Slide Set 5
advertisement

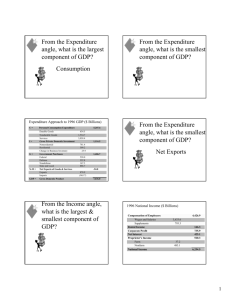
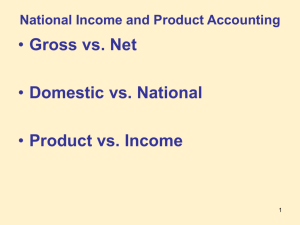
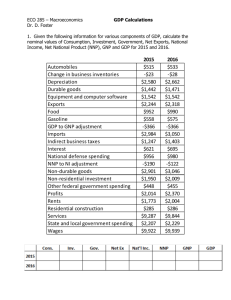
From the Expenditure angle, what is the largest component of GDP? Consumption From the Expenditure angle, what is the smallest component of GDP? Expenditure Approach to 1996 GDP ($ Billions) C= I= G= X-M = GDP = Personal Consumption Expenditure Durable Goods Nondurable Goods Services Gross Private Domestic Investment Nonresidential Residential Change in Business Inventory Government Purchases Federal Defense Nondefense State and Local Net Exports of Goods & Services Exports Imports Gross Domestic Product 5 5,207.6 634.5 1,534.7 3,038.4 1,116.5 781.4 309.2 25.9 1,406.7 520.0 352.8 167.3 886.7 -94.8 870.9 (965.7) 7,636.0 From the Expenditure angle, what is the smallest component of GDP? Net Exports From the Income angle, what is the largest & smallest component of GDP? 1996 National Income ($ Billions) Compensation of Employees Wages and Salaries Supplements Rental Income Corporate Profit Net Interest Proprietor’s Income Farm Nonfarm National Income 4,426.9 3,633.6 793.3 146.3 735.9 425.1 520.3 37.2 483.1 6,254.5 From the Income angle, what is the largest & smallest component of GDP? Largest: Compensation of Employees. Smallest: Rental Income. Bringing GDP & National Income into accord: GDP + Net Factor Payments from Abroad = GNP Receipt of Factor Incomes from the rest of the world – Payment of Factor Incomes to the rest of the world GNP - Depreciation = NNP Net National Product NNP - Indirect Business Taxes = National Income Reconciliation between GNP and NI: Minus Plus Equals Minus Equals Minus Gross Domestic Product (GDP) Factor Payments to the rest of the world Factor Payments from the rest of the world Gross National Product (GNP) Capital Depriciation Net National Product (NNP) Indirect Business Taxes 7,636.0 -232.6 234.3 7,637.7 830.1 6,807.6 553.1 Equals National Income (NI) 6,254.5 GDP – depreciation = NDP Net Domestic Product In a closed economy: NDP – indirect business taxes = NI • Sales taxes • Excise taxes • Customs duty • Property taxes • License Fees National Income (NI) is what people earn. Personal Income (PI) is what people receive. PI = NI + income received but not earned – income earned but not received Disposable Personal Income = PI – Direct Taxes How Comprehensive is GDP? Value of Housework The Underground Economy Leisure Quality of Goods and Services Costs of Environmental Damage Use the following data to compute GDP, GNP, NNP, NI, PI and Personal Disposable Income. Personal Consumption Expenditures Interest Corporate Profit Government Purchases Depreciation Rent Gross Private Domestic Investment Compensation of Employees Exports Imports Indirect Business Taxes Proprietor’s Income Income Tax Income Earned but not Received Income Received but not Earned Factor Income from abroad Factor Incoem to the world $800 80 120 300 80 40 100 750 100 60 70 110 100 120 140 60 50 Suppose next year, the following changes in economic activity occur in the country. What effect would these changes have on GDP? Durable Goods +30 Business Inventory +10 Imports Income Tax +20 +10