. What would be the molecular formula for 10 glucoses linked together? LIPIDS Three Major Groups of Lipids • Oils, Fats, and Waxes • Phospholipids • Steroids (Cholesterol, Estrogen, Testosterone, etc…) Similarities of Fats and Oils • All contain C, H, and O • Usually no ring structures • Made up of fatty acid subunits (long chain of carbons and hydrogen with a carboxyl end) Triglycerides • Fats and Oils have 3 fatty acids linked to a glycerol (condensation) The synthesis and structure of a fat, or triacylglycerol Fatty Acid Subunits: FATS vs. OILS • Solid at room temperature • From animal sources, coco & palm • Saturated with hydrogens • Liquid at room temp. • From plants • Unsaturated Types of Fatty acids Saturated Unsaturated Polyunsaturated Saturated Unsaturated Unsaturated Fats • Monounsaturated: One C=C – olive, canola, nut oils • Polyunsaturated: More than one C=C – corn safflower, soy oils • Hydrogenated: Oils made solid by breaking C=C bonds and replacing with H (Hydrogenation) – Partially hydrogenated - margarine Phospholipids • One fatty acid chain (non-polar, hydrophobic) of triglyceride replaced with a phosphate group (charged, hydrophilic) • chief component of lipid bilayer, outer membrane of all cells Phospholipids Steroids • Four fused rings of carbon • steroid hormones: estrogen, testosterone • cholesterol: vital component of cell membranes Cholesterol, a steroid Cholesterol •Body will make if not enough in diet •Part of lipid membrane around cells •Helps stabilize, strengthen membrane The structure of a phospholipid Phospholipid Two structures formed by self-assembly of phospholipids in aqueous environments Question • What is the difference between the two ring forms of glucose (alpha & beta)? Question • Human sex hormones belong to what family of lipids? Question • How many water molecules are needed to completely hydrolyze a polymer that is 100 monomers long? Question Unsaturated fats: A. B. C. D. Are more common in animals than plants Have double bonds in their carbon chains Solidify at room temperature Contain more H than saturated fats having the same # of C E. Have fewer fatty acid chains