World War I
advertisement

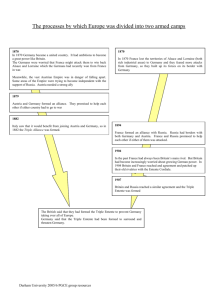
World War I What actually caused the First World War? • World War I was caused by many factors but ultimately, leaders’ aggression towards other countries fueled by growing nationalism brought the conflict to a head. Economic and imperial competition and fear of war pushed countries into military alliances and an arms race; these factors caused the outbreak of the First World War. Causes of World War I • • • • • • • • Nationalism Imperialism Collapse of Bismarckian Alliances Arms Race Crises in Africa Bosnian Crisis of 1908 Morocco II Assassination of Sarajevo Nationalism – The belief that one country is superior to others. • Congress of Vienna 1815: the problem of nationalism was ignored in favor of preserving peace. It was called to reorganize Europe after the fall of Napoleonic France. – Unfortunately, during this meeting they did not take into account the various ethnic groups they were attempting to force into countries with the hope of a peaceful existence…it was doomed to failure! Nationalism • Franco-Prussian War 1870-71: Dispute between France and Germany, Alsace-Lorraine was originally part of the Holy Roman Empire, but gradually slipped to French control. The Treaty of Frankfurt returned AlsaceLorraine to German rule. Both countries were desperate for Alsace-Lorraine because it was a major industrial center. • Alliances: Austria-Hungary was pro-German; Serbia and Russia were Pan Slavism. Imperialism The Industrial Revolutions of the 19th C. in Germany, Britain, and France caused these world leaders to compete for new markets to sell their goods. Africa became the market of choice; France and Britain were able to resolve their difference over the region, but Germany continued to clash with both of them. This foreshadows the Great War! The Ottoman Empire appealed to Austria-Hungary, the Balkans, and Russia. Otto von Bismarck • German Chancellor • Concentrated on balancing alliances – Three Emperor’s League 1872 – Triple Alliance 1882 – Reinsurance Treaty 1887 • Collapse of Bismarckian Diplomacy – – – – – Franco-Russian Entente 1891 Kruger Telegram 1896 Entente Cordiale in 1904 Russia’s Entente with Britain 1907 Triple Entente Three Emperor’s League 1872 • Isolated France • Austria-Hungary, Germany, and Russia aligned forces of conservative Europe. Triple Alliance 1882 • AustriaHungary, Germany and Italy would defend one another if any of the other great powers attacked any of the three. – Exploited Italy’s deep resentment towards the French occupation of Tunisia. Reinsurance Treaty 1887 Attempt by Bismarck to remain friendly with Russia after the failure of the Three Emperor’s League; he felt it was imperative to maintain French isolation and protect German interests. 1. Germany and Russia both agreed to observe neutrality should the other be involved in a war with the third. Neutrality would not apply should Germany attack France or Russia attack Austria-Hungary 2. In the most secret completion protocol Germany declared herself neutral in the even of a Russian intervention in the Bosporus and the Dardanelles. Collapse of Bismarckian Alliances Kaiser William II was crowned Emperor of Germany in the Hall of Mirrors at Versailles; his first order of business was firing Bismarck. Franco-Russian Entente 1891 Kruger Telegram 1896 Entente Cordial 1904 Russia’s Entente with Britain 1907 Triple Entente Franco-Russian Entente 1894 • William II did not like people of Slavic descent (Russians are Slavic) so he chose to not update the legislation to maintain peace with Russia. In turn, France assumed that Russia would become upset due to the ethnic insult; the French were correct and aligned themselves with Russia. • FRANCE WAS NO LONGER ISOLATED Kruger Telegram 1896 • William II sent a telegram to congratulate the Boers on their defeat over the British in 1896. He gave them instructions to the German soldiers to “behave like Huns during the Boxer Rebellion.” • This along with the large Navy Germany was building put Great Britain in an alarmed state, and added to British distrust of Germany. Entente Cordiale 1904 As a result, Britain and France put their differences aside and aided each other because of mutual distrust of Germany. Russia’s Entente with Britain 1907 Russia formed an entente with Britain after they had reached an understanding with Britain’s ally Japan. Triple