Feudalism
advertisement

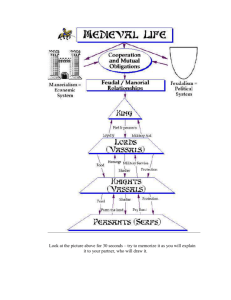
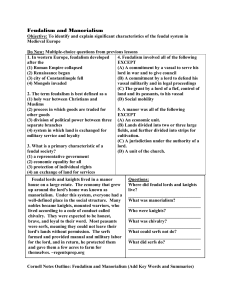
Feudalism With collapse of a central power and the Viking invasions, Europe is militarized Leads to the rise of feudalism Feudalism has several elements and best understood using PERSIA Political Lords and vassals A lord give a fief (land) to a vassal in return for military support Vassals would wear armor and use large horses wielding long lances to fight for their lord – they are commonly called knights All of Europe was engaged in small bloody fights between rival lords – think gang warfare Economic New agriculture – iron plowshare, mills, windmills, and three-field system Manor – agricultural estate operated by a lord and worked by serfs. Serfs were bound to the land and could not leave without the lord’s permission. Usually contained a castle Rise of cities like Venice and Bruges increases trade Northern European cities began to hold fairs Burghers: townspeople or merchants A typical middle ages manor Notice the 3 field system Medieval Fair Venice Bruges Rothenburg Guilds Craftspeople began to organize themselves into guilds Guilds controlled the quality of the product, price of the product, and membership Process: apprentice, journeymen, then master craftsmen Had to produce a “masterpiece” judged by the guild in order to be a master craftsmen Guilds Social Pyramid Intellectual Rise of universities -Bologna, Italy -Oxford, England -Salamanca, Spain Lecture – Latin for “read” Studied grammar, geometry, logic, etc. No exams, after 4 years they took oral exam Scholasticism Scholarly attempt to reconcile faith and reason Harmonize Christian teaching with the work of Greek philosopher Aristotle Thomas Aquinas – Summa Theologica Vernacular Writers To write in the local language Dante Alighierir – The Divine Comedy – Italian Geoffrey chaucer – The Cantebury Tales – English Giovanni Bocaccio – The Decameron - Italian Artistic Book Of Kells The Four Evangelists Madonna in Majesty By Cimabue Madonna Enthroned by Duccio