Entente William II further alienated Russia by supporting Austrian ambitions in the Balkans. It was an informal coalition between Great Britain, France, and Russia. It countered the Triple Alliance. International tension was greatly increased by the division of Europe into two armed camps. Arms Race • Two separate armed camps in Europe led to the bolstering of militaries on both sides. • The most well known plan created was Bismarck & Schlieffen’s “Von Schlieffen Plan” • The Von Schlieffen plan focused extreme military organization to create the most efficient mobilization in Europe. – Universal conscription, large reserves, and detailed planning – Technological advances and organizational advances led to general staffs with precise plans for mobilization attacks could rarely be reversed once begun. Alfred Graf Von Schlieffen Von Schlieffen Plan Germany could mobilize in two weeks; which would allow them to attack France long before either Russia or France could mobilize. This allowed them to defeat France and then turn and face Russia. Prevented Germany from fighting a two front war. German soldiers practiced mobilization regularly in elaborate drills; their efficiency has not been matched since! Later the plan was changed by Von Moltke, and these changes included avoided invading Holland, and going through Belgium instead. In order for the plans to work, there were certain assumptions made by the German military; if these assumptions were incorrect, failure was immanent. •Russia would take at least 6 weeks to mobilize. •France would be easily defeated in 6 weeks. •Belgium would not resist any German attack. •Britain would remain neutral. Armies and navies were both greatly expanded; standing armies of France and Germany doubled in size between 1870-1914. Britain decided that they would have to maintain a navy two and a half times larger than the second largest navy in the world. The British launched the Dreadnought, invented by Admiral Sir John Fisher, in 1906. Germany quickly responded by instituting a similar plan. Although efforts were made at the Hague Conferences of 1899 & 1907, international rivalry caused the arms race to continue to feed on itself. These conferences advocated world wide disarmament. Crises in Africa • Due to the high tensions of Europe, there were several crises in Morocco and the Balkans which nearly ended in war. • In 1905, Germany announced their support of Moroccan independence. Morocco was a colony that Great Britain owned and had given to France as a gift in 1904. – Britain came to France’s defense and the near war was avoided by an international conference in Algeciras in 1906. Bosnian Crisis of 1908 When Austria-Hungary annexed the former Turkish province of Bosnia in 1908, war nearly broke out. Bosnia AustriaHungary German Support <<<war<<< Serbia >>>war>>> Russian Support >>>>>> Russia backed down Morocco II A second Moroccan crisis occurred in 1911 when Germany sent a warship to Agadir in protest of French supremacy in Morocco, claiming the French had violated the agreement at Algeciras. – Britain again rose to France’s defense and gave Germany stern warnings; the Germans agree to allow France to rule Morocco without interfering in exchange for part of the French Congo. •The Balkan Wars of 1912-13: the Balkan state drove the Turks back to Constantinople and fought among themselves over territory. – When Austria-Hungary forced Serbia to relinquish some of its gains, and this pushed tensions to the boiling point. Assassination at Sarajevo • On June 28, 1914, Archduke Francis Ferdinand, heir to the Austria-Hungarian throne, was assassinated in Sarajevo, Bosnia. – The assassin was a member of a Serbian Nationalist organization known as the “Black Hand” Immediately, Germany threw their support behind Austria-Hungary and encouraged them to declare war on Serbia. Convinced that the Serbian government had conspired against them, Austria-Hungary issued Serbia an unacceptable ultimatum, to which Serbia consented almost entirely. It was too late, Austria-Hungary still wasn’t satisfied; they declared war on Serbia on July 28, 1914. July 29, 1914 Russia announced a partial mobilization in support of Serbia. August 1, 1914 Germany declares war on Russia and France in defense of Austria-Hungary. When Germany went to attack France, they crossed through neutral Belgium; in turn, Britain declared war on Germany